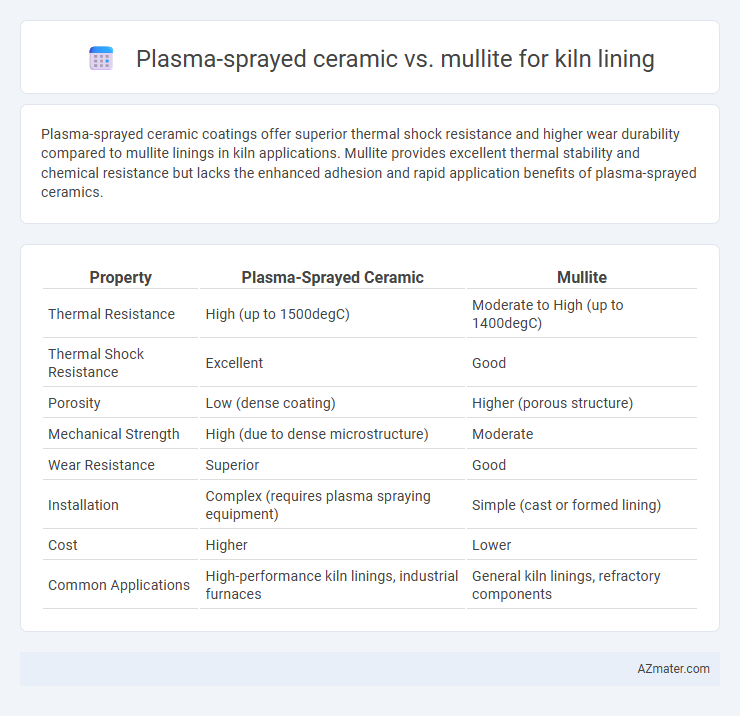
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior thermal shock resistance and higher wear durability compared to mullite linings in kiln applications. Mullite provides excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but lacks the enhanced adhesion and rapid application benefits of plasma-sprayed ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 1500degC) | Moderate to High (up to 1400degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Porosity | Low (dense coating) | Higher (porous structure) |
| Mechanical Strength | High (due to dense microstructure) | Moderate |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Installation | Complex (requires plasma spraying equipment) | Simple (cast or formed lining) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | High-performance kiln linings, industrial furnaces | General kiln linings, refractory components |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials are critical for thermal insulation and structural integrity in high-temperature industrial processes. Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior thermal shock resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional Mullite bricks, allowing for enhanced energy efficiency and longer service life. Mullite remains a popular choice due to its excellent mechanical strength and chemical stability at elevated temperatures, but plasma-sprayed ceramics provide a more uniform and adaptable lining solution in modern kiln designs.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Linings
Plasma-sprayed ceramic linings offer superior thermal insulation and enhanced resistance to thermal shock compared to traditional Mullite linings used in kiln applications. These linings exhibit higher hardness, improved adherence, and greater chemical stability at elevated temperatures, extending service life and reducing maintenance frequency. The dense, uniform coating formed by plasma spraying minimizes porosity, resulting in better protection against slag and corrosive environments inherent in high-temperature kiln operations.
Understanding Mullite as a Kiln Lining Material
Mullite, a crystalline aluminosilicate ceramic, is highly valued as a kiln lining material due to its excellent thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and strong resistance to chemical corrosion at high temperatures up to 1780degC. Compared to plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings, mullite offers superior dimensional stability and durability under rapid thermal cycling, reducing maintenance frequency and operational downtime. Its intrinsic properties, such as high melting point and compatibility with thermal insulating bricks, make mullite an optimal choice for enhancing kiln efficiency and lifespan.
Thermal Stability Comparison: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic vs Mullite
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior thermal stability compared to Mullite, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, whereas Mullite typically endures up to 1400degC before experiencing significant phase changes. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of plasma-sprayed ceramics reduces crack formation under rapid temperature fluctuations, providing longer service life in kiln lining applications. Mullite's lower thermal conductivity also contributes to its insulating properties but does not match the high-temperature resilience and durability demonstrated by advanced plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Plasma-sprayed ceramics exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to mullite, making them ideal for high-stress kiln lining applications. The dense microstructure of plasma-sprayed coatings offers improved resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and chemical corrosion, extending the service life of kiln components. In contrast, mullite, while boasting good thermal stability and lower thermal expansion, tends to have lower fracture toughness and may suffer from microcracking under extreme mechanical loads.
Resistance to Chemical Corrosion
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior resistance to chemical corrosion compared to Mullite, making them ideal for harsh kiln environments with aggressive slags and molten materials. The dense, non-porous microstructure of plasma-sprayed ceramics significantly minimizes the infiltration of corrosive chemicals, enhancing the longevity of kiln linings. Mullite, while offering good thermal stability, is more susceptible to chemical attack due to its relatively higher porosity and reactive alumina-silicate composition.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Retention
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior energy efficiency and heat retention in kiln linings compared to traditional Mullite due to their lower thermal conductivity and higher density, which minimize heat loss. Mullite, while known for its thermal stability and chemical resistance, typically exhibits higher porosity and thermal conductivity, leading to greater energy consumption. Optimizing kiln lining with plasma-sprayed ceramics enhances operational lifespan and reduces fuel costs by maintaining more consistent internal temperatures.
Installation Techniques and Flexibility
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer rapid installation with the ability to form uniform, dense layers directly onto complex kiln surfaces, enhancing thermal protection and reducing downtime compared to traditional methods. Mullite linings require precise casting or brick installation, demanding skilled labor and longer curing times but providing excellent structural stability and resistance to thermal shock. The flexibility of plasma spraying accommodates intricate geometries and quick repairs, while mullite's rigid form is better suited for standard, high-wear kiln zones.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer a high-density, wear-resistant lining that reduces maintenance frequency but incur higher initial costs due to advanced equipment and specialized application techniques. Mullite kiln linings provide cost-effective installation with lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent inspections and repairs because of lower thermal shock resistance and porosity. Choosing plasma-sprayed ceramic over mullite can lower long-term maintenance costs despite the premium investment, making it suitable for high-performance or high-wear kiln environments.
Choosing the Right Kiln Lining: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic or Mullite?
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior thermal shock resistance and faster installation times compared to traditional mullite bricks, making them ideal for high-temperature, rapidly cycling kiln environments. Mullite, known for its excellent refractory strength and chemical stability, provides long-term durability in continuous, steady-state kiln operations with lower thermal gradients. Selecting the right kiln lining depends on operational conditions, where plasma-sprayed ceramics enhance efficiency in dynamic processes, while mullite ensures reliability and longevity under stable thermal loads.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com