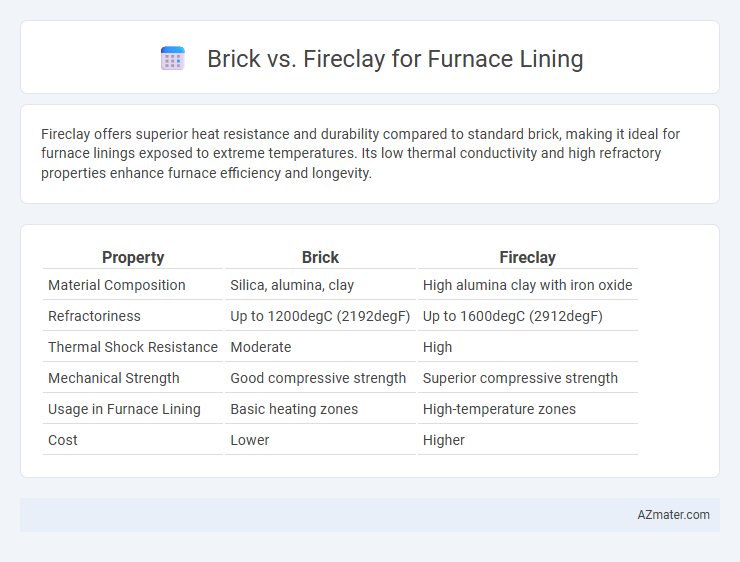
Fireclay offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to standard brick, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to extreme temperatures. Its low thermal conductivity and high refractory properties enhance furnace efficiency and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Fireclay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica, alumina, clay | High alumina clay with iron oxide |
| Refractoriness | Up to 1200degC (2192degF) | Up to 1600degC (2912degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good compressive strength | Superior compressive strength |
| Usage in Furnace Lining | Basic heating zones | High-temperature zones |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Understanding Furnace Lining Materials
Fireclay offers higher thermal shock resistance and better durability compared to standard firebrick, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to intense heat cycles. Firebrick, composed primarily of alumina and silica, provides cost-effective insulation but may degrade faster under extreme thermal stress. Selecting furnace lining materials depends on balancing heat resistance, mechanical strength, and lifespan requirements for specific industrial applications.
Brick: Composition and Key Properties
Brick used for furnace lining primarily consists of alumina, silica, and clay, offering high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Its dense structure provides excellent mechanical strength and durability under high temperatures, making it suitable for prolonged exposure to heat. The low porosity of furnace bricks ensures minimal slag infiltration, enhancing the longevity and performance of the furnace lining.
Fireclay: Composition and Key Properties
Fireclay for furnace lining primarily consists of alumina, silica, and kaolin, providing exceptional heat resistance and thermal stability. Its high alumina content enhances refractory strength, allowing it to withstand temperatures above 1600degC without deformation or chemical degradation. Fireclay's low thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to thermal shock make it a superior choice for maintaining furnace integrity in high-temperature industrial applications.
Thermal Resistance Comparison: Brick vs Fireclay
Fireclay offers superior thermal resistance compared to standard firebrick, with the ability to withstand temperatures up to 1800degC, whereas typical firebrick endures up to 1400degC. The higher alumina content in fireclay enhances its refractoriness, making it more suitable for furnace linings exposed to extreme heat cycles. Fireclay also exhibits improved thermal shock resistance and durability, reducing maintenance frequency and extending furnace lifespan.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fireclay offers superior mechanical strength compared to traditional brick, making it more resistant to cracking and wear under high-temperature furnace conditions. Its enhanced durability stems from a higher alumina content, which provides better thermal shock resistance and longer service life in aggressive environments. Brick, while more economical, tends to have lower mechanical strength and is more susceptible to erosion and deformation over time.
Chemical Resistance and Longevity
Fireclay lining exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to traditional brick, effectively withstanding acidic and alkaline environments commonly encountered in furnace operations. Its dense microstructure limits chemical penetration, reducing degradation and extending service life under high-temperature, corrosive conditions. Brick linings, while durable, typically offer less resistance to slag and aggressive chemical exposure, resulting in more frequent maintenance and shorter operational longevity.
Cost Analysis of Brick and Fireclay Linings
Brick linings for furnaces typically offer lower initial installation costs compared to fireclay, making them a budget-friendly option for many industrial applications. Fireclay linings, while more expensive upfront due to higher material and manufacturing costs, provide superior thermal resistance and longer service life, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. When conducting a cost analysis, it is crucial to consider the total lifecycle cost, including installation, durability, thermal efficiency, and maintenance frequency, rather than just the initial expenditure.
Installation Process and Maintenance Needs
Fireclay furnace lining offers easier installation due to its pre-formed shapes and consistent thermal properties, reducing the need for extensive fitting compared to traditional brick lining, which requires precise masonry work and curing time. Maintenance of fireclay linings typically involves fewer repairs since its dense, refractory nature resists cracking and spalling, whereas brick linings demand regular inspection and occasional replacement of damaged bricks to maintain insulation efficiency. Choosing fireclay can lead to lower long-term upkeep costs and quicker downtime recovery, benefiting high-performance or continuous-operation furnaces.
Best Applications: When to Choose Brick or Fireclay
Firebrick is best suited for furnace linings exposed to extremely high temperatures and rapid thermal cycling due to its superior thermal shock resistance and high melting point of around 1,770degC (3,218degF). Fireclay bricks perform well in moderate heat applications up to approximately 1,400degC (2,552degF), offering excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and abrasion, making them ideal for less intensive furnace zones or as backup insulation. Choosing between firebrick and fireclay depends on the furnace's maximum operating temperature, chemical exposure, and required durability under thermal stress.
Final Recommendations for Furnace Lining Selection
Choosing between brick and fireclay for furnace lining depends on the operating temperature and chemical exposure; fireclay excels in moderate heat settings up to 1,400degC, offering superior resistance to thermal shock and corrosion. High-temperature industrial furnaces exceeding 1,600degC benefit from refractory bricks, which provide enhanced structural strength and long-term durability. For optimal furnace performance and lifespan, select fireclay linings for mid-range applications and dense refractory bricks for high-heat environments demanding maximum thermal and mechanical resistance.
Infographic: Brick vs Fireclay for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com