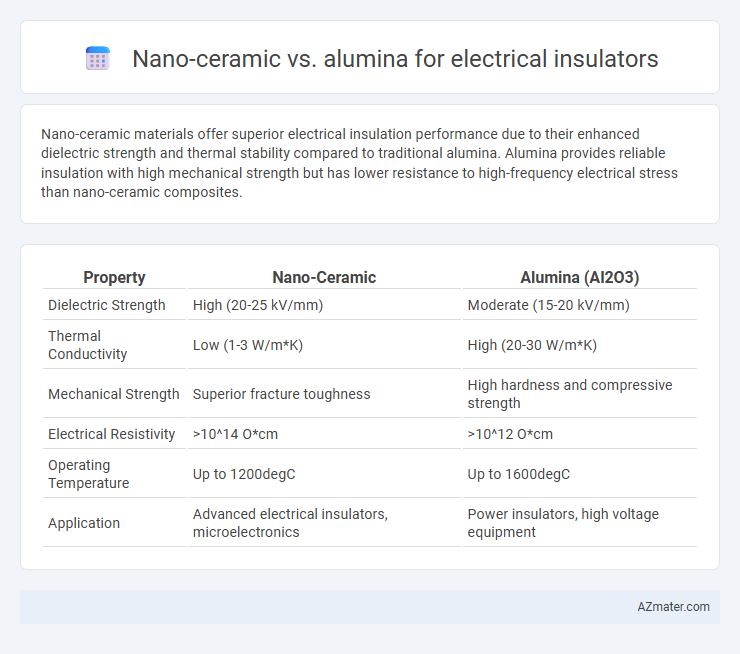
Nano-ceramic materials offer superior electrical insulation performance due to their enhanced dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to traditional alumina. Alumina provides reliable insulation with high mechanical strength but has lower resistance to high-frequency electrical stress than nano-ceramic composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Ceramic | Alumina (Al2O3) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | High (20-25 kV/mm) | Moderate (15-20 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (1-3 W/m*K) | High (20-30 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior fracture toughness | High hardness and compressive strength |
| Electrical Resistivity | >10^14 O*cm | >10^12 O*cm |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Application | Advanced electrical insulators, microelectronics | Power insulators, high voltage equipment |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are materials that inhibit the flow of electric current, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Nano-ceramic insulators offer enhanced dielectric strength and thermal stability due to their fine particle size and uniform microstructure, while alumina insulators are valued for their high mechanical strength and excellent electrical resistivity at elevated temperatures. The choice between nano-ceramic and alumina insulators depends on specific application requirements such as voltage levels, environmental conditions, and thermal management.
Understanding Nano-Ceramic Materials
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties due to their ultra-fine grain structure, which enhances dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to conventional alumina insulators. These nanostructured ceramics offer improved resistance to electrical breakdown, lower dielectric loss, and superior mechanical toughness, making them ideal for high-performance electrical insulator applications. The controlled nano-scale morphology in nano-ceramics facilitates better electron scattering and reduced leakage currents, outperforming traditional alumina in demanding electrical environments.
Overview of Alumina as an Insulator
Alumina (Al2O3) is a widely used electrical insulator known for its high dielectric strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and chemical stability, making it ideal for electronic substrates and insulator components. Its ability to maintain insulation properties under high voltage and temperature conditions ensures reliable performance in power electronics and industrial applications. The material's superior hardness and resistance to wear also contribute to its durability in demanding electrical environments.
Electrical Properties: Nano-Ceramic vs Alumina
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior dielectric strength and lower dielectric loss compared to traditional alumina, enhancing energy efficiency in high-voltage applications. The nano-scale grain structure in nano-ceramics reduces electron mobility, resulting in higher resistivity and improved insulation performance under varying frequencies. While alumina offers reliable thermal stability, nano-ceramics outperform in electrical insulation due to their enhanced permittivity and breakdown voltage characteristics.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Nano-ceramic insulators exhibit superior thermal stability and higher thermal conductivity compared to alumina, enabling more efficient heat dissipation in high-power electrical applications. Alumina, while offering good electrical insulation, has lower thermal conductivity and can experience thermal stress under rapid temperature changes. The enhanced thermal performance of nano-ceramic materials reduces the risk of thermal degradation, ensuring longer service life and reliability in demanding electrical insulation environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their fine-grained microstructure, which enhances crack resistance and fracture toughness compared to traditional alumina insulators. Alumina offers high hardness and thermal stability but is more prone to brittle failure under mechanical stress. The advanced nanostructure in nano-ceramics ensures improved durability and longer service life in high-voltage applications subjected to mechanical wear and thermal cycling.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemical corrosion compared to alumina, enhancing their longevity in harsh electrical insulation applications. Alumina offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength but may be more susceptible to surface degradation under prolonged exposure to aggressive environments. The nano-ceramic's enhanced surface properties and hydrophobicity improve its dielectric reliability and reduce maintenance needs in outdoor and industrial electrical insulators.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators offer enhanced dielectric properties and thermal stability, enabling thinner, lighter designs that reduce material usage and manufacturing costs compared to traditional alumina insulators. Alumina remains cost-effective for high-volume production due to well-established manufacturing processes and lower raw material expenses. Manufacturing nano-ceramic insulators involves advanced techniques like sol-gel processing or nanopowder sintering, which can increase initial costs but improve long-term cost efficiency through performance gains and reduced energy consumption in electronic systems.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to alumina, making them ideal for high-voltage electrical insulators in power transmission systems. Alumina remains widely used due to its excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness in medium-voltage switchgear and transformers. Both materials are crucial for insulating components in electrical systems, with nano-ceramics offering enhanced performance in compact, high-frequency applications such as advanced microelectronic devices and electric vehicle components.
Future Trends in Insulator Technology
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to alumina, making them prime candidates for next-generation electrical insulators. Innovations in nano-ceramic composites are enhancing insulation performance under extreme environmental conditions, supporting advanced applications in smart grids and renewable energy systems. The trend towards integrating nano-ceramics promises increased efficiency, miniaturization, and improved reliability in future electrical insulating technologies.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Alumina for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com