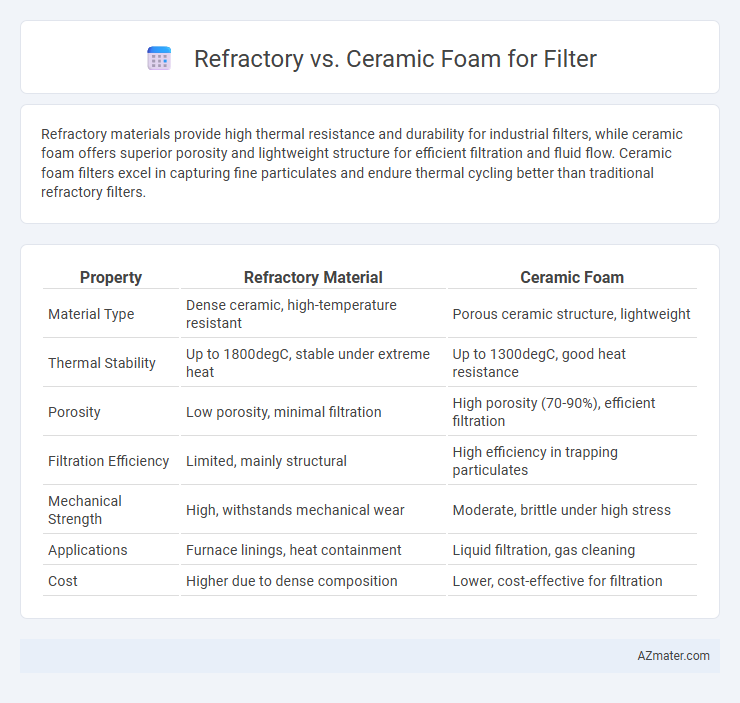
Refractory materials provide high thermal resistance and durability for industrial filters, while ceramic foam offers superior porosity and lightweight structure for efficient filtration and fluid flow. Ceramic foam filters excel in capturing fine particulates and endure thermal cycling better than traditional refractory filters.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory Material | Ceramic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Dense ceramic, high-temperature resistant | Porous ceramic structure, lightweight |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1800degC, stable under extreme heat | Up to 1300degC, good heat resistance |
| Porosity | Low porosity, minimal filtration | High porosity (70-90%), efficient filtration |
| Filtration Efficiency | Limited, mainly structural | High efficiency in trapping particulates |
| Mechanical Strength | High, withstands mechanical wear | Moderate, brittle under high stress |
| Applications | Furnace linings, heat containment | Liquid filtration, gas cleaning |
| Cost | Higher due to dense composition | Lower, cost-effective for filtration |
Introduction to Filtration Materials
Filtration materials like refractory and ceramic foam are essential in high-temperature industrial processes for capturing impurities and protecting equipment. Refractory filters offer high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for molten metal filtration. Ceramic foam filters provide a porous structure with excellent permeability and fine filtration capabilities, enhancing the removal of inclusions during metal casting.
Overview of Refractory Filters
Refractory filters, composed of materials such as alumina, silicon carbide, or zirconia, offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to ceramic foam filters. These filters effectively remove inclusions and impurities in molten metals during casting, ensuring enhanced metal quality and structural integrity. Their dense, engineered porous structures provide precise filtration capabilities, crucial for high-temperature industrial applications like steel and superalloy production.
Understanding Ceramic Foam Filters
Ceramic foam filters offer superior filtration efficiency compared to traditional refractory filters by utilizing an interconnected porous structure that traps inclusions in molten metals. These filters enhance the quality of castings by improving melt cleanliness and thermal stability during high-temperature operations. Optimizing pore size and material composition in ceramic foam filters directly influences filtering performance and lifespan in applications like aluminum and steel casting.
Key Properties: Refractory vs Ceramic Foam
Refractory filters provide high resistance to extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for molten metal filtration in foundries. Ceramic foam filters feature a porous structure with interconnected cells, offering superior filtration efficiency and improved flow rates by trapping inclusions while maintaining mechanical strength. Comparing key properties, refractory filters excel in thermal stability and durability, whereas ceramic foam filters optimize filtration performance and minimize clogging in metal casting processes.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Refractory filters typically offer higher filtration efficiency due to their dense microstructure, enabling superior retention of fine particles in molten metal processing. Ceramic foam filters provide effective filtration with a porous network that traps inclusions while allowing better flow rates, balancing efficiency and permeability. The choice between refractory and ceramic foam filters depends on specific filtration requirements, with refractory filters excelling in fine particle capture and ceramic foam filters optimizing fluid dynamics and inclusion removal.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Refractory materials offer exceptional thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1600degC, making them ideal for high-temperature filtration applications. Ceramic foam filter media exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance due to their porous structure, which allows rapid heat dissipation while maintaining filtration efficiency. Comparing both, refractory filters are preferred for extreme heat endurance, whereas ceramic foam filters balance thermal resistance with lightweight, high permeability properties for effective particulate capture.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Refractory filters generally incur lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes, but they may require more frequent replacement leading to higher long-term expenses. Ceramic foam filters exhibit higher upfront investment driven by advanced material properties and durability, which often translates to cost savings through extended lifespan and improved casting quality. Economic impact favors ceramic foam filters in high-volume or precision casting industries where reduced defects and maintenance outweigh the initial price difference.
Typical Applications and Industries
Refractory filters are commonly used in high-temperature applications such as steelmaking and foundry operations, where durability and thermal resistance are critical. Ceramic foam filters find typical use in the metal casting industry for molten metal filtration, effectively removing impurities in aluminum, cast iron, and steel production. Both materials serve crucial roles in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery manufacturing due to their ability to improve metal quality and reduce defects.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Filter
Refractory filters excel in high-temperature resistance and durability, making them ideal for molten metal filtration, but they can be brittle and prone to cracking under thermal shock. Ceramic foam filters offer superior porosity and lightweight structure, enhancing filtration efficiency and slag removal, yet their lower mechanical strength limits their use in highly abrasive environments. Choosing between refractory and ceramic foam filters depends on balancing thermal stability, filtration precision, and physical robustness for specific metallurgical applications.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate filter material between refractory and ceramic foam depends on factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and filtration precision. Refractory filters excel in high-temperature environments with strong thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for molten metal filtration, while ceramic foam filters offer superior pore structure for capturing fine inclusions in processes requiring high cleanliness. Understanding the process temperature, molten material composition, and desired filtration efficiency ensures optimum performance and longevity of the filter in industrial applications.
Infographic: Refractory vs Ceramic foam for Filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com