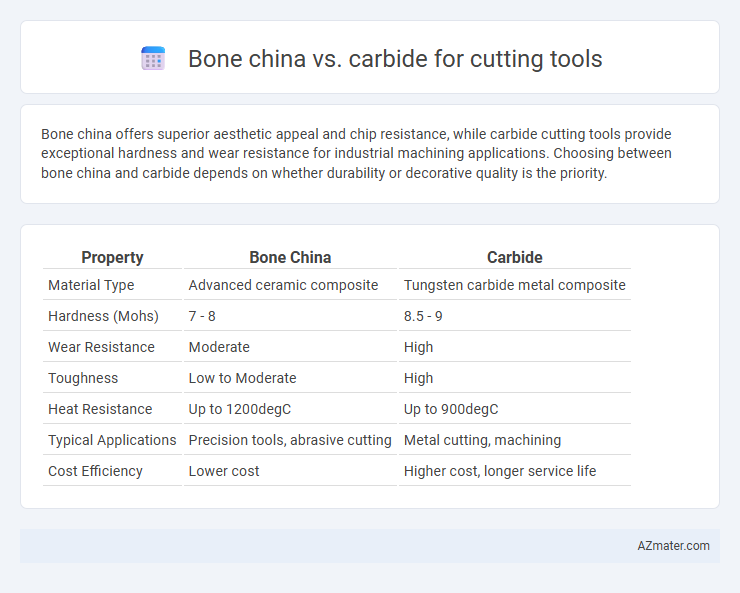
Bone china offers superior aesthetic appeal and chip resistance, while carbide cutting tools provide exceptional hardness and wear resistance for industrial machining applications. Choosing between bone china and carbide depends on whether durability or decorative quality is the priority.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China | Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced ceramic composite | Tungsten carbide metal composite |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7 - 8 | 8.5 - 9 |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Toughness | Low to Moderate | High |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 900degC |
| Typical Applications | Precision tools, abrasive cutting | Metal cutting, machining |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost | Higher cost, longer service life |
Introduction to Cutting Tools: Bone China vs Carbide
Bone china cutting tools offer superior edge sharpness and are ideal for delicate precision tasks, leveraging their fine-grained ceramic structure for smooth finishes. Carbide cutting tools, made from tungsten carbide composites, provide exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty machining and prolonged tool life. Understanding the material properties of bone china versus carbide is crucial for selecting the appropriate cutting tool based on application requirements and machining conditions.
Material Composition: Bone China and Carbide Explained
Bone china consists primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and bone ash, offering high strength, translucency, and whiteness. Carbide, typically tungsten carbide combined with cobalt binder, provides exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat tolerance ideal for cutting tools. The fundamental difference lies in bone china's ceramic properties suited for delicate dinnerware versus carbide's metallic matrix designed for industrial cutting performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bone china exhibits lower hardness and fracture toughness compared to carbide, limiting its suitability for high-stress cutting applications. Carbide cutting tools demonstrate superior wear resistance, higher flexural strength, and excellent impact resistance, enhancing tool life and performance in machining hard materials. The mechanical properties of carbide, including a hardness of 1600-2400 HV and a bending strength around 2000 MPa, significantly outperform bone china's average hardness below 1000 HV and brittle nature.
Hardness and Durability Analysis
Bone china, composed primarily of kaolin and bone ash, exhibits moderate hardness but lacks the extreme durability required for cutting tools, making it unsuitable for high-stress industrial applications. Carbide, particularly tungsten carbide, is renowned for its superior hardness on the Mohs scale (around 9), combined with exceptional wear resistance and toughness, which ensures long-lasting performance in cutting operations. The significant difference in material properties positions carbide as the preferred choice for cutting tools demanding high hardness and durability, whereas bone china's brittleness limits its functional application to non-mechanical environments.
Cutting Efficiency and Precision
Bone china cutting tools offer limited cutting efficiency and precision due to their brittleness and lower hardness compared to carbide. Carbide cutting tools excel in cutting efficiency and precision because of their superior hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp edge under high-stress machining conditions. This makes carbide the preferred choice for applications requiring high-precision cuts and prolonged tool life.
Heat Resistance in Cutting Applications
Bone china cutters exhibit limited heat resistance, making them unsuitable for high-temperature cutting applications that generate significant friction and thermal stress. Carbide cutting tools excel in heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,200degC, preserving hardness and wear resistance during intense machining operations. The superior thermal stability of carbide directly contributes to longer tool life and improved cutting performance in demanding industrial environments.
Wear and Longevity of Bone China vs Carbide Tools
Bone china cutting tools exhibit lower wear resistance compared to carbide tools, making them less suitable for high-intensity industrial applications. Carbide tools, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with metal, provide superior hardness and significantly longer tool life under abrasive conditions. Their enhanced wear resistance ensures sustained sharpness and reduced maintenance intervals, making carbide the preferred choice for precision machining and heavy-duty cutting tasks.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Bone china cutting tools offer moderate cost-effectiveness due to their lower material cost but often lack the durability needed for high-precision industrial applications, leading to frequent replacements. Carbide cutting tools provide superior wear resistance and longer tool life, which significantly reduces downtime and overall expenses despite their higher initial price. Availability of carbide tools is widespread in industrial markets, ensuring easier procurement compared to bone china tools that are less common and more niche in usage.
Common Uses in Industrial Settings
Bone china is rarely used in industrial cutting tools due to its brittleness and fragility, being more common in tableware and decorative applications. Carbide, specifically tungsten carbide, dominates cutting tool manufacturing for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication because of its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain sharp edges at high temperatures. Industrial settings rely on carbide tooling for milling, turning, drilling, and cutting operations to achieve precision and durability under harsh manufacturing conditions.
Choosing the Right Tool: Bone China or Carbide?
When selecting a cutting tool, choosing between bone china and carbide depends on the application's precision and durability requirements. Bone china, known for its smooth finish and cost-effectiveness, is suitable for light-duty cutting with minimal wear. Carbide offers superior hardness and resistance to heat, making it ideal for heavy-duty machining and high-speed operations where longevity and performance are critical.
Infographic: Bone china vs Carbide for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com