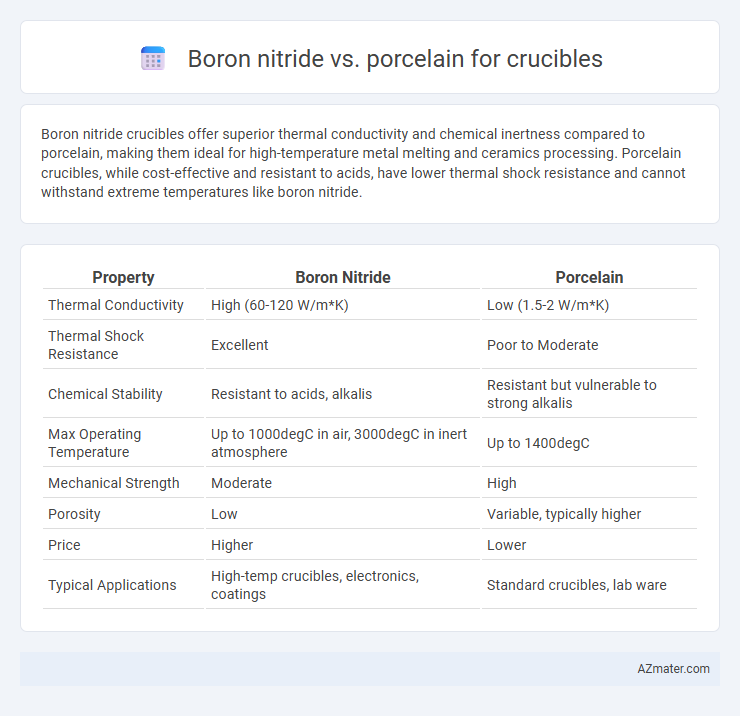
Boron nitride crucibles offer superior thermal conductivity and chemical inertness compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-temperature metal melting and ceramics processing. Porcelain crucibles, while cost-effective and resistant to acids, have lower thermal shock resistance and cannot withstand extreme temperatures like boron nitride.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Boron Nitride | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (60-120 W/m*K) | Low (1.5-2 W/m*K) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Poor to Moderate |
| Chemical Stability | Resistant to acids, alkalis | Resistant but vulnerable to strong alkalis |
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1000degC in air, 3000degC in inert atmosphere | Up to 1400degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Porosity | Low | Variable, typically higher |
| Price | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High-temp crucibles, electronics, coatings | Standard crucibles, lab ware |
Introduction to Crucible Materials
Boron nitride and porcelain are common materials used for crucibles in laboratory and industrial applications, each offering unique thermal and chemical properties. Boron nitride provides exceptional thermal shock resistance, high-temperature stability up to 2,973degC, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for handling reactive metals and corrosive substances. Porcelain crucibles, typically made from kaolin and other clay materials, excel in cost-effectiveness, moderate heat resistance up to around 1,200degC, and general-purpose use in non-reactive or low-temperature applications.
Overview of Boron Nitride Crucibles
Boron nitride crucibles offer exceptional thermal stability, chemical inertness, and high resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-temperature applications in metal, chemical, and electronics industries. Their unique hexagonal crystal structure provides excellent lubrication properties and non-wettability by molten metals, ensuring easy material release and durability. Compared to porcelain crucibles, boron nitride crucibles withstand higher temperatures up to 3000degC, resist corrosion from strong acids and molten metals, and provide superior mechanical strength for demanding laboratory and industrial processes.
Overview of Porcelain Crucibles
Porcelain crucibles offer exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-temperature applications in laboratories. Their non-porous surface prevents contamination and ensures accurate results during chemical analysis and testing. Porcelain's durability and low thermal conductivity provide effective insulation, which helps maintain consistent temperatures during heating processes.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Boron nitride crucibles exhibit superior thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 2,800degC in inert atmospheres, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Porcelain crucibles, in contrast, typically endure temperatures only up to 1,200degC before compromising structural integrity. This significant difference in thermal resistance positions boron nitride as the preferred choice for extreme thermal processes requiring enhanced durability and performance.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Boron nitride crucibles exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to porcelain, particularly against aggressive acids, molten metals, and corrosive slags, due to their inert and non-reactive nature. Porcelain crucibles, while resistant to thermal shock and moderate chemicals, are susceptible to degradation when exposed to strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. The enhanced chemical stability of boron nitride makes it a preferred choice for high-purity applications and environments requiring resistance to harsh chemical agents.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Boron nitride crucibles exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making them highly durable under rapid temperature changes and high-stress conditions. Porcelain crucibles, while chemically inert and cost-effective, tend to have lower mechanical strength and are more prone to cracking or chipping during thermal cycling. The enhanced durability of boron nitride crucibles ensures prolonged service life in demanding laboratory and industrial environments.
Temperature Limits and Performance
Boron nitride crucibles offer exceptional temperature resistance up to 2,800degC, outperforming porcelain crucibles, which typically withstand temperatures up to 1,200degC. The superior thermal stability and chemical inertness of boron nitride make it ideal for high-temperature applications such as metal casting and crystal growth. Porcelain crucibles, while cost-effective for lower-temperature processes, lack the high-temperature durability and thermal shock resistance found in boron nitride.
Cost and Availability
Boron nitride crucibles typically cost significantly more than porcelain due to their superior thermal resistance and chemical inertness, making them a premium choice for high-temperature applications. Porcelain crucibles are widely available and more affordable, favored for general laboratory use where extreme conditions are not a factor. The cost-effectiveness and accessibility of porcelain make it ideal for routine tasks, while boron nitride is preferred despite higher investment for specialized, high-performance requirements.
Suitability for Various Applications
Boron nitride crucibles offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as metal melting and semiconductor processing. Porcelain crucibles excel in durability and affordability, suitable for low to moderate temperature lab experiments involving acids and salts. Choosing between boron nitride or porcelain depends on specific application requirements, including temperature range, chemical compatibility, and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Crucible
Boron nitride crucibles offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness, making them ideal for handling reactive or high-temperature materials. Porcelain crucibles excel in affordability and general chemical resistance but are prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Selecting the right crucible depends on the specific thermal and chemical demands of your application, with boron nitride preferred for high-performance laboratory or industrial processes.
Infographic: Boron nitride vs Porcelain for Crucible
 azmater.com
azmater.com