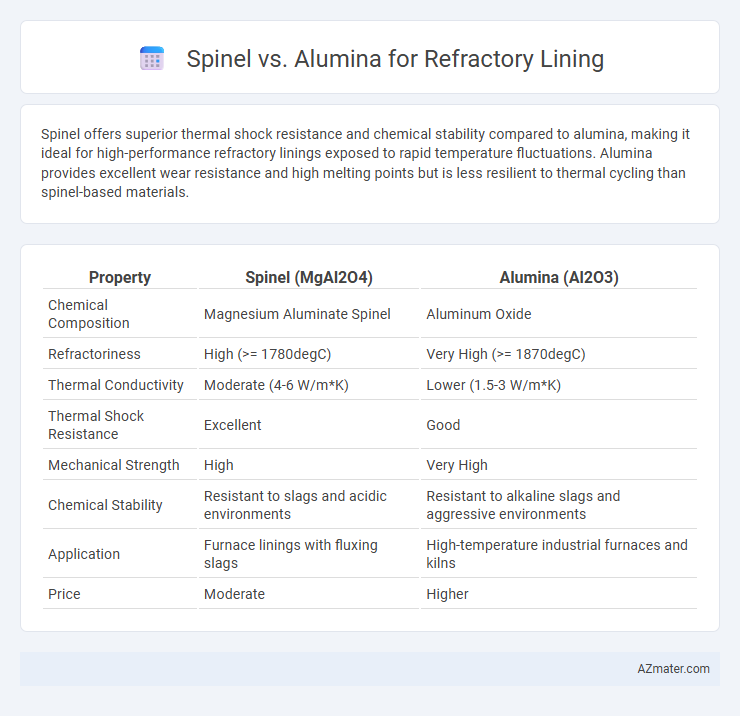
Spinel offers superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to alumina, making it ideal for high-performance refractory linings exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations. Alumina provides excellent wear resistance and high melting points but is less resilient to thermal cycling than spinel-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spinel (MgAl2O4) | Alumina (Al2O3) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Magnesium Aluminate Spinel | Aluminum Oxide |
| Refractoriness | High (>= 1780degC) | Very High (>= 1870degC) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (4-6 W/m*K) | Lower (1.5-3 W/m*K) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Very High |
| Chemical Stability | Resistant to slags and acidic environments | Resistant to alkaline slags and aggressive environments |
| Application | Furnace linings with fluxing slags | High-temperature industrial furnaces and kilns |
| Price | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Refractory Lining Materials
Spinel and alumina are critical refractory lining materials known for their high melting points and chemical stability, essential for protecting furnace walls in harsh thermal environments. Spinel (MgAl2O4) offers superior resistance to slag corrosion and thermal shock compared to alumina (Al2O3), which excels in pure oxidizing atmospheres due to its high alumina content and density. The choice between spinel and alumina linings depends on specific operating conditions such as temperature, slag composition, and mechanical stress levels to optimize furnace longevity and performance.
Overview of Spinel and Alumina
Spinel (MgAl2O4) and alumina (Al2O3) are widely used refractory materials known for their high melting points and chemical stability. Spinel offers superior thermal shock resistance and improved mechanical strength due to its unique crystal structure, making it ideal for harsh operating conditions. Alumina is valued for its high alumina content, exceptional abrasion resistance, and acid and alkali corrosion tolerance, commonly used in furnaces and kilns requiring durability and stability.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Spinel refractory linings primarily consist of magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4), offering excellent thermal shock resistance and chemical stability. Alumina refractory linings contain high percentages of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), providing superior corrosion resistance and high melting point performance. The distinct chemical composition of Spinel provides better resistance to slag corrosion, whereas Alumina excels in environments with predominant acidic slags.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Spinel offers superior thermal stability and resistance in refractory linings due to its high melting point of approximately 2135degC and excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Alumina, with a melting point near 2072degC, provides strong mechanical strength and good resistance to abrasion but can be less resistant to rapid temperature fluctuations compared to spinel. Both materials perform well under extreme conditions, yet spinel's enhanced phase stability under high temperatures makes it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to severe thermal cycling.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Spinel exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to alumina, offering enhanced resistance to abrasion and impact in refractory linings. Its spinel structure provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, resulting in longer service life under harsh operating conditions. Alumina, while durable, tends to have lower toughness and is more prone to spalling under thermal stress, making spinel a preferred choice for high-performance refractory applications.
Corrosion and Slag Resistance
Spinel refractory linings exhibit superior corrosion and slag resistance compared to alumina due to their unique crystalline structure, which enhances chemical stability in aggressive environments. Alumina refractories offer high melting points but tend to suffer from slag infiltration and chemical degradation in harsh industrial conditions. Spinel's enhanced resistance to acidic slags and molten metals makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring prolonged durability and minimal maintenance.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Spinel refractory linings offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to alumina, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance frequency. Alumina linings, while easier to install due to their lower density and better workability, may require more frequent inspections and repairs to address spalling and wear under high-stress conditions. Installation teams must account for spinel's higher hardness and brittleness, which demand precise handling and specialized tools to prevent cracking during application.
Cost Analysis: Spinel vs Alumina
Spinel refractory linings typically incur higher initial material costs compared to alumina due to their complex manufacturing processes and superior thermal shock resistance. Alumina offers a more economical solution with lower purchase prices and widespread availability, making it ideal for applications with moderate temperature demands. While spinel's durability can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time, alumina remains cost-effective for general refractory lining needs with lower operational budgets.
Application Suitability in Industry
Spinel offers superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for refractory linings in steelmaking furnaces and cement kilns where exposure to rapid temperature fluctuations occurs. Alumina provides excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for glass furnaces and petrochemical reactors requiring prolonged service at elevated temperatures. Choosing between spinel and alumina depends on specific industry demands such as thermal cycling frequency and chemical attack severity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Refractory Material
Spinel offers superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to alumina, making it ideal for high-temperature applications involving rapid temperature fluctuations. Alumina provides excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for environments with abrasive wear but less thermal cycling. Selecting the right refractory lining depends on operational conditions, with spinel recommended for dynamic thermal stresses and alumina preferred for steady, abrasive exposures.
Infographic: Spinel vs Alumina for Refractory lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com