Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-voltage electrical insulators. Glass ceramic provides excellent electrical insulation with enhanced resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
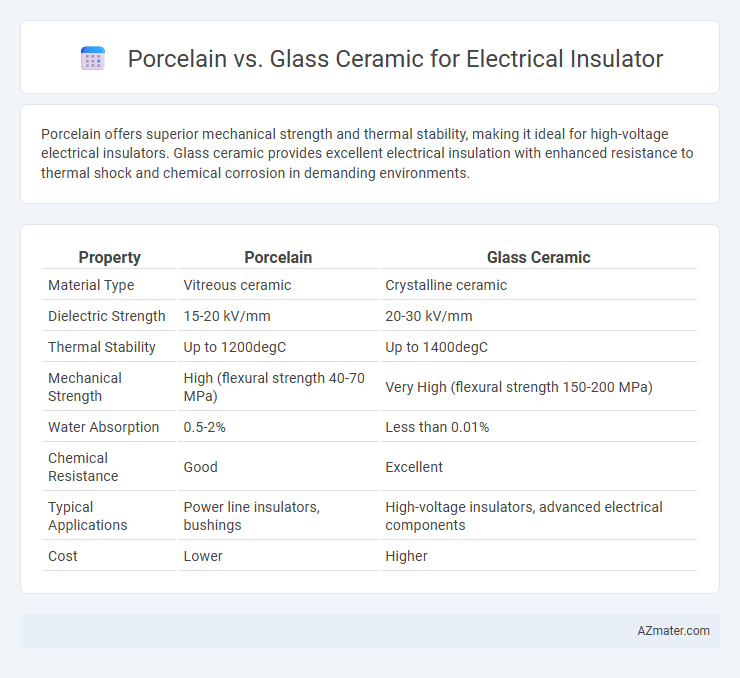
| Property | Porcelain | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitreous ceramic | Crystalline ceramic |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-20 kV/mm | 20-30 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1400degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High (flexural strength 40-70 MPa) | Very High (flexural strength 150-200 MPa) |
| Water Absorption | 0.5-2% | Less than 0.01% |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | Power line insulators, bushings | High-voltage insulators, advanced electrical components |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators like porcelain and glass ceramics play a crucial role in preventing unwanted current flow and maintaining safety in power systems. Porcelain offers high mechanical strength, excellent thermal resistance, and long-term durability, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Glass ceramics provide superior electrical insulation, low dielectric loss, and resistance to thermal shock, suitable for compact and high-frequency electrical components.
Overview of Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators, composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offer high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Their dense, non-porous structure ensures superior resistance to environmental contaminants and moisture, maintaining performance in harsh outdoor conditions. Porcelain insulators also exhibit outstanding thermal stability and durability, which reduces maintenance needs and prolongs service life in electrical power distribution systems.
Overview of Glass Ceramic Insulators
Glass ceramic insulators offer superior thermal stability and electrical insulation properties compared to traditional porcelain materials, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Their microcrystalline structure combines the advantages of both glass and ceramics, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock. These features contribute to improved durability and reliability in electrical insulator performance under extreme environmental conditions.
Material Composition and Structure
Porcelain for electrical insulators is composed mainly of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, forming a dense, crystalline structure with high mechanical strength and excellent dielectric properties. Glass ceramic insulators consist of glassy and crystalline phases created by controlled crystallization of glass, providing superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. The microstructure of porcelain offers high compressive strength and moisture resistance, while glass ceramics deliver enhanced fracture toughness and minimal porosity, optimizing performance in electrical insulation applications.
Electrical Performance and Properties Comparison
Porcelain offers high dielectric strength and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high voltage electrical insulators, while glass ceramic provides superior electrical insulation with lower dielectric loss and enhanced resistance to thermal shock. Porcelain's microstructure contributes to its robustness and moisture resistance, whereas glass ceramic's engineered crystalline phases enable better control over electrical properties and improved mechanical strength. Both materials exhibit excellent insulation, but glass ceramic's tunable electrical performance often suits advanced electronic applications requiring precise dielectric characteristics.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain electrical insulators offer high mechanical strength due to their dense, vitrified microstructure, making them resistant to cracking under mechanical stress and environmental impact. Glass ceramics provide superior durability with enhanced thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, maintaining performance over longer periods in harsh conditions. Both materials are widely used, but porcelain is favored for its robust mechanical properties while glass ceramics excel in extending insulator lifespan through improved durability.
Environmental Resistance and Aging
Porcelain exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, maintaining stable insulating properties over extended periods. Glass ceramic offers excellent aging resistance with minimal surface degradation and consistent dielectric strength under harsh conditions, though it may be more susceptible to mechanical damage in highly polluted environments. Both materials provide reliable electrical insulation, but porcelain's robustness against environmental stress makes it preferable for outdoor and industrial applications.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Porcelain electrical insulators typically cost less due to widespread manufacturing and raw material availability, making them a budget-friendly choice for large-scale projects. Glass ceramic insulators generally carry higher expenses because of advanced production processes and limited suppliers, influencing overall project budgets. Availability favors porcelain, with established global supply chains ensuring easier procurement compared to the more specialized glass ceramic variants.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Porcelain insulators are widely preferred in high-voltage transmission and outdoor electrical applications due to their excellent mechanical strength, weather resistance, and long service life. Glass ceramic insulators, favored in power distribution and railway systems, offer superior thermal stability, low surface contamination, and easier visual inspection for damage detection. The electrical industry prioritizes porcelain for heavy-duty, high-stress environments, while glass ceramics are chosen for applications requiring reduced maintenance and enhanced reliability in polluted or industrial settings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Porcelain offers exceptional mechanical strength and high resistance to weathering, making it ideal for outdoor electrical insulators in harsh environments, while glass ceramic provides superior thermal stability and better electrical insulation properties for high-voltage applications. The decision between porcelain and glass ceramic insulators should consider specific operational conditions such as temperature fluctuations, mechanical load, and environmental exposure to optimize performance and longevity. Selecting the right material ensures enhanced reliability and safety in electrical infrastructure, balancing cost, durability, and functional requirements.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Glass Ceramic for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com