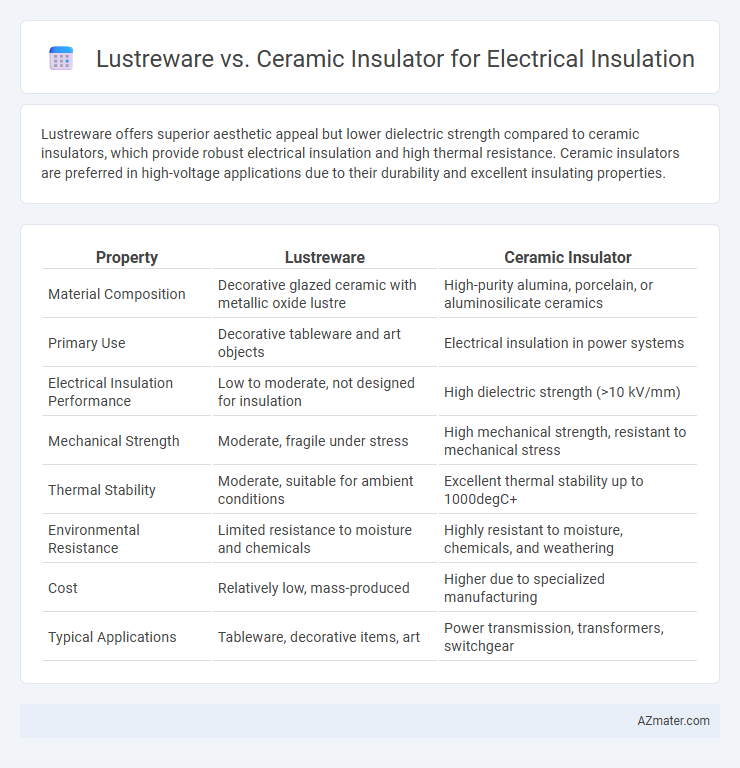
Lustreware offers superior aesthetic appeal but lower dielectric strength compared to ceramic insulators, which provide robust electrical insulation and high thermal resistance. Ceramic insulators are preferred in high-voltage applications due to their durability and excellent insulating properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Ceramic Insulator |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Decorative glazed ceramic with metallic oxide lustre | High-purity alumina, porcelain, or aluminosilicate ceramics |
| Primary Use | Decorative tableware and art objects | Electrical insulation in power systems |
| Electrical Insulation Performance | Low to moderate, not designed for insulation | High dielectric strength (>10 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, fragile under stress | High mechanical strength, resistant to mechanical stress |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, suitable for ambient conditions | Excellent thermal stability up to 1000degC+ |
| Environmental Resistance | Limited resistance to moisture and chemicals | Highly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and weathering |
| Cost | Relatively low, mass-produced | Higher due to specialized manufacturing |
| Typical Applications | Tableware, decorative items, art | Power transmission, transformers, switchgear |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Lustreware and ceramic insulators both serve critical roles in electrical insulation by preventing current leakage and maintaining electrical safety. Ceramic insulators, renowned for their high dielectric strength, thermal stability, and resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion, offer superior performance in high-voltage applications compared to lustreware, which is primarily decorative and lacks the necessary insulating properties. The intrinsic material composition of ceramics, including alumina and silica, ensures reliable electrical insulation in various industrial environments, making them the preferred choice over lustreware for electrical insulation purposes.
Overview of Lustreware in Electrical Applications
Lustreware, a ceramic material coated with a metallic glaze, exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties combined with enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for specific electrical insulation applications. Its unique surface finish improves dielectric strength and minimizes surface leakage currents, crucial for high-voltage equipment and insulating components in electrical systems. Lustreware's ability to maintain stability under thermal stress and its aesthetic appeal also contribute to its use in decorative yet functional electrical insulators.
Ceramic Insulators: Properties and Uses
Ceramic insulators exhibit exceptional electrical resistance, high mechanical strength, and outstanding thermal stability, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure ensures reliable performance in power transmission and distribution systems. Commonly used in substations, transmission towers, and electrical connectors, ceramic insulators prevent electrical leakage and maintain system safety and efficiency.
Electrical Insulation Efficiency: Lustreware vs Ceramic
Lustreware insulators exhibit moderate electrical insulation efficiency, often limited by their glazed surface which can be prone to micro-cracks affecting dielectric strength. Ceramic insulators, specifically porcelain-based types, offer superior electrical insulation due to their high dielectric strength, thermal stability, and resistance to moisture ingress. The dense, non-porous structure of ceramic materials ensures enhanced performance in high voltage applications compared to lustreware's decorative, less uniform glaze.
Material Composition and Its Impact on Performance
Lustreware insulators are typically made from vitrified ceramics with a glossy glaze that enhances moisture resistance and mechanical strength, improving electrical insulation properties by minimizing surface conductivity and contamination. Ceramic insulators, composed mainly of alumina and silica, offer excellent thermal stability and dielectric strength but may be more porous unless treated, which can affect performance in humid environments. The material composition directly influences insulation durability, with lustreware's glazed surface providing better protection against environmental degradation compared to untreated ceramic insulators.
Durability and Longevity in Harsh Environments
Lustreware insulators exhibit superior resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion, making them highly durable in harsh environments with fluctuating temperatures and high humidity. Ceramic insulators maintain excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability, ensuring long-term performance under extreme electrical and environmental stresses. Both materials provide reliable electrical insulation, but ceramics generally offer enhanced longevity due to their high resistance to abrasion and UV degradation.
Cost Efficiency: Production and Maintenance
Lustreware offers lower production costs due to simpler manufacturing processes but may incur higher maintenance expenses from lower durability and susceptibility to chipping. Ceramic insulators, although more expensive to produce because of high-temperature firing and material quality, provide superior longevity and require less frequent replacement, reducing overall maintenance costs. Cost efficiency in electrical insulation depends on balancing initial investment against long-term performance, with ceramics typically favored for high-reliability applications.
Safety Considerations and Standards Compliance
Lustreware insulators provide basic electrical insulation but often lack the rigorous safety standards required for high-voltage applications, making them less reliable compared to ceramic insulators. Ceramic insulators meet international safety standards such as IEC 60273 and ANSI C29, ensuring superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental hazards. The enhanced dielectric properties and compliance with stringent testing protocols of ceramic insulators significantly reduce the risk of electrical failure and improve overall safety in electrical installations.
Common Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Lustreware insulators are commonly used in decorative and low-voltage electrical applications due to their aesthetic finish and moderate insulating properties, making them ideal for household switches and ornamental fixtures. Ceramic insulators excel in high-voltage and outdoor environments, offering superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to weathering, which makes them the preferred choice for power transmission lines, transformers, and industrial electrical equipment. Both materials serve specific niches: lustreware is valued for design-centric, low-stress insulation, while ceramics dominate demanding electrical infrastructure applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Electrical Insulation
Lustreware insulators incorporate advanced glazing techniques that enhance dielectric strength and thermal stability, positioning them as promising materials in next-generation electrical insulation applications. Ceramic insulators continue to evolve through nanotechnology integration, improving mechanical robustness and electrical performance for high-voltage power systems. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid materials combining lustreware's surface properties with ceramic's intrinsic durability to achieve superior insulation efficiency and longevity in smart grid infrastructures.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Ceramic insulator for Electrical insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com