Porcelain tiles offer superior durability and water resistance compared to glass tiles, making them ideal for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas. Glass tiles provide a glossy, reflective surface that enhances light and aesthetic appeal but are more prone to chipping and scratching.
Table of Comparison
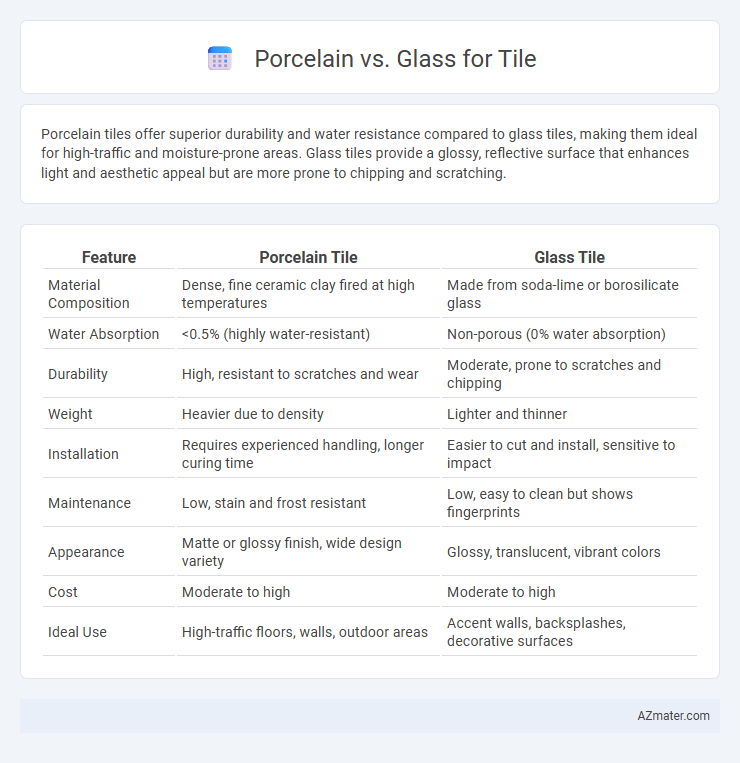
| Feature | Porcelain Tile | Glass Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Dense, fine ceramic clay fired at high temperatures | Made from soda-lime or borosilicate glass |
| Water Absorption | <0.5% (highly water-resistant) | Non-porous (0% water absorption) |
| Durability | High, resistant to scratches and wear | Moderate, prone to scratches and chipping |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter and thinner |
| Installation | Requires experienced handling, longer curing time | Easier to cut and install, sensitive to impact |
| Maintenance | Low, stain and frost resistant | Low, easy to clean but shows fingerprints |
| Appearance | Matte or glossy finish, wide design variety | Glossy, translucent, vibrant colors |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
| Ideal Use | High-traffic floors, walls, outdoor areas | Accent walls, backsplashes, decorative surfaces |
Introduction to Porcelain and Glass Tiles
Porcelain tiles are made from highly refined clay and fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a dense, durable surface ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. Glass tiles consist of thin pieces of glass fused with backing material, offering a translucent, reflective finish that enhances natural light in spaces. Both materials provide unique aesthetic qualities and functional benefits tailored to various design and environmental needs.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Porcelain tiles are made from a denser mixture of fine clay, kaolin, and feldspar, fired at higher temperatures above 1200degC, resulting in a harder, less porous surface compared to glass tiles, which are crafted by fusing silica sand, soda ash, and limestone through a melting process. The vitrification process in porcelain manufacturing enhances durability and water resistance, whereas glass tiles achieve their strength and translucency through controlled cooling and tempering methods. These compositional and manufacturing differences influence each tile's suitability for high-traffic areas, moisture-prone environments, and aesthetic applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Variety
Porcelain tiles offer a wide range of design options with high-resolution printing technology, allowing for intricate patterns and realistic natural stone or wood looks that enhance aesthetic appeal. Glass tiles provide a unique luminosity and reflective quality, creating vibrant, light-enhancing surfaces ideal for contemporary and artistic designs. Both materials support diverse color palettes and finishes, but porcelain excels in replicating traditional textures while glass delivers a sleek, modern visual impact.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Porcelain tiles demonstrate superior durability and strength compared to glass tiles, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-duty applications. Porcelain's dense, vitrified composition offers resistance to cracking, chipping, and wear, while glass tiles, although aesthetically pleasing, are more prone to scratches and breakage under impact. The Mohs hardness of porcelain typically ranges between 6 and 7, whereas glass tiles generally score around 5, highlighting porcelain's enhanced resilience and longevity in flooring and wall installations.
Water and Stain Resistance
Porcelain tiles offer superior water resistance due to their dense, non-porous composition, making them ideal for wet areas such as bathrooms and kitchens. Glass tiles also resist water effectively but are more prone to staining from oils and other substances because of their smooth surface. Choosing porcelain ensures enhanced durability and minimal absorption, reducing the risk of moisture damage and stubborn stains.
Installation Process and Techniques
Porcelain tiles require precise cutting tools such as a wet saw with a diamond blade due to their density and hardness, making installation more labor-intensive compared to glass tiles. Glass tiles demand careful handling and specialized adhesive to prevent cracking and ensure proper adhesion, often requiring a slower, more meticulous installation process. Both materials benefit from substrate preparation and appropriate grout selection, but porcelain's durability allows for a wider range of installation environments and techniques.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Porcelain tiles require minimal maintenance due to their dense, non-porous surface, which resists stains and moisture, making them easy to clean with just mild detergents and water. Glass tiles are also low-maintenance but can show water spots and smudges more easily, often needing regular wiping with a glass cleaner to maintain their shine. Both materials benefit from routine cleaning, but porcelain's durability and stain resistance make it the preferred option for areas with heavy foot traffic or frequent spills.
Cost and Value Analysis
Porcelain tiles generally have a higher upfront cost than glass tiles, but their durability and low maintenance contribute to better long-term value. Glass tiles, while often less expensive initially, can be prone to chipping and require more frequent replacement or repair, increasing overall costs over time. Evaluating cost-effectiveness involves balancing porcelain's resilience and longevity against glass's aesthetic appeal and lower purchase price.
Ideal Applications for Each Tile Type
Porcelain tiles offer superior durability and water resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, and commercial spaces that require long-lasting performance and minimal maintenance. Glass tiles, prized for their reflective and translucent qualities, are best suited for decorative applications like backsplashes, accent walls, and shower niches where aesthetic appeal and light enhancement are key. Selecting porcelain or glass depends on balancing functional demands with design goals, as porcelain excels in toughness while glass provides vibrant, luminous finishes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Porcelain tiles have a lower environmental impact due to their dense composition and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste. Glass tiles are often made from recycled materials, contributing to sustainability by repurposing waste and lowering landfill contributions. Both materials support eco-friendly building practices, but porcelain's durability and energy-efficient production process generally result in a smaller carbon footprint.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Glass for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com