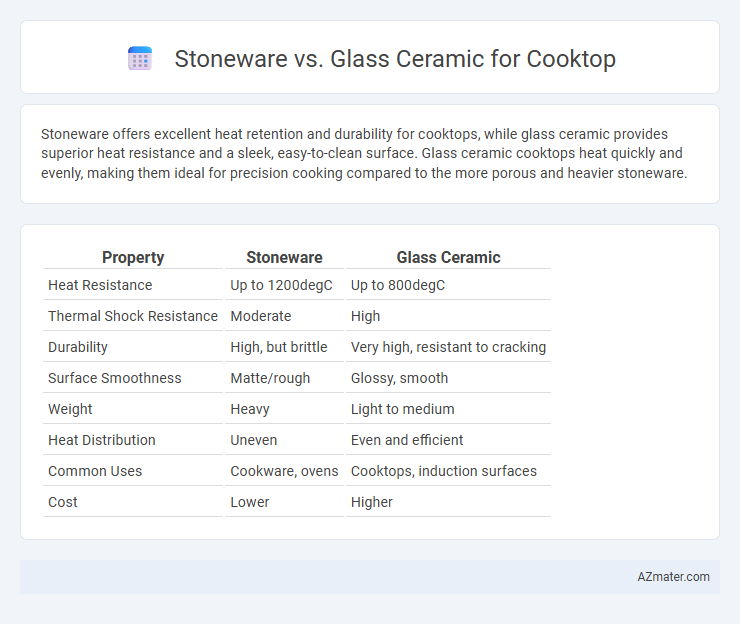
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and durability for cooktops, while glass ceramic provides superior heat resistance and a sleek, easy-to-clean surface. Glass ceramic cooktops heat quickly and evenly, making them ideal for precision cooking compared to the more porous and heavier stoneware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | High, but brittle | Very high, resistant to cracking |
| Surface Smoothness | Matte/rough | Glossy, smooth |
| Weight | Heavy | Light to medium |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven | Even and efficient |
| Common Uses | Cookware, ovens | Cooktops, induction surfaces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cooktop Cookware Materials
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for slow-cooked meals on cooktops, while glass ceramic provides a sleek surface and rapid temperature changes suited for precise cooking control. Glass ceramic cooktops require compatible cookware that allows even heat distribution without scratching the surface, whereas stoneware's durability and resistance to thermal shock support versatile cooktop use. Both materials enhance cooking performance, but choosing between stoneware and glass ceramic depends on heat conduction needs and cooktop surface compatibility.
What Is Stoneware? Key Properties
Stoneware is a type of ceramic material known for its dense, non-porous structure and high heat resistance, making it ideal for durable cooktops. It retains heat efficiently and provides excellent thermal shock resistance, reducing the risk of cracks during temperature changes. Stoneware's natural mineral composition contributes to its robustness and resistance to scratches and stains, enhancing long-term cookware performance.
Understanding Glass Ceramic: Features and Benefits
Glass ceramic cooktops feature a smooth, durable surface resistant to thermal shock and scratches, ensuring longevity and ease of cleaning. Its excellent heat distribution allows for precise temperature control, enhancing cooking efficiency and energy savings. The sleek, modern design complements contemporary kitchens while providing safety with cool-to-touch zones and automatic shut-off functions.
Heat Resistance: Stoneware vs Glass Ceramic
Stoneware exhibits exceptional heat resistance, tolerating temperatures up to 1200degF, making it ideal for high-heat cooking applications without cracking or warping. Glass ceramic cooktops are engineered for rapid heat transfer and can withstand thermal shocks up to 1000degF, providing precise temperature control with minimal heat retention. When comparing heat resistance, stoneware excels in durability under extreme heat, whereas glass ceramic offers superior thermal responsiveness and even heat distribution.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Stoneware cooktops offer excellent durability with high resistance to scratches and thermal shock, making them suitable for long-term use in demanding kitchen environments. Glass ceramic cooktops, while sleek and modern, are more prone to scratches and can crack under sudden temperature changes but often feature easier cleaning surfaces. When comparing lifespan, stoneware generally outlasts glass ceramic due to its robust material structure, though proper maintenance can extend the functional life of both types significantly.
Cooking Performance and Heat Distribution
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and even distribution, ideal for slow-cooking and baking, providing consistent temperatures across the surface. Glass ceramic cooktops heat up quickly and allow precise temperature control, but the heat distribution can be less uniform compared to stoneware, which may affect cooking performance for certain recipes. Choosing between stoneware and glass ceramic depends on the need for rapid heat adjustment versus steady, consistent heat maintenance.
Safety Considerations for Cooktop Use
Stoneware cooktops offer excellent heat retention and resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of cracking under sudden temperature changes. Glass ceramic cooktops feature a smooth surface with heat-resistant properties, but they require careful handling to avoid scratches and impact damage that can compromise safety. Both materials demand proper cookware and cleaning methods to maintain their integrity and ensure safe, efficient cooking.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Stoneware cooktops require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to avoid surface scratches and maintain their matte finish. Glass ceramic cooktops benefit from specialized scraper tools and ceramic cooktop cleaners that effectively remove burnt-on residues and streaks without damaging the smooth, glossy surface. Regular wiping and avoiding harsh chemicals ensure long-lasting performance and aesthetic appeal for both materials.
Price and Value for Money
Stoneware cooktops generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to glass ceramic options, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. Glass ceramic cooktops provide superior heat distribution and durability, resulting in better long-term value despite a higher initial price. Consumers seeking a balance between affordability and performance often find glass ceramic cooktops justified by their longevity and enhanced cooking efficiency.
Which Is Better for Your Cooktop?
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for slow, even cooking on cooktops, while glass ceramic cooktops provide a smooth, easy-to-clean surface that heats quickly and evenly. Glass ceramic is generally better for modern electric or induction cooktops due to its compatibility and durability under rapid temperature changes, whereas stoneware excels on gas or traditional stoves requiring steady, consistent heat. Choosing the best option depends on your cooktop type, cooking style, and maintenance preferences.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com