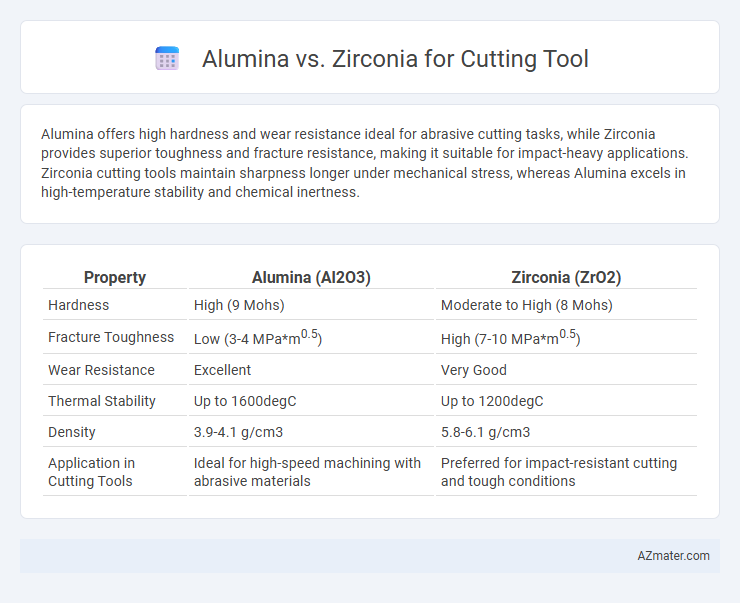
Alumina offers high hardness and wear resistance ideal for abrasive cutting tasks, while Zirconia provides superior toughness and fracture resistance, making it suitable for impact-heavy applications. Zirconia cutting tools maintain sharpness longer under mechanical stress, whereas Alumina excels in high-temperature stability and chemical inertness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Zirconia (ZrO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (9 Mohs) | Moderate to High (8 Mohs) |
| Fracture Toughness | Low (3-4 MPa*m0.5) | High (7-10 MPa*m0.5) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1600degC | Up to 1200degC |
| Density | 3.9-4.1 g/cm3 | 5.8-6.1 g/cm3 |
| Application in Cutting Tools | Ideal for high-speed machining with abrasive materials | Preferred for impact-resistant cutting and tough conditions |
Introduction to Ceramic Cutting Tools
Ceramic cutting tools primarily utilize alumina and zirconia due to their superior hardness, heat resistance, and wear properties. Alumina offers excellent thermal stability and toughness, making it ideal for high-speed machining of steel and cast iron. Zirconia exhibits higher fracture toughness and impact resistance, suitable for interrupted cutting and applications requiring enhanced durability.
Alumina: Composition and Key Properties
Alumina, primarily composed of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is prized in cutting tools for its exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and excellent thermal stability. Its inherent chemical inertness and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for machining tough materials, maintaining sharp edges under high temperatures. This ceramic's microstructure ensures superior toughness and fracture resistance, enhancing tool longevity and performance in industrial cutting applications.
Zirconia: Chemical Structure and Unique Features
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), features a crystalline structure that can exist in monoclinic, tetragonal, and cubic phases, enabling exceptional toughness and thermal stability in cutting tools. Its unique transformation toughening mechanism enhances resistance to crack propagation, making zirconia superior in impact resistance compared to alumina. This combination of chemical stability and mechanical strength allows zirconia cutting tools to maintain sharpness and durability in high-stress machining environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Alumina cutting tools offer moderate mechanical strength with high hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for machining softer metals and wood. Zirconia cutting tools exhibit superior mechanical strength and fracture toughness due to their transformation toughening mechanism, allowing them to withstand higher impact forces and thermal stress during heavy-duty cutting operations. The enhanced toughness of zirconia significantly reduces chipping and tool failure compared to alumina, extending tool life in demanding industrial applications.
Wear Resistance and Tool Longevity
Zirconia outperforms alumina in wear resistance due to its higher fracture toughness and ability to maintain sharp edges under extreme cutting conditions. Alumina offers excellent hardness and thermal stability but tends to exhibit more rapid wear and chipping in abrasive or interrupted cuts. Tool longevity is significantly enhanced in zirconia cutting tools, making them ideal for high-speed machining and demanding applications where durability and minimal tool replacement are critical.
Thermal Stability and Performance at High Temperatures
Alumina exhibits excellent thermal stability with a melting point around 2072degC, making it ideal for cutting tools that operate under high-temperature conditions. Zirconia surpasses alumina in toughness and maintains structural integrity through phase transformation toughening up to approximately 2700degC, offering superior performance in extremely high-temperature cutting applications. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of zirconia ensures sustained cutting efficiency and longer tool life compared to alumina in demanding machining environments.
Machining Applications: Suitable Uses for Each Material
Alumina cutting tools excel in machining applications involving ferrous metals and abrasive materials due to their high hardness and thermal stability, making them ideal for roughing and finishing operations in steel and cast iron. Zirconia cutting tools offer superior toughness and wear resistance, making them suitable for machining non-ferrous metals, composites, and materials requiring impact resistance and higher edge strength. Both materials enhance tool life and machining precision but are selected based on workpiece material and required cutting conditions.
Cost-Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Alumina cutting tools offer superior cost-efficiency due to their lower material and manufacturing costs, making them ideal for high-volume, budget-sensitive applications. Zirconia tools, while more expensive upfront, provide enhanced toughness and wear resistance, extending tool life and reducing replacement frequency in demanding machining processes. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that alumina is economically advantageous for general machining, whereas zirconia yields better returns in precision or heavy-duty cutting where tool longevity offsets initial investment.
Advances in Hybrid Alumina-Zirconia Composites
Hybrid alumina-zirconia composites combine the high hardness and thermal stability of alumina with the fracture toughness and crack resistance of zirconia, resulting in cutting tools with enhanced wear resistance and durability. Advances in nano-engineering and optimized microstructures have enabled the development of composites that exhibit superior mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance compared to traditional single-phase ceramics. These innovations contribute to longer tool life, improved cutting precision, and reduced downtime in high-speed machining applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Choosing between alumina and zirconia for cutting tools depends on hardness, toughness, and operating conditions. Alumina offers high hardness and wear resistance ideal for machining ferrous metals, while zirconia provides superior toughness and fracture resistance suitable for interrupted cuts and abrasive materials. Consider cutting speed, material compatibility, and tool life requirements to determine the optimal ceramic for specific machining applications.
Infographic: Alumina vs Zirconia for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com