Photonic ceramics exhibit superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to traditional porcelain ceramics, making them ideal for high-voltage transformer insulators. Their enhanced transparency to electromagnetic waves improves signal integrity and reduces energy loss in transformer applications.
Table of Comparison
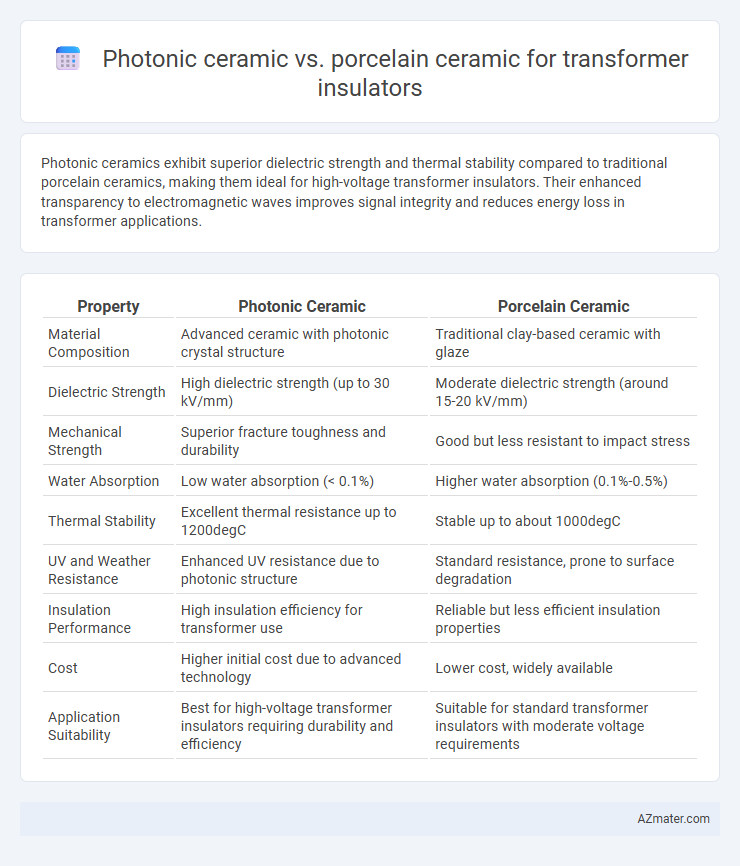
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Porcelain Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced ceramic with photonic crystal structure | Traditional clay-based ceramic with glaze |
| Dielectric Strength | High dielectric strength (up to 30 kV/mm) | Moderate dielectric strength (around 15-20 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior fracture toughness and durability | Good but less resistant to impact stress |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption (< 0.1%) | Higher water absorption (0.1%-0.5%) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal resistance up to 1200degC | Stable up to about 1000degC |
| UV and Weather Resistance | Enhanced UV resistance due to photonic structure | Standard resistance, prone to surface degradation |
| Insulation Performance | High insulation efficiency for transformer use | Reliable but less efficient insulation properties |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Best for high-voltage transformer insulators requiring durability and efficiency | Suitable for standard transformer insulators with moderate voltage requirements |
Introduction to Transformer Insulator Materials
Transformer insulator materials primarily include photonic ceramics and porcelain ceramics, each offering distinct dielectric and mechanical properties essential for reliable insulation performance. Photonic ceramics provide superior electrical breakdown strength and enhanced optical transparency, facilitating advanced monitoring applications, while porcelain ceramics are valued for their high mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and proven long-term durability in high-voltage environments. Selecting the appropriate material impacts transformer reliability, insulation efficiency, and operational lifespan in power distribution systems.
Overview of Photonic Ceramic Insulators
Photonic ceramic insulators for transformers utilize advanced materials engineered to enhance electrical insulation and thermal stability compared to traditional porcelain ceramics. These insulators exhibit superior dielectric strength, reduced surface contamination, and enhanced hydrophobic properties, resulting in improved performance under high voltage and harsh environmental conditions. The integration of photonic ceramics offers increased reliability and longevity in transformer insulation systems, making them a compelling alternative to conventional porcelain counterparts.
Key Properties of Porcelain Ceramic Insulators
Porcelain ceramic insulators for transformers exhibit excellent dielectric strength, high mechanical robustness, and superior resistance to environmental degradation, making them ideal for sustaining high-voltage insulation. Their hydrophobic surface prevents moisture accumulation, reducing the risk of electrical leakage and flashover under harsh weather conditions. Compared to photonic ceramics, porcelain insulators provide better thermal stability and long-term durability crucial for reliable transformer performance.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Photonic ceramic insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to porcelain ceramic insulators, providing enhanced resistance to impact and mechanical stresses in transformer applications. Advanced microstructure engineering in photonic ceramics results in higher fracture toughness and better load-bearing capacity than traditional porcelain materials. These mechanical advantages lead to increased durability and reliability in high-voltage transformer insulators.
Electrical Performance and Insulation Capability
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior electrical performance and higher insulation capability compared to porcelain ceramics, making them ideal for transformer insulators in high-voltage applications. Their enhanced dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity reduce leakage currents and improve energy efficiency under varying load conditions. Porcelain ceramics, while durable, generally have lower breakdown voltage and higher susceptibility to surface contamination, limiting their effectiveness in demanding electrical insulation environments.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Photonic ceramic transformer insulators exhibit superior thermal stability compared to porcelain ceramics, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC. Their advanced microstructure enhances resistance to thermal shock and electrical stress, reducing the risk of crack formation and premature failure. Porcelain ceramics, although widely used, show lower thermal tolerance and are more susceptible to degradation under rapid temperature fluctuations and high voltage conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Power Systems
Photonic ceramic insulators exhibit superior durability compared to porcelain ceramic due to their enhanced resistance to thermal shock, mechanical stress, and environmental degradation in power systems. Their advanced microstructure minimizes water absorption and surface contamination, leading to extended service life and reduced maintenance needs. Porcelain ceramics, while historically reliable, are more prone to cracking and spalling under harsh operational conditions, making photonic ceramics a more robust choice for transformer insulator applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Photonic ceramics for transformer insulators offer advanced dielectric properties but involve higher costs due to specialized raw materials and complex fabrication processes like sintering under controlled atmospheres. Porcelain ceramics remain more cost-effective, benefiting from established manufacturing methods such as slip casting and firing, which enable mass production with consistent quality and lower energy consumption. The choice between photonic and porcelain ceramics hinges on balancing enhanced electrical performance against budget constraints and production scalability.
Applications in Modern Transformer Technology
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-voltage transformer insulators in advanced power grids. Porcelain ceramics, favored for their mechanical robustness and cost-effectiveness, remain widely used in traditional transformer designs but may face limitations in extreme environmental conditions. Modern transformer technology increasingly leverages photonic ceramics for enhanced insulation performance, improving longevity and reducing maintenance in smart grid applications.
Future Trends: Photonic vs. Porcelain Ceramic Insulators
Photonic ceramic insulators offer enhanced dielectric strength and superior resistance to environmental degradation compared to conventional porcelain ceramic insulators, positioning them as a key material in the evolution of transformer insulation technology. Future trends indicate a shift towards photonic ceramics due to their ability to integrate smart sensing capabilities, enabling real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance of transformers. Innovations in nanostructured photonic ceramics further improve thermal stability and mechanical robustness, driving their adoption over traditional porcelain in high-performance electrical insulation applications.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Porcelain ceramic for Transformer insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com