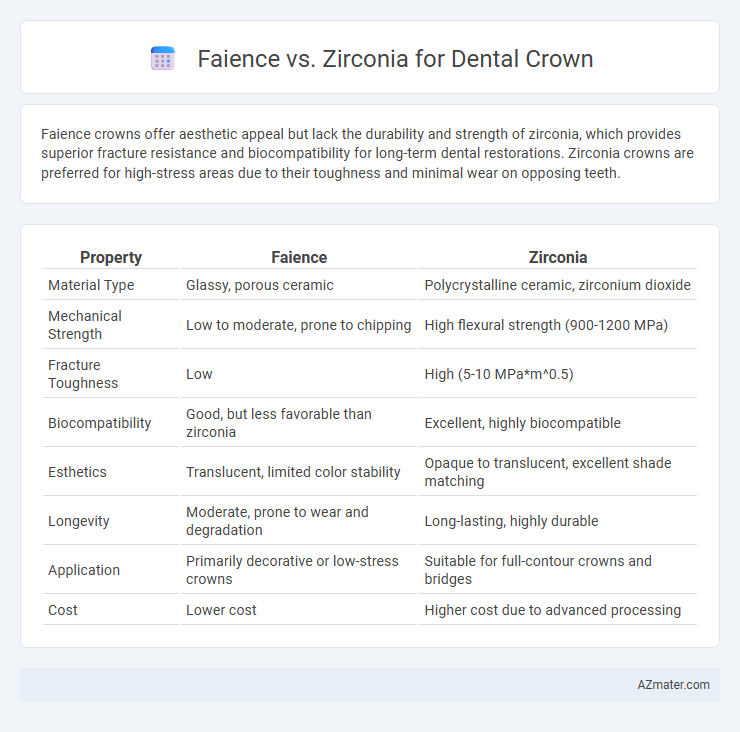
Faience crowns offer aesthetic appeal but lack the durability and strength of zirconia, which provides superior fracture resistance and biocompatibility for long-term dental restorations. Zirconia crowns are preferred for high-stress areas due to their toughness and minimal wear on opposing teeth.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glassy, porous ceramic | Polycrystalline ceramic, zirconium dioxide |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate, prone to chipping | High flexural strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Fracture Toughness | Low | High (5-10 MPa*m^0.5) |
| Biocompatibility | Good, but less favorable than zirconia | Excellent, highly biocompatible |
| Esthetics | Translucent, limited color stability | Opaque to translucent, excellent shade matching |
| Longevity | Moderate, prone to wear and degradation | Long-lasting, highly durable |
| Application | Primarily decorative or low-stress crowns | Suitable for full-contour crowns and bridges |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials such as faience and zirconia differ significantly in composition and performance. Faience, a type of glazed ceramic, offers aesthetic translucency but has limited strength compared to zirconia, which is a high-strength, biocompatible ceramic known for its durability and fracture resistance. Understanding these materials' properties is crucial for selecting the most suitable crown option based on patient needs and clinical requirements.
What is Faience in Dentistry?
Faience in dentistry refers to a type of ceramic material often used for dental crowns and restorations, prized for its aesthetic qualities and translucence that mimic natural tooth enamel. Unlike zirconia, which is a high-strength, opaque ceramic known for its durability and fracture resistance, faience offers superior cosmetic appeal but generally lower mechanical strength. This makes faience suitable for patients prioritizing appearance in anterior teeth, whereas zirconia is preferred for posterior crowns requiring enhanced toughness.
Understanding Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and durability compared to faience crowns, making them a preferred choice for restoring molars and back teeth subjected to heavy chewing forces. Their biocompatibility and resistance to wear and fracture provide long-lasting dental restoration with minimal risk of allergic reactions or gum irritation. Advanced CAD/CAM technology allows precise customization of zirconia crowns, ensuring optimal fit and aesthetics that closely mimic natural teeth.
Aesthetic Comparison: Faience vs Zirconia
Faience dental crowns offer a natural translucency that closely mimics the appearance of real teeth, providing superior aesthetic appeal for front teeth restorations. Zirconia crowns, while highly durable, tend to have a more opaque finish that can appear less lifelike but are increasingly enhanced with layering techniques to improve aesthetics. Both materials balance visual appeal with strength, yet faience excels in replicating the subtle color variations and translucency of natural enamel.
Strength and Durability Differences
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to faience, with a flexural strength typically exceeding 900 MPa, making them highly resistant to fractures under occlusal forces. Faience crowns, composed of glazed ceramic materials, generally have lower fracture toughness and are more prone to chipping or cracking over time. Zirconia's high density and toughness also contribute to its long-lasting performance in posterior restorations, whereas faience is more suitable for aesthetic anterior crowns with less mechanical stress.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to faience, as zirconia is a highly inert, non-toxic ceramic that minimizes allergic reactions and inflammation in oral tissues. Faience, being a glazed ceramic, has limited durability and may release ions that could potentially cause localized irritation or sensitivity. The enhanced biocompatibility and mechanical strength of zirconia contribute to improved patient safety by reducing the risk of crown failure and adverse tissue response.
Longevity and Maintenance
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior longevity compared to faience crowns due to their high fracture toughness and resistance to wear, often lasting 10-15 years or more with proper care. Faience crowns, made from glazed ceramic materials, tend to be more brittle and prone to chipping, requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement. Maintenance for zirconia crowns is minimal, involving routine dental hygiene and professional check-ups, whereas faience crowns may need additional polishing or repairs to address surface degradation.
Cost Analysis: Faience vs Zirconia Crowns
Faience dental crowns generally cost less than zirconia crowns due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for patients. Zirconia crowns, while more expensive, offer superior durability, biocompatibility, and aesthetic appeal, which can reduce long-term replacement costs. Cost analysis should also factor in clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction, as the initial investment in zirconia may provide better value over time.
Indications and Best Use Cases
Faience dental crowns are best suited for patients seeking cost-effective, aesthetically pleasing solutions in low-stress areas such as front teeth restorations due to their good translucency but lower strength. Zirconia crowns excel in posterior teeth applications and patients with bruxism, providing superior durability, fracture resistance, and biocompatibility under heavy masticatory forces. Indications for faience include cosmetic improvements and temporary crowns, while zirconia is preferred for long-term restorations requiring high strength and wear resistance.
Choosing the Right Dental Crown Material
Choosing the right dental crown material depends on factors like durability, aesthetics, and biocompatibility. Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and fracture resistance, making them ideal for molars and long-lasting restorations, while faience crowns provide excellent translucency suited for front teeth requiring a natural appearance. Evaluating patient-specific needs, such as bite pressure and cosmetic preferences, ensures optimal results with either material.
Infographic: Faience vs Zirconia for Dental Crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com