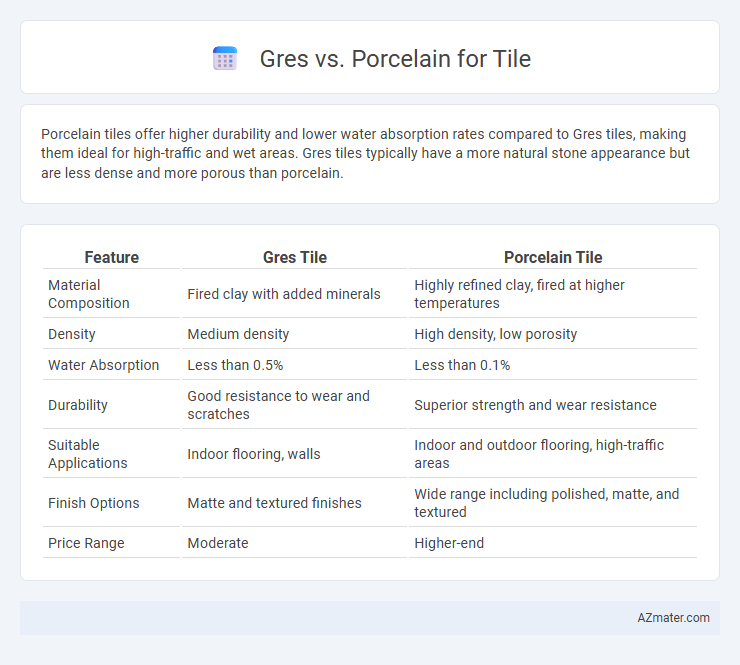
Porcelain tiles offer higher durability and lower water absorption rates compared to Gres tiles, making them ideal for high-traffic and wet areas. Gres tiles typically have a more natural stone appearance but are less dense and more porous than porcelain.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres Tile | Porcelain Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fired clay with added minerals | Highly refined clay, fired at higher temperatures |
| Density | Medium density | High density, low porosity |
| Water Absorption | Less than 0.5% | Less than 0.1% |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and scratches | Superior strength and wear resistance |
| Suitable Applications | Indoor flooring, walls | Indoor and outdoor flooring, high-traffic areas |
| Finish Options | Matte and textured finishes | Wide range including polished, matte, and textured |
| Price Range | Moderate | Higher-end |
Introduction to Gres and Porcelain Tiles
Gres and porcelain tiles are both types of ceramic tiles known for their durability and low porosity, making them ideal for floors and walls. Gres tiles, originating from Italy, are typically made with a mixture of clay and feldspar, fired at high temperatures to achieve strength and resistance to wear. Porcelain tiles are a subtype of gres, characterized by a denser composition and even lower water absorption rate, which enhances their suitability for heavy-traffic areas and outdoor use.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gres tiles are composed primarily of natural clay mixed with quartz, feldspar, and kaolin, fired at high temperatures to achieve a dense, durable surface. Porcelain tiles, a subset of gres, undergo a more refined manufacturing process involving finer raw materials and higher firing temperatures, resulting in low porosity and superior strength. Both types utilize a dry pressing method, but porcelain's meticulous composition and firing process create tiles that are harder and more resistant to moisture and wear.
Key Differences Between Gres and Porcelain
Gres tiles are a type of porcelain tile, distinguished primarily by their manufacturing process and density, resulting in gres being denser and less porous than standard porcelain. Porcelain tiles often have a wider range of design options and are slightly more brittle, whereas gres tiles excel in durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. The key differences lie in gres's enhanced strength and minimal water absorption compared to regular porcelain tiles, influencing their suitability for high-traffic and harsh environments.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres tile, also known as stoneware, offers high durability with excellent resistance to wear, scratches, and heavy foot traffic, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. Porcelain tile, a subset of gres, is denser and less porous due to its fine-grain clay and high-temperature firing process, resulting in superior strength and water resistance. This makes porcelain tiles ideal for areas exposed to moisture and heavy usage, ensuring longer lifespan and minimal maintenance compared to standard gres tiles.
Water Absorption and Stain Resistance
Porcelain tiles exhibit a water absorption rate of less than 0.5%, making them highly resistant to moisture and ideal for wet areas, while gres tiles typically show slightly higher absorption rates but still maintain good durability. The dense, non-porous surface of porcelain significantly reduces stain penetration compared to gres, which may require more frequent sealing to prevent discoloration. Both tile types offer strong stain resistance, but porcelain's lower porosity ensures superior long-term performance in environments prone to spills and humidity.
Design, Color, and Finish Options
Gres tiles offer a versatile range of designs with natural stone and rustic patterns, featuring earthy tones perfect for warm, traditional aesthetics. Porcelain tiles excel in color variety and precision finishes, including glossy, matte, and textured surfaces that suit modern, sleek interiors. Both materials provide durable finishes, but porcelain's advanced firing process allows for sharper color retention and more consistent texture options.
Installation Requirements and Techniques
Gres tiles, known for their durability and low water absorption, require careful substrate preparation and often benefit from using flexible adhesives during installation to accommodate slight movement and prevent cracking. Porcelain tiles demand a flat, solid foundation due to their rigidity and are typically installed with thin-set mortar using a notched trowel for even adhesion, followed by proper grout to ensure longevity. Both tile types require precise cutting tools and appropriate sealing techniques to protect edges and maintain the surface integrity over time.
Cost Comparison: Gres vs Porcelain Tiles
Gres tiles typically cost less than porcelain tiles due to their lower manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly choice for large-scale projects. Porcelain tiles, known for their density and durability, often carry a higher price point but offer enhanced longevity and resistance to wear. Factoring in installation and maintenance, porcelain tiles may provide better long-term value despite the upfront cost difference between gres and porcelain.
Best Applications for Each Tile Type
Gres tiles, made from natural clay and fired at high temperatures, offer superior resistance to wear, making them ideal for high-traffic areas like commercial spaces and outdoor patios. Porcelain tiles boast low water absorption and high density, making them perfect for bathrooms, kitchens, and areas prone to moisture exposure. Both tile types provide durability, but gres excels in strength for heavy use, while porcelain excels in moisture resistance and fine finishes.
Pros and Cons: Making the Right Choice
Gres tiles offer excellent durability and stain resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic areas, but they can be heavier and harder to cut compared to porcelain. Porcelain tiles provide a wide variety of designs and a smoother finish, while also being highly water-resistant and suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, yet often come at a higher price point. Choosing between gres and porcelain depends on factors such as intended location, aesthetic preferences, budget, and required maintenance level.
Infographic: Gres vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com