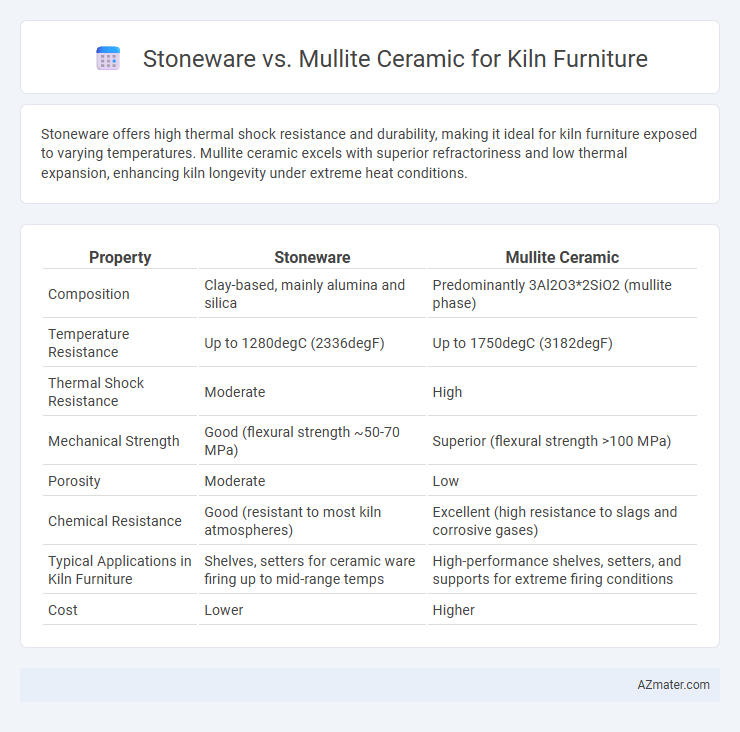
Stoneware offers high thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for kiln furniture exposed to varying temperatures. Mullite ceramic excels with superior refractoriness and low thermal expansion, enhancing kiln longevity under extreme heat conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Mullite Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay-based, mainly alumina and silica | Predominantly 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (mullite phase) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1280degC (2336degF) | Up to 1750degC (3182degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good (flexural strength ~50-70 MPa) | Superior (flexural strength >100 MPa) |
| Porosity | Moderate | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to most kiln atmospheres) | Excellent (high resistance to slags and corrosive gases) |
| Typical Applications in Kiln Furniture | Shelves, setters for ceramic ware firing up to mid-range temps | High-performance shelves, setters, and supports for extreme firing conditions |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials like stoneware and mullite ceramics are essential for supporting wares during firing, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties. Stoneware ceramics provide affordability and good thermal stability, making them suitable for lower-temperature firings, while mullite ceramics exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and longevity at higher temperatures due to their high alumina content. Choosing between stoneware and mullite depends on firing temperature range, durability requirements, and cost considerations in ceramic production.
Overview of Stoneware Ceramics
Stoneware ceramics offer excellent durability and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for kiln furniture that must withstand high firing temperatures around 1200degC to 1300degC. These ceramics exhibit a dense, non-porous structure with high mechanical strength and good chemical stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in kiln environments. Compared to mullite, stoneware typically provides greater resistance to glaze adherence and deformation during repeated firings, enhancing its suitability for supporting ceramic wares in kilns.
Characteristics of Mullite Ceramics
Mullite ceramics exhibit exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making them ideal for kiln furniture exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations. Their high strength and resistance to thermal shock surpass stoneware, ensuring durability and dimensional stability during prolonged high-temperature firings. Mullite's chemical inertness and excellent creep resistance enhance performance in harsh kiln environments, outperforming traditional stoneware materials.
Thermal Resistance: Stoneware vs Mullite
Mullite ceramic exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to stoneware, withstanding temperatures up to 1750degC, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Stoneware typically resists temperatures up to 1300degC, which limits its use in more extreme firing conditions. The higher melting point and thermal stability of mullite reduce deformation and increase durability under repeated thermal cycling.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Stoneware kiln furniture offers moderate mechanical strength suitable for general firing applications, with resistance to thermal shock and deformation up to 1300degC. Mullite ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its higher alumina content and crystalline structure, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1600degC. The enhanced flexural strength and thermal stability of mullite make it ideal for high-temperature and heavy-duty kiln furniture compared to stoneware.
Weight and Density Differences
Stoneware kiln furniture typically has higher density, ranging between 2.3 to 2.5 g/cm3, resulting in heavier weight compared to mullite ceramic, which has a lower density around 2.0 to 2.4 g/cm3. The increased density of stoneware contributes to greater mass and thermal inertia, affecting kiln loading and heat distribution. Mullite's lower density reduces overall weight, improving handling and energy efficiency during high-temperature firing processes.
Chemical Stability in Kiln Environments
Stoneware offers moderate chemical stability in kiln environments, with resistance primarily to alkaline slags but susceptibility to acidic fluxes under high temperatures. Mullite ceramic excels in chemical stability, maintaining structural integrity and resisting corrosive effects from both acidic and alkaline atmospheres at temperatures up to 1750degC. The superior resistance of mullite to chemical attack enhances the longevity and performance of kiln furniture in aggressive firing conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Stoneware kiln furniture offers higher cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly option for many ceramic manufacturers. Mullite ceramics, though more expensive initially, provide superior thermal stability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and overall operational costs. Availability of mullite can be limited compared to stoneware, impacting lead times and project scalability in large-scale kiln operations.
Typical Applications in Kilns
Stoneware is commonly used in kiln furniture for firing pottery, tiles, and bricks due to its moderate thermal shock resistance and good mechanical strength at high temperatures. Mullite ceramics outperform stoneware in applications requiring higher temperature endurance, such as precision firing of technical ceramics, glass, and advanced refractories, because of their superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Both materials are essential in kiln furniture, with stoneware preferred for general ceramic production and mullite favored in high-performance industrial kiln environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Kiln Furniture
Stoneware kiln furniture offers excellent thermal shock resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for lower temperature firing processes. Mullite ceramic, with its superior thermal stability and high melting point above 1840degC, is suited for high-temperature applications requiring long-term durability. Selecting the right kiln furniture depends on firing temperature, load weight, and specific kiln atmosphere to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Mullite ceramic for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com