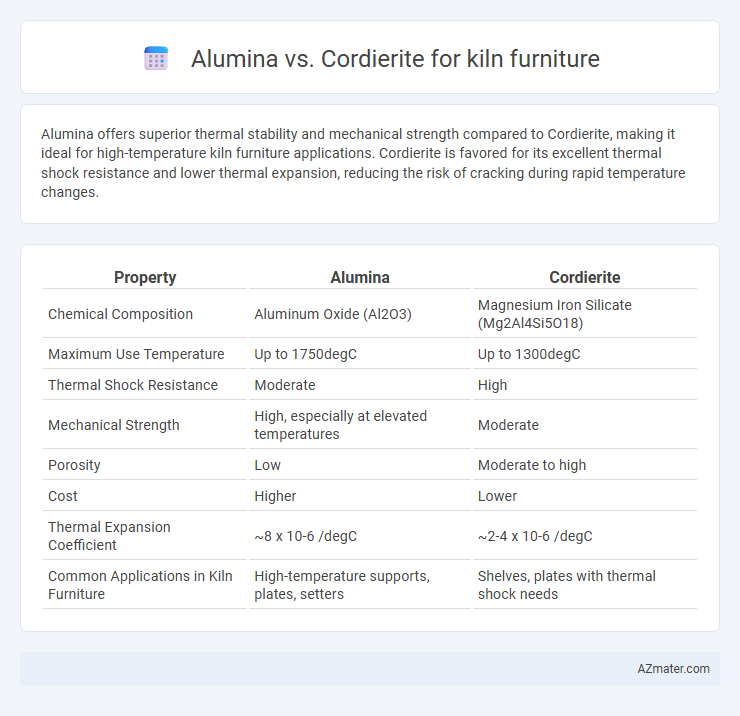
Alumina offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to Cordierite, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Cordierite is favored for its excellent thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking during rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina | Cordierite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) | Magnesium Iron Silicate (Mg2Al4Si5O18) |
| Maximum Use Temperature | Up to 1750degC | Up to 1300degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | High, especially at elevated temperatures | Moderate |
| Porosity | Low | Moderate to high |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~8 x 10-6 /degC | ~2-4 x 10-6 /degC |
| Common Applications in Kiln Furniture | High-temperature supports, plates, setters | Shelves, plates with thermal shock needs |
Introduction: Alumina vs Cordierite in Kiln Furniture
Alumina and cordierite are widely used materials in kiln furniture, valued for their high thermal stability and mechanical strength. Alumina offers superior resistance to thermal shock and higher melting points, making it ideal for demanding firing conditions. Cordierite, known for its excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, is preferred in applications requiring rapid temperature changes and energy efficiency.
Material Composition and Structure
Alumina kiln furniture primarily consists of high-purity aluminum oxide (Al2O3), known for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion at temperatures exceeding 1700degC. Cordierite, composed of magnesium, aluminum, and silicate minerals (2MgO*2Al2O3*5SiO2), features a highly porous structure with low thermal expansion, making it resistant to thermal shock up to 1300degC. The dense and hard microstructure of alumina offers superior mechanical strength, whereas cordierite's intricate crystalline framework provides enhanced thermal shock resistance and lightweight properties for diverse kiln applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Alumina exhibits higher mechanical strength than cordierite, making it more suitable for applications requiring resistance to heavy loads and thermal shock in kiln furniture. Alumina typically has a flexural strength of 250-400 MPa, whereas cordierite ranges between 80-150 MPa, highlighting alumina's superior durability under mechanical stress. This strength difference impacts the lifespan and performance of kiln furniture, especially in high-temperature industrial processes.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Alumina offers superior thermal shock resistance compared to cordierite, making it ideal for kiln furniture subjected to rapid temperature changes. Its high melting point and low thermal expansion ensure durability and reduced risk of cracking during intense firing cycles. Cordierite, while cost-effective and lightweight, exhibits lower thermal shock resistance, limiting its use in extreme firing environments.
Maximum Operating Temperatures
Alumina kiln furniture offers a maximum operating temperature typically around 1750degC (3182degF), making it highly suitable for high-temperature ceramic and glass firings. Cordierite kiln furniture operates effectively up to approximately 1275degC (2327degF), ideal for applications requiring thermal shock resistance at lower maximum temperatures. Choosing between alumina and cordierite depends on the specific kiln atmosphere and firing temperature requirements, as alumina withstands higher heat but cordierite excels in thermal shock performance.
Weight and Density Considerations
Alumina kiln furniture exhibits a higher density, typically around 3.9 to 4.1 g/cm3, resulting in increased weight compared to cordierite, which ranges from 2.5 to 2.6 g/cm3. This density difference impacts handling and kiln load capacity, with cordierite favored for applications requiring lighter, more manageable components. Weight and density influence thermal mass and heat retention, making cordierite suitable for rapid thermal cycling but alumina ideal for support under heavy loads and high-temperature stability.
Chemical Stability and Reactivity
Alumina exhibits superior chemical stability in kiln furniture applications, resisting corrosion and deformation at high temperatures up to 1750degC, making it ideal for processing highly reactive or corrosive materials. Cordierite offers excellent thermal shock resistance but has lower chemical stability, as it can react with certain slags and alkalis, limiting its use in aggressive chemical environments. Choosing between alumina and cordierite depends on the kiln atmosphere and the chemical nature of the fired materials.
Cost and Availability
Alumina kiln furniture generally costs more than cordierite due to its higher purity and superior thermal stability, making it a preferred choice for high-temperature applications. Cordierite offers greater availability at lower prices because it is widely produced and suitable for moderate firing ranges, providing cost-effective durability for many ceramics processes. The budget-conscious kiln operators often select cordierite for economic efficiency, while alumina is reserved for demanding conditions where longevity and performance justify the investment.
Typical Applications in Kilns
Alumina kiln furniture is commonly used in high-temperature applications such as metal casting, ceramics firing, and glass manufacturing due to its superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Cordierite kiln furniture excels in applications requiring rapid thermal cycling and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for pottery and tile production where thermal shock resistance is critical. Both materials are chosen for their compatibility with specific firing conditions, optimizing kiln performance and product quality in industrial and artistic settings.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Kiln Furniture
Alumina and cordierite are two popular materials for kiln furniture, each suited for different firing conditions. Alumina offers excellent thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature firings above 1700degC, while cordierite exhibits superior thermal shock resistance at temperatures up to 1300degC to 1400degC. Choosing the right material depends on kiln temperature, firing atmosphere, and the need for mechanical strength versus thermal shock tolerance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Alumina vs Cordierite for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com