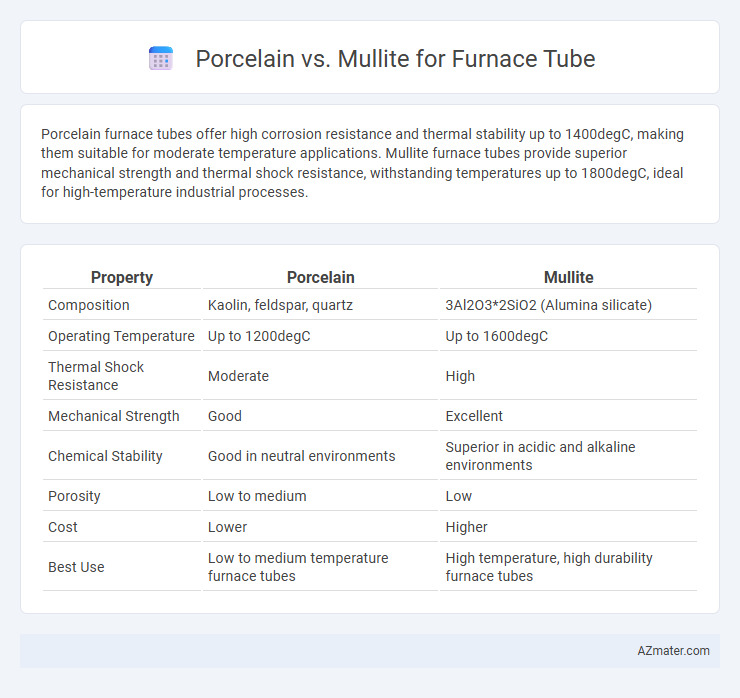
Porcelain furnace tubes offer high corrosion resistance and thermal stability up to 1400degC, making them suitable for moderate temperature applications. Mullite furnace tubes provide superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1800degC, ideal for high-temperature industrial processes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina silicate) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Stability | Good in neutral environments | Superior in acidic and alkaline environments |
| Porosity | Low to medium | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use | Low to medium temperature furnace tubes | High temperature, high durability furnace tubes |
Introduction to Furnace Tube Materials
Furnace tubes are critical components in high-temperature industrial applications, requiring materials with exceptional thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength. Porcelain, known for its excellent insulation properties and chemical inertness, offers cost-effective durability but can be prone to brittleness under extreme conditions. Mullite, characterized by its superior thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and resistance to thermal shock, provides enhanced performance in harsh environments, making it a preferred choice for advanced furnace tube materials.
Overview of Porcelain Tubes
Porcelain furnace tubes are engineered from high-quality ceramic materials known for exceptional thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures up to 1300degC. These tubes offer excellent chemical inertness, making them ideal for corrosive environments in industrial furnaces. Their superior dielectric strength and mechanical durability ensure long-term reliability in high-temperature applications compared to other materials like mullite.
Overview of Mullite Tubes
Mullite tubes, composed primarily of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-temperature furnace applications. Their high melting point of approximately 1830degC and low thermal expansion coefficient enhance durability under extreme operating conditions. These properties ensure mullite tubes maintain structural integrity and resist corrosion, extending the lifespan of furnace components.
Thermal Stability: Porcelain vs Mullite
Mullite exhibits superior thermal stability compared to porcelain, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 1800degC, whereas porcelain typically withstands temperatures only up to 1300degC. This higher thermal resistance makes mullite more suitable for high-temperature furnace tube applications where prolonged exposure to thermal cycling and thermal shock is common. Porcelain's lower thermal stability can lead to cracking and deformation under extreme conditions, limiting its use in advanced thermal environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Porcelain furnace tubes exhibit moderate mechanical strength with good resistance to thermal shock but tend to be more brittle under high mechanical stress. Mullite furnace tubes offer superior mechanical strength and enhanced thermal stability, making them more durable in high-temperature and demanding industrial environments. The high alumina content in mullite improves toughness and resistance to deformation, outperforming porcelain in maintaining structural integrity under mechanical loads.
Chemical Resistance in High-Temperature Environments
Porcelain furnace tubes exhibit excellent chemical resistance against acidic slags and gases at temperatures up to 1300degC, making them ideal for environments with corrosive compounds. Mullite furnace tubes offer superior resistance to alkaline slags and thermal shock due to their high alumina content and stability above 1400degC. The choice between porcelain and mullite depends on specific chemical exposure and operating temperature, with mullite preferred for more aggressive or higher-temperature conditions.
Lifespan and Durability Factors
Porcelain furnace tubes offer good thermal resistance but are prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes, limiting their lifespan and durability in high-stress environments. Mullite tubes exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, resulting in a longer operational lifespan and enhanced durability for continuous high-temperature applications. The high alumina content in mullite significantly improves resistance to corrosion and wear, making it the preferred choice for industrial furnace tubes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Porcelain furnace tubes generally offer lower initial costs and widespread availability due to their common usage and ease of manufacturing. Mullite tubes, though more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal stability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and overall maintenance costs. The cost-effectiveness of choosing between porcelain and mullite depends on balancing initial investment against durability and availability in specific industrial applications.
Application Suitability: Industrial Use Cases
Porcelain furnace tubes offer excellent electrical insulation and temperature resistance, making them ideal for low to medium-temperature industrial applications such as electrical heating elements and chemical processing. Mullite furnace tubes excel in high-temperature environments, with superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, suited for glass manufacturing, kiln furniture, and metallurgical furnaces. Selecting between porcelain and mullite depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to the industrial use case.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Porcelain and Mullite
Mullite furnace tubes offer superior thermal stability, higher corrosion resistance, and enhanced mechanical strength compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Porcelain tubes, while cost-effective and suitable for moderate temperatures, lack the durability and thermal shock resistance required for more demanding environments. Selecting between porcelain and mullite depends on operational temperature ranges, budget constraints, and the specific chemical exposure of the furnace environment.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Mullite for Furnace Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com