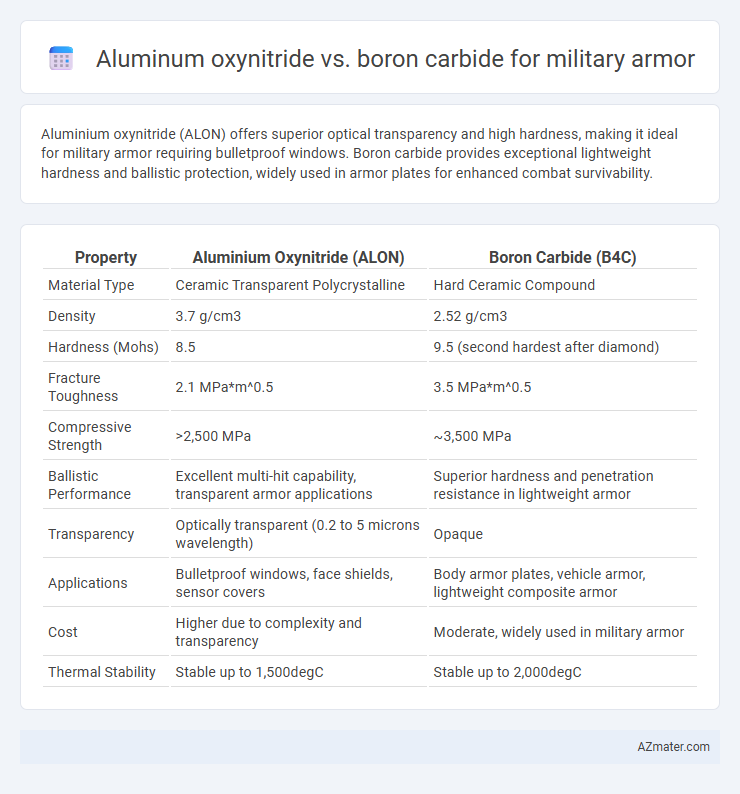
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) offers superior optical transparency and high hardness, making it ideal for military armor requiring bulletproof windows. Boron carbide provides exceptional lightweight hardness and ballistic protection, widely used in armor plates for enhanced combat survivability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminium Oxynitride (ALON) | Boron Carbide (B4C) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic Transparent Polycrystalline | Hard Ceramic Compound |
| Density | 3.7 g/cm3 | 2.52 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8.5 | 9.5 (second hardest after diamond) |
| Fracture Toughness | 2.1 MPa*m^0.5 | 3.5 MPa*m^0.5 |
| Compressive Strength | >2,500 MPa | ~3,500 MPa |
| Ballistic Performance | Excellent multi-hit capability, transparent armor applications | Superior hardness and penetration resistance in lightweight armor |
| Transparency | Optically transparent (0.2 to 5 microns wavelength) | Opaque |
| Applications | Bulletproof windows, face shields, sensor covers | Body armor plates, vehicle armor, lightweight composite armor |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity and transparency | Moderate, widely used in military armor |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 1,500degC | Stable up to 2,000degC |
Introduction to Advanced Military Armor Materials
Aluminium oxynitride (AlON) and boron carbide (B4C) are leading advanced materials in military armor due to their exceptional hardness and lightweight properties. AlON offers superior optical transparency and impact resistance, making it ideal for transparent armor applications like vehicle windows and face shields. Boron carbide provides outstanding ballistic protection with exceptional hardness and low density, widely used in personal body armor and vehicle armor plating for effective threat mitigation.
Overview of Aluminium Oxynitride (ALON)
Aluminium Oxynitride (ALON) is a transparent ceramic composed of aluminum, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms, renowned for its exceptional hardness and optical clarity. ALON offers superior ballistic resistance, allowing it to stop high-velocity projectiles while providing clear vision, making it ideal for military armor applications like vehicle windows and face shields. Its combination of light weight, toughness, and chemical stability surpasses traditional materials such as boron carbide in environments requiring transparency and durability.
