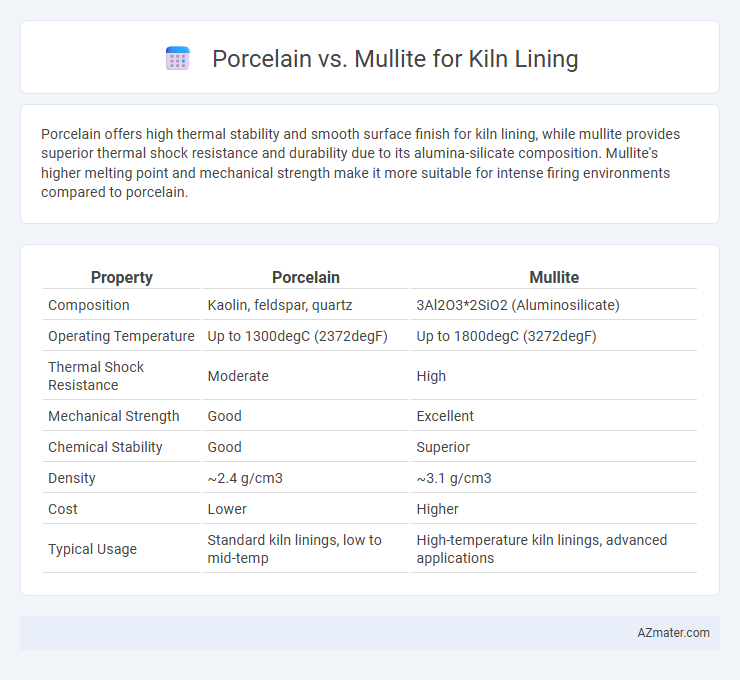
Porcelain offers high thermal stability and smooth surface finish for kiln lining, while mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability due to its alumina-silicate composition. Mullite's higher melting point and mechanical strength make it more suitable for intense firing environments compared to porcelain.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Aluminosilicate) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1300degC (2372degF) | Up to 1800degC (3272degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Stability | Good | Superior |
| Density | ~2.4 g/cm3 | ~3.1 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Usage | Standard kiln linings, low to mid-temp | High-temperature kiln linings, advanced applications |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Porcelain and mullite are two common kiln lining materials, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties essential for optimal kiln performance. Mullite, a high-temperature ceramic, provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for industrial kilns exposed to rapid temperature changes. Porcelain, characterized by its smooth surface and moderate heat tolerance, is often favored for applications requiring electrical insulation and moderate thermal stability.
Overview of Porcelain as a Kiln Lining
Porcelain is valued for kiln linings due to its excellent thermal resistance, low thermal expansion, and high mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. Its smooth, non-porous surface reduces dust generation and enhances durability against thermal shock and chemical attack from kiln atmospheres. Porcelain kiln linings provide a reliable, long-lasting barrier that maintains structural integrity during intense firing cycles.
Key Properties of Mullite in Kiln Applications
Mullite, a superior ceramic material used in kiln linings, offers excellent thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 1800degC, far exceeding the limits of porcelain. Its low thermal expansion minimizes crack formation, enhancing durability during rapid heating and cooling cycles typical in kiln operations. High resistance to thermal shock and mechanical strength makes mullite ideal for maintaining kiln integrity under extreme conditions, outperforming porcelain in long-term kiln performance.
Thermal Resistance: Porcelain vs Mullite
Mullite offers superior thermal resistance compared to porcelain, withstanding temperatures up to 1800degC, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln linings. Porcelain, while durable, generally tolerates temperatures around 1300degC to 1400degC, limiting its effectiveness in intense firing environments. Mullite's excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion enhance kiln longevity and performance, surpassing porcelain in demanding thermal applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mullite exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to porcelain, making it more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical wear in kiln linings. Porcelain, while offering good insulating properties, generally has lower fracture toughness and is more prone to cracking under high-stress conditions. The enhanced durability of mullite kiln linings extends service life and reduces maintenance in industrial high-temperature environments.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Porcelain exhibits excellent chemical durability due to its low porosity and high resistance to acidic and alkaline substances, making it suitable for kiln linings exposed to corrosive environments. Mullite offers superior corrosion resistance at high temperatures because of its stable aluminosilicate structure, which resists slag and molten metals more effectively than porcelain. In kiln lining applications, mullite's enhanced thermal and chemical stability often results in longer service life under aggressive operating conditions.
Cost Analysis: Porcelain versus Mullite
Porcelain kiln linings offer a lower initial cost compared to mullite, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. Mullite, despite its higher price, provides superior thermal stability and longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights mullite's cost-effectiveness for high-temperature, industrial kiln operations where durability is critical.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Porcelain kiln linings offer smoother surfaces that simplify cleaning but require careful handling during installation to prevent chipping and cracking. Mullite linings provide superior thermal shock resistance and durability, reducing maintenance frequency but often demand specialized tools and techniques for proper fitting. Maintenance of porcelain linings involves regular inspections for glaze wear, while mullite requires monitoring for potential grain growth or structural shifts under high temperatures.
Performance Longevity and Lifespan
Porcelain kiln linings offer moderate thermal resistance and good insulation but tend to have a shorter lifespan due to their susceptibility to thermal shock and mechanical wear. Mullite, a high-strength aluminosilicate ceramic, provides superior thermal stability and durability, resulting in enhanced performance and significantly longer service life in kiln environments. The high refractoriness and resistance to thermal cycling of mullite make it the preferred choice for applications demanding extended longevity and consistent heat retention.
Best Application Scenarios for Each Material
Porcelain kiln linings excel in low to medium temperature applications up to 1300degC, offering excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance, ideal for ceramics and glass production. Mullite kiln linings withstand higher temperatures up to 1750degC with superior thermal shock resistance, making them best suited for industrial furnaces and high-temperature metallurgy processes. Selecting porcelain or mullite depends on operational temperature ranges and specific thermal stresses encountered in kiln environments.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Mullite for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com