Photonic ceramics offer superior light manipulation and enhanced thermal resistance compared to traditional clay ceramics used in tiles. Their advanced microstructure provides improved durability and energy efficiency in architectural applications.
Table of Comparison
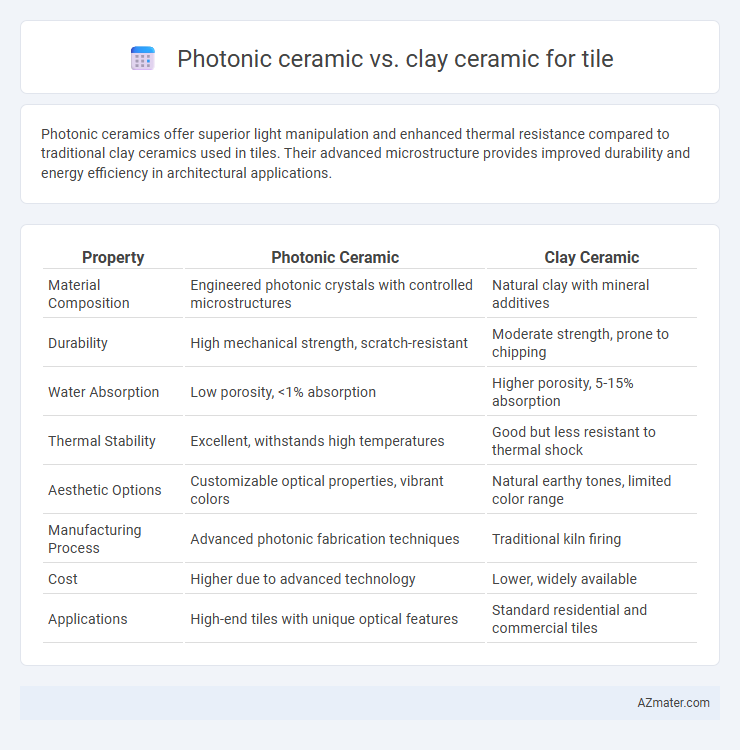
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Clay Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered photonic crystals with controlled microstructures | Natural clay with mineral additives |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, scratch-resistant | Moderate strength, prone to chipping |
| Water Absorption | Low porosity, <1% absorption | Higher porosity, 5-15% absorption |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Good but less resistant to thermal shock |
| Aesthetic Options | Customizable optical properties, vibrant colors | Natural earthy tones, limited color range |
| Manufacturing Process | Advanced photonic fabrication techniques | Traditional kiln firing |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced technology | Lower, widely available |
| Applications | High-end tiles with unique optical features | Standard residential and commercial tiles |
Introduction to Photonic Ceramic and Clay Ceramic Tiles
Photonic ceramic tiles utilize advanced nano-engineered materials that enhance light manipulation and thermal insulation properties, making them ideal for energy-efficient architectural applications. Clay ceramic tiles, traditionally made from natural clay and fired at high temperatures, offer durability, natural aesthetics, and moisture resistance suited for both indoor and outdoor use. Comparing these, photonic ceramics provide superior performance in thermal regulation, while clay ceramics excel in classic design and environmental compatibility.
Composition and Material Properties
Photonic ceramics for tiles typically consist of advanced engineered materials such as alumina or zirconia, offering superior optical properties, high thermal stability, and enhanced mechanical strength. Clay ceramics, composed mainly of natural clay minerals combined with feldspar and silica, provide excellent plasticity and workability but generally exhibit lower hardness and thermal resistance compared to photonic ceramics. The choice between photonic and clay ceramics depends on the application requirements, balancing optical performance and durability with traditional ceramic characteristics.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Photonic ceramics utilize advanced sintering techniques such as microwave or spark plasma sintering, resulting in highly uniform microstructures and enhanced optical properties, while clay ceramics rely on traditional slip casting and kiln firing methods that involve longer drying and firing cycles. Photonic ceramic manufacturing benefits from precise temperature control and faster densification, enabling the production of tiles with superior strength and light-transmitting capabilities. Clay ceramic tile production emphasizes raw material shaping and glaze application, often leading to more porous and less optically efficient final products compared to photonic ceramics.
Durability and Longevity
Photonic ceramics for tiles exhibit significantly higher durability due to their engineered microstructure that resists abrasion, fractures, and chemical corrosion better than traditional clay ceramics. Clay ceramic tiles tend to absorb more moisture, which can weaken their integrity over time, especially in freeze-thaw conditions. The advanced composition of photonic ceramics enhances longevity by maintaining structural stability and surface finish in high-traffic or harsh environmental applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishes
Photonic ceramics offer superior aesthetic qualities with enhanced light-reflective properties and vibrant finishes that create a dynamic visual appeal compared to traditional clay ceramics. Their smooth, glossy surfaces and ability to incorporate advanced pigments result in more consistent coloration and innovative design options. Clay ceramics often exhibit a more rustic, earthy texture with matte or semi-gloss finishes, emphasizing natural tones and handcrafted appeal.
Thermal and Light Management Capabilities
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior thermal conductivity and exceptional light management capabilities compared to traditional clay ceramics, enabling efficient heat dissipation and enhanced control of light transmission in tile applications. Their engineered microstructures allow for precise manipulation of photonic bandgaps, resulting in improved thermal insulation and selective light filtering properties. Clay ceramics typically offer lower thermal conductivity and limited light management, making photonic ceramics a preferred choice for advanced architectural and energy-efficient tile solutions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Photonic ceramics exhibit higher energy efficiency during production, consuming less water and generating fewer CO2 emissions compared to traditional clay ceramics. Their advanced manufacturing processes enable lower raw material usage and incorporate recycled contents, significantly reducing environmental footprints. Clay ceramics, while naturally abundant and biodegradable, require higher firing temperatures leading to increased fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in tile production.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Photonic ceramics typically have higher manufacturing costs than clay ceramics due to advanced materials and technology requirements, impacting overall tile prices. Clay ceramics dominate the market with widespread availability, making them more cost-effective and accessible for large-scale construction projects. The economic feasibility of photonic ceramic tiles remains limited by production expenses and lower market penetration compared to traditional clay ceramic tiles.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Photonic ceramic tiles excel in high-tech environments requiring precise light manipulation, such as optical sensors, photonics devices, and advanced electronics, due to their superior dielectric properties and thermal stability. Clay ceramic tiles are ideal for traditional construction and decorative applications, including flooring, wall cladding, and roofing, benefiting from their natural durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The choice depends on performance needs: photonic ceramics suit specialized technology sectors, while clay ceramics excel in architectural and everyday building uses.
Future Trends in Ceramic Tile Innovations
Photonic ceramics, leveraging advanced light manipulation properties, are poised to revolutionize tile technology by enhancing energy efficiency and enabling smart, responsive surfaces. Clay ceramics continue to evolve with improvements in natural sourcing and eco-friendly processing, aligning with sustainability trends in the construction industry. Future innovations will integrate photonic technology into traditional clay ceramic bases, merging durability with high-tech functionalities for next-generation tile applications.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Clay ceramic for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com