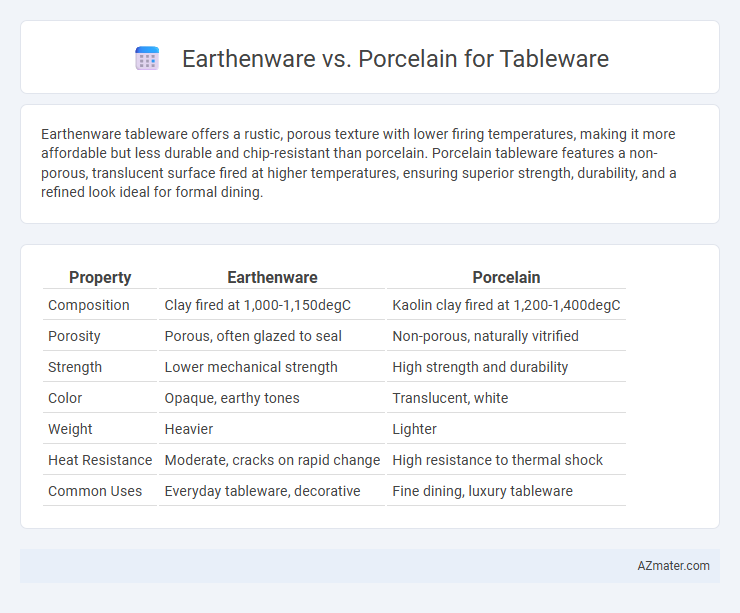
Earthenware tableware offers a rustic, porous texture with lower firing temperatures, making it more affordable but less durable and chip-resistant than porcelain. Porcelain tableware features a non-porous, translucent surface fired at higher temperatures, ensuring superior strength, durability, and a refined look ideal for formal dining.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay fired at 1,000-1,150degC | Kaolin clay fired at 1,200-1,400degC |
| Porosity | Porous, often glazed to seal | Non-porous, naturally vitrified |
| Strength | Lower mechanical strength | High strength and durability |
| Color | Opaque, earthy tones | Translucent, white |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, cracks on rapid change | High resistance to thermal shock |
| Common Uses | Everyday tableware, decorative | Fine dining, luxury tableware |
Introduction to Earthenware and Porcelain
Earthenware is a porous ceramic fired at lower temperatures, characterized by its rustic texture and warmth, commonly used for casual tableware due to its affordability and ease of shaping. Porcelain, made from refined kaolin clay and fired at high temperatures above 1,200degC, offers a translucent, durable, and non-porous surface ideal for elegant, fine dining settings. The key differences lie in firing temperature, density, and durability, influencing their suitability and aesthetic in tableware collections.
Historical Origins and Cultural Significance
Earthenware, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia around 5000 BCE, is recognized for its porous nature and rustic aesthetic, whereas porcelain originated in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE), celebrated for its strength, translucency, and refined quality. Historically, earthenware was widely used in daily life for utilitarian purposes across cultures, reflecting regional clay resources and firing techniques, while porcelain became a symbol of elite artistry and trade, especially prominent in the Ming and Qing Dynasties. The cultural significance of earthenware lies in its accessibility and folk traditions, contrasting with porcelain's association with imperial prestige, global export, and the evolution of sophisticated ceramic craftsmanship.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Earthenware tableware is made from clay fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and more fragile material that is often glazed to improve durability. Porcelain, by contrast, is crafted from refined kaolin clay and fired at higher temperatures around 1,200degC to 1,400degC, producing a dense, non-porous, and highly durable ceramic that is translucent when held to light. The manufacturing process of porcelain includes multiple firings and meticulous control to achieve its strength and delicate appearance, whereas earthenware's simpler production results in a rustic finish suitable for everyday use.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Earthenware is less durable and more porous compared to porcelain, making it prone to chipping and cracking with regular use. Porcelain offers superior strength due to its dense, vitrified composition, which provides greater resistance to thermal shock and mechanical damage. This makes porcelain the preferred choice for high-quality, long-lasting tableware in both domestic and professional settings.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Versatility
Earthenware offers a rustic, handcrafted aesthetic with warm, earthy tones and textured surfaces that complement casual or farmhouse-style table settings. Porcelain boasts a smooth, translucent finish with a refined, elegant appearance, ideal for formal dining and intricate designs. Porcelain's high durability and fine detail capabilities allow for versatile shapes and delicate patterns, whereas earthenware's thicker walls and matte glazes favor bold, artisanal styles.
Practicality in Everyday Use
Earthenware tableware offers durability and affordability, making it ideal for casual, everyday use due to its resistance to chipping and microwave compatibility. Porcelain, while more fragile and expensive, provides a non-porous surface that resists stains and retains heat longer, enhancing meal presentation and dining experience. Both materials require careful handling, but porcelain's sleek finish lends itself to formal settings, whereas earthenware suits daily practicality.
Porosity, Glazing, and Stain Resistance
Porcelain tableware features a dense, low-porosity structure that significantