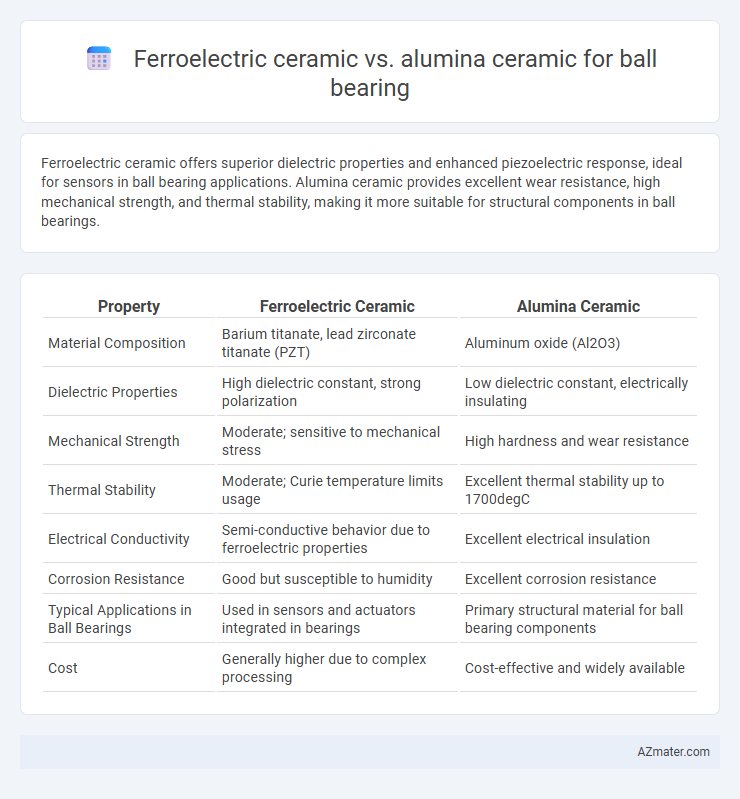
Ferroelectric ceramic offers superior dielectric properties and enhanced piezoelectric response, ideal for sensors in ball bearing applications. Alumina ceramic provides excellent wear resistance, high mechanical strength, and thermal stability, making it more suitable for structural components in ball bearings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Alumina Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Barium titanate, lead zirconate titanate (PZT) | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Dielectric Properties | High dielectric constant, strong polarization | Low dielectric constant, electrically insulating |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; sensitive to mechanical stress | High hardness and wear resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; Curie temperature limits usage | Excellent thermal stability up to 1700degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | Semi-conductive behavior due to ferroelectric properties | Excellent electrical insulation |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good but susceptible to humidity | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Typical Applications in Ball Bearings | Used in sensors and actuators integrated in bearings | Primary structural material for ball bearing components |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complex processing | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Ceramic Ball Bearings
Ceramic ball bearings are valued for their superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and low friction compared to steel bearings. Ferroelectric ceramic offers unique dielectric properties and stability under high temperatures, making it suitable for specialized applications demanding electrical insulation. Alumina ceramic, widely used in ball bearings, provides excellent wear resistance, high hardness, and thermal stability, ensuring durability and reliable performance in harsh industrial environments.
Overview of Ferroelectric and Alumina Ceramics
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit spontaneous electric polarization reversible by an external electric field, making them ideal for sensors and actuators but less common in ball bearing applications due to their electrical properties. Alumina ceramics, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), are renowned for their exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making them the preferred choice for ball bearing components in demanding industrial environments. The contrasting physical and electrical characteristics define alumina's dominance in mechanical applications while ferroelectric ceramics serve specialized roles in electronics.
Material Properties Comparison
Ferroelectric ceramic offers high dielectric constant and excellent piezoelectric properties, making it suitable for applications requiring precise vibration control, whereas alumina ceramic excels in hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability essential for ball bearing durability. Alumina typically exhibits superior mechanical strength with a flexural strength of around 300-400 MPa and hardness close to 15-20 GPa, compared to ferroelectric ceramics that have lower mechanical robustness. Thermal conductivity in alumina ceramics, approximately 25-30 W/m*K, surpasses that of ferroelectric ceramics, enhancing heat dissipation during ball bearing operation.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit lower mechanical strength and hardness compared to alumina ceramics, making alumina the preferred choice for ball bearing applications requiring high wear resistance and durability. Alumina ceramics typically offer a hardness value of around 15-20 GPa and superior fracture toughness, ensuring better performance under mechanical stress. The inherent brittleness of ferroelectric ceramics limits their use where high load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance are critical.
Wear Resistance in Bearing Applications
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit moderate wear resistance but are less suitable for ball bearing applications due to their brittleness and lower mechanical strength compared to alumina ceramics. Alumina ceramics offer superior wear resistance, high hardness, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-performance ball bearings subjected to heavy loads and abrasive environments. The enhanced durability of alumina ceramics results in longer service life and reduced maintenance in bearing applications.
Electrical Properties and Performance
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit high dielectric constants and piezoelectric properties, making them suitable for applications requiring electrical responsiveness in ball bearings. Alumina ceramics provide excellent electrical insulation and high dielectric strength, ensuring minimal electrical conductivity and resistance to electrical erosion in bearing environments. Ferroelectric ceramics enable active electrical functionality, whereas alumina ceramics offer superior electrical isolation and durability under high-voltage conditions.
Thermal Stability and Operating Temperatures
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit excellent thermal stability with operating temperatures typically ranging from -55degC to 150degC, making them suited for applications requiring stable electrical properties under temperature fluctuations. Alumina ceramics offer superior thermal stability and can withstand much higher operating temperatures, often up to 1700degC, making them ideal for high-temperature environments in ball bearing applications. The inherent high thermal conductivity and exceptional mechanical strength of alumina ceramics provide enhanced durability and performance under extreme thermal conditions compared to ferroelectric ceramics.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit moderate corrosion resistance, making them vulnerable to acidic and alkaline environments compared to alumina ceramics, which demonstrate superior chemical inertness and excellent resistance to a wide range of corrosive substances. Alumina ceramics, with their dense microstructure and stable oxide composition, provide enhanced protection against oxidizing agents and aggressive chemicals commonly encountered in ball bearing applications. This chemical resilience ensures longer service life and reliability of alumina ceramic ball bearings in harsh, corrosive environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Ferroelectric ceramics offer unique piezoelectric properties but typically come with higher material and processing costs compared to alumina ceramics, which are favored for ball bearings due to their superior hardness, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Alumina ceramics provide consistent manufacturing scalability with well-established sintering and machining techniques, resulting in lower production expenses and enhanced reliability in high-stress bearing applications. Choosing alumina ceramic for ball bearings optimizes cost-efficiency while maintaining excellent mechanical performance, making it the preferred option in industrial manufacturing.
Best Use Cases: Ferroelectric vs Alumina Ceramic Ball Bearings
Ferroelectric ceramic ball bearings excel in applications requiring precise electrical insulation and voltage responsiveness, making them ideal for sensors and actuators in advanced electronic systems. Alumina ceramic ball bearings offer superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making them optimal for high-speed machinery and harsh industrial environments. The best use case for ferroelectric ceramics centers on electronic integration, while alumina ceramics are preferred for durability and performance under heavy mechanical stress.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Alumina ceramic for Ball bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com