Piezoelectric ceramic offers high sensitivity and energy conversion efficiency, making it ideal for sensor and actuator applications, while stoneware provides superior durability, water resistance, and aesthetic versatility for tile flooring. Choosing between piezoelectric ceramic and stoneware depends on whether functionality or structural resilience is the priority.
Table of Comparison
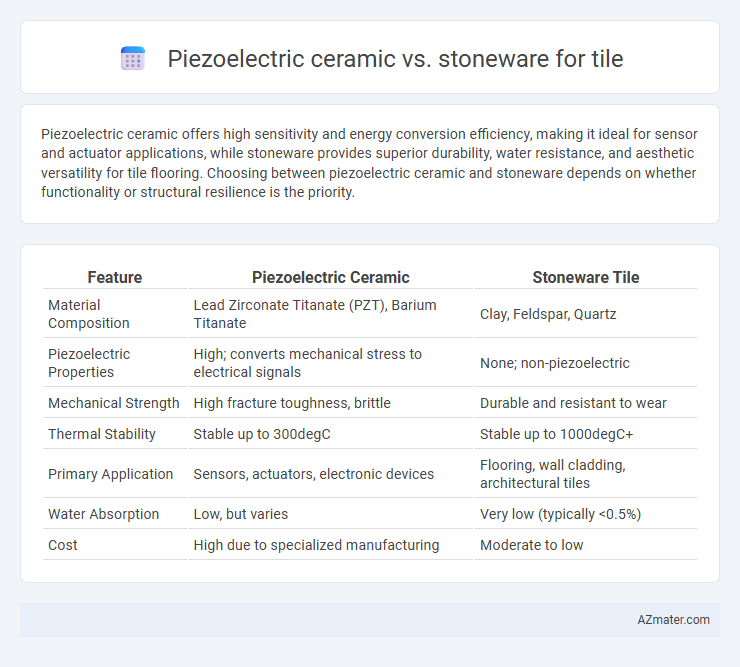
| Feature | Piezoelectric Ceramic | Stoneware Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT), Barium Titanate | Clay, Feldspar, Quartz |
| Piezoelectric Properties | High; converts mechanical stress to electrical signals | None; non-piezoelectric |
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness, brittle | Durable and resistant to wear |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 300degC | Stable up to 1000degC+ |
| Primary Application | Sensors, actuators, electronic devices | Flooring, wall cladding, architectural tiles |
| Water Absorption | Low, but varies | Very low (typically <0.5%) |
| Cost | High due to specialized manufacturing | Moderate to low |
Introduction: Piezoelectric Ceramic vs Stoneware Tiles
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles harness electric charge generated by mechanical stress, offering innovative applications in sensors and energy harvesting, unlike traditional stoneware tiles primarily valued for durability and aesthetic appeal. Stoneware tiles, composed of dense clay fired at high temperatures, excel in resistance to wear, water, and staining, making them a staple in residential and commercial settings. Comparing piezoelectric ceramics and stoneware highlights distinct functional and material properties influencing tile selection based on performance requirements and design goals.
Composition and Material Properties
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles are composed of crystalline materials such as lead zirconate titanate (PZT), which exhibit strong electromechanical coupling, enabling them to generate electrical charge under mechanical stress. Stoneware tiles are made from dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures, offering exceptional hardness, durability, and resistance to moisture and wear. The key difference lies in piezoelectric ceramics' ability to convert mechanical energy to electrical signals, while stoneware focuses on robust physical properties suited for heavy-duty flooring and decorative surfaces.
Manufacturing Processes
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles are produced through a specialized sintering process that involves shaping piezoelectric powders and firing at high temperatures to develop their unique electrical properties, enabling energy harvesting and sensor applications. Stoneware tiles are manufactured by pressing refined clay mixtures, followed by firing in kilns at temperatures typically ranging between 1100degC and 1300degC, resulting in dense, durable, and water-resistant products. The key distinction lies in the material composition and firing conditions, where piezoelectric ceramics require precise control of crystal structure for functionality, whereas stoneware focuses on mechanical strength and surface finish for architectural uses.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Piezoelectric ceramics exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to stoneware tiles, offering high resistance to cracking under stress due to their dense microstructure and high fracture toughness. Stoneware tiles provide excellent durability with enhanced wear resistance and low porosity, making them suitable for heavy-traffic areas. However, piezoelectric ceramics outperform in applications requiring both mechanical strength and functional electrical properties, while stoneware excels in traditional flooring durability.
Electrical and Functional Characteristics
Piezoelectric ceramics exhibit strong electrical responsiveness by converting mechanical stress into electric charge, making them ideal for sensor and actuator applications in smart tile systems. Stoneware tiles, lacking inherent piezoelectric properties, provide excellent durability and resistance to abrasion but do not generate or respond to electrical signals. Functional differences highlight piezoelectric ceramics' capacity for energy harvesting and signal transduction, whereas stoneware focuses on structural integrity and aesthetics in flooring solutions.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Options
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles offer high precision in design with vibrant colors and intricate patterns due to their controlled manufacturing process, making them ideal for modern, customizable aesthetics. Stoneware tiles provide a natural, earthy appearance with unique textures and subtle color variations that enhance rustic and traditional interior designs. Both materials support diverse design options, but piezoelectric ceramics excel in uniformity and innovation, while stoneware emphasizes organic beauty and tactile appeal.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles typically cost more due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes, with prices ranging from $50 to $150 per square meter, whereas stoneware tiles are more affordable, generally priced between $15 and $40 per square meter. Market availability favors stoneware tiles because of their widespread production and established distribution channels, especially in residential and commercial flooring markets. Piezoelectric ceramic tiles remain niche products, mainly used in specialized industrial applications, limiting their presence in mainstream retail.
Application Suitability: Residential and Commercial Uses
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles offer advanced energy-harvesting capabilities ideal for smart residential floors and commercial spaces requiring sensor integration, while stoneware tiles provide robust durability and moisture resistance suited for high-traffic areas in both settings. Piezoelectric ceramics excel in applications demanding electronic responsiveness, such as interactive flooring and security systems, whereas stoneware's strength and ease of maintenance make it preferred for kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor walkways. Residential environments benefit from the comfort and technology of piezoelectric tiles, and commercial spaces rely on stoneware for long-lasting performance and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Piezoelectric ceramic tiles harness mechanical energy to generate electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints, highlighting their sustainability in energy-efficient building designs. Stoneware tiles, made from natural clays fired at high temperatures, offer durability and low maintenance but require significant energy during production, impacting environmental sustainability. Choosing piezoelectric ceramics promotes renewable energy integration and reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional stoneware tiles, which rely more heavily on energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right Tile: Key Considerations
Selecting between piezoelectric ceramic and stoneware tiles hinges on the specific application and performance requirements. Piezoelectric ceramics offer advanced sensing and energy harvesting capabilities ideal for smart, responsive flooring, while stoneware excels in durability, water resistance, and aesthetic versatility for traditional and high-traffic environments. Prioritizing factors such as mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and functional integration ensures optimal tile selection for long-lasting results.
Infographic: Piezoelectric ceramic vs Stoneware for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com