Overview of Boron Carbide
Boron carbide (B4C) is a ceramic material widely recognized for its exceptional hardness, ranking third after diamond and cubic boron nitride, making it highly effective for military armor applications. Its low density combined with superior ballistic resistance enables lightweight armor solutions that provide protection against high-velocity projectiles and shrapnel. Boron carbide's thermal stability and chemical inertness further enhance its performance in extreme combat environments, distinguishing it from aluminum oxynitride in terms of durability and impact resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Aluminium oxynitride (AlON) exhibits superior transparency and hardness with a Vickers hardness of approximately 1800 HV, making it highly effective for transparent armor applications, whereas boron carbide boasts one of the highest hardness values among ceramics, around 2900 HV, delivering exceptional ballistic resistance. AlON offers better fracture toughness, typically in the range of 3.5-4.2 MPa*m^0.5, which enhances its durability against impact compared to boron carbide's lower toughness of about 2-3 MPa*m^0.5. The density of AlON (~3.7 g/cm3) is moderately higher than boron carbide (~2.5 g/cm3), impacting the overall weight of armor systems designed for military vehicles and personal protection.
Ballistic Performance and Protective Capabilities
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) offers superior transparency and high hardness, making it ideal for bulletproof windows and visors in military armor with enhanced ballistic performance against small arms and shrapnel. Boron carbide displays exceptional lightweight hardness and compressive strength, providing excellent protection in composite armor plates against high-velocity projectiles and armor-piercing rounds. Combining ALON's optical clarity with boron carbide's impact resistance allows for optimized protective capabilities in advanced armor systems designed for both visibility and maximum threat mitigation.
Weight and Density Considerations
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) offers a density of approximately 3.7 g/cm3, making it significantly lighter than boron carbide, which has a density around 2.52 g/cm3 but typically requires thicker plates for comparable ballistic protection. The higher density of ALON contributes to its superior hardness and optical transparency, enabling multi-functional armor solutions such as transparent bulletproof windows, while boron carbide's lower density ensures weight efficiency for wearable soldier armor. Balancing weight and density, ALON is preferred in scenarios demanding integrated visibility, whereas boron carbide excels in lightweight, opaque ballistic protection.
Transparency and Visibility Factors
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) offers superior transparency and optical clarity compared to boron carbide, making it ideal for military armor applications requiring high visibility and situational awareness. ALON maintains excellent ballistic protection while enabling clear visibility through armored windows and viewports, a critical factor for soldier safety and operational effectiveness. Boron carbide, although highly effective as a hard ceramic armor, lacks the optical transparency needed for applications demanding clear lines of sight.
Cost and Manufacturing Challenges
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) offers superior optical transparency and high hardness but incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex sintering processes and limited large-scale production techniques. Boron carbide, while more cost-effective and widely available, poses challenges in brittle fracture and machining, impacting armor durability and fabrication speed. Cost-efficiency in mass production favors boron carbide, whereas ALON's advanced properties come with significant manufacturing investments.
Recent Military Applications and Case Studies
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) exhibits superior optical transparency and high hardness, making it ideal for transparent armor in military vehicles and aircraft, demonstrated in recent U.S. Army projects for multi-function windows and sensor protection. Boron carbide is favored for lightweight, ultra-hard armor plates used in personal body armor and vehicle ballistic panels, with extensive deployment in NATO forces highlighting its exceptional performance against high-velocity projectiles. Recent case studies indicate that ALON's resilience to blast impacts complements Boron carbide's ability to provide multi-hit protection, suggesting a hybrid armor system can enhance overall battlefield survivability.
Future Prospects for ALON and Boron Carbide in Defense
Aluminium oxynitride (ALON) exhibits superior optical clarity and multi-hit resistance, making it ideal for transparent armor applications in future military vehicles and aircraft. Boron carbide maintains a high hardness-to-weight ratio, essential for lightweight ballistic protection in body armor and vehicle plating, but its brittleness limits multi-hit capability. Advances in composite integration and manufacturing techniques for both ALON and boron carbide are poised to enhance durability, reduce weight, and expand their deployment in next-generation defense armor systems.
Infographic: Aluminium oxynitride vs Boron carbide for Military armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com