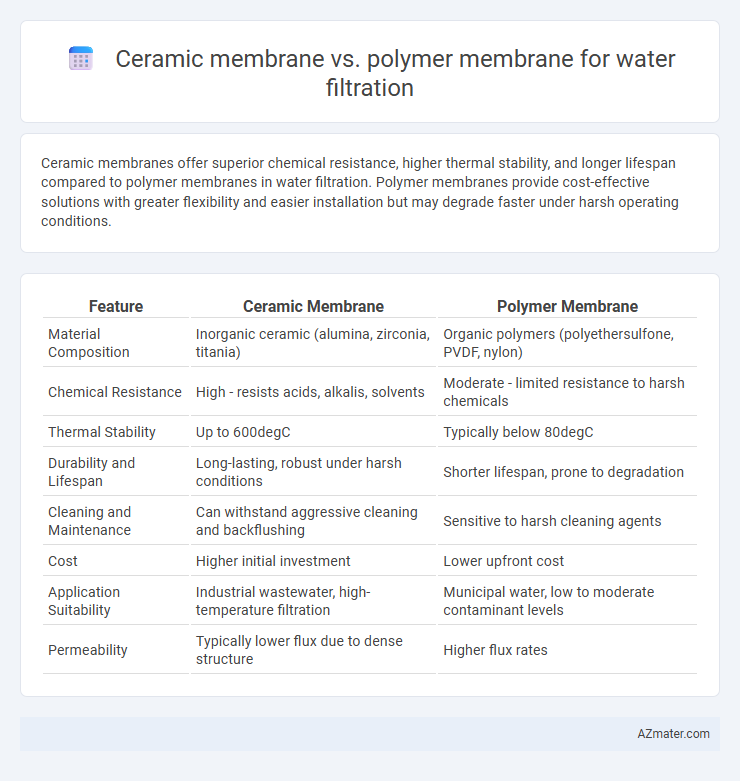
Ceramic membranes offer superior chemical resistance, higher thermal stability, and longer lifespan compared to polymer membranes in water filtration. Polymer membranes provide cost-effective solutions with greater flexibility and easier installation but may degrade faster under harsh operating conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Membrane | Polymer Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic ceramic (alumina, zirconia, titania) | Organic polymers (polyethersulfone, PVDF, nylon) |
| Chemical Resistance | High - resists acids, alkalis, solvents | Moderate - limited resistance to harsh chemicals |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Typically below 80degC |
| Durability and Lifespan | Long-lasting, robust under harsh conditions | Shorter lifespan, prone to degradation |
| Cleaning and Maintenance | Can withstand aggressive cleaning and backflushing | Sensitive to harsh cleaning agents |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Application Suitability | Industrial wastewater, high-temperature filtration | Municipal water, low to moderate contaminant levels |
| Permeability | Typically lower flux due to dense structure | Higher flux rates |
Introduction to Water Filtration Technologies
Ceramic membranes offer superior chemical and thermal resistance, making them ideal for harsh water filtration environments compared to polymer membranes, which are more prone to fouling and degradation. Polymer membranes provide cost-effective and flexible solutions with high permeability but lack the durability of ceramic options. Advances in water filtration technologies leverage ceramic membranes for wastewater treatment and polymer membranes for residential and commercial applications due to their specific material advantages.
Overview of Ceramic Membranes
Ceramic membranes offer exceptional chemical and thermal stability, making them highly durable for water filtration applications compared to polymer membranes. Their micro-porous structure allows effective removal of suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses while resisting fouling and harsh cleaning agents. These membranes support extended operational lifespan and maintain consistent filtration performance in industrial and municipal water treatment processes.
Overview of Polymer Membranes
Polymer membranes dominate the water filtration market due to their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and ease of fabrication. Common materials include polyethersulfone (PES), polysulfone (PS), and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), offering high permeability and selectivity for microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and nanofiltration applications. While polymer membranes generally exhibit lower chemical and thermal resistance compared to ceramic membranes, their scalability and ability to handle diverse water treatment processes make them a preferred choice for municipal and industrial filtration systems.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Ceramic membranes exhibit higher filtration efficiency than polymer membranes due to their superior pore size uniformity and chemical stability, enabling effective removal of fine particles, bacteria, and viruses. Polymer membranes, while cost-effective, often suffer from fouling and lower tolerance to harsh chemical cleaning, reducing filtration performance over time. The advanced durability of ceramic membranes results in consistent filtration rates and longer operational lifespan, especially in demanding water treatment applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Ceramic membranes exhibit superior durability and longer lifespan compared to polymer membranes due to their high resistance to chemical, thermal, and mechanical degradation. With typical lifespans exceeding 10 years, ceramic membranes withstand harsh cleaning processes and extreme pH conditions without significant performance loss. Polymer membranes generally last 3 to 5 years and are more prone to damage from oxidation and fouling, leading to more frequent replacement and higher maintenance costs.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Ceramic membranes exhibit superior chemical resistance, withstanding harsh acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents, making them ideal for aggressive industrial water treatment processes. Their thermal stability allows operation at temperatures above 300degC without degradation, significantly outperforming polymer membranes, which generally tolerate only up to 60-80degC. The enhanced durability of ceramic membranes ensures longer lifespan and consistent filtration efficiency under extreme chemical and thermal conditions compared to polymer-based alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational
Ceramic membranes generally have a higher initial cost compared to polymer membranes due to their durable materials and manufacturing process. Operational costs for ceramic membranes tend to be lower over time because of their chemical resistance, longer lifespan, and ability to withstand harsh cleaning procedures. Polymer membranes, while cheaper upfront, often incur higher maintenance and replacement expenses due to lower durability and sensitivity to cleaning chemicals.
Maintenance and Fouling Characteristics
Ceramic membranes exhibit superior resistance to chemical and thermal degradation, enabling easier cleaning and reduced fouling compared to polymer membranes, which are more prone to biofouling and chemical sensitivity. The inorganic nature of ceramic membranes allows for aggressive cleaning protocols, such as high-temperature steam or chemical cleaning, extending their operational lifespan. Polymer membranes require gentler maintenance and frequent cleaning cycles to manage fouling, resulting in higher operational costs and shorter membrane lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic membranes offer greater environmental sustainability due to their longer lifespan, resistance to harsh chemicals, and ability to withstand high temperatures, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste. Polymer membranes, while initially more energy-efficient in manufacturing, tend to degrade faster and require more frequent replacement, leading to increased landfill waste and resource consumption. The recyclability of ceramic membranes and their compatibility with aggressive cleaning agents contribute to a lower carbon footprint compared to polymer-based filtration systems.
Application Suitability and Industry Preferences
Ceramic membranes excel in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments, making them ideal for industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and petrochemicals, where durability and resistance to fouling are critical. Polymer membranes are preferred in municipal water treatment and wastewater applications due to their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and ease of installation, despite lower chemical and thermal stability. Industry preferences favor ceramic membranes for processes requiring long-term stability and minimal maintenance, whereas polymer membranes dominate large-scale, low-cost filtration projects.
Infographic: Ceramic membrane vs Polymer membrane for Water filtration
 azmater.com
azmater.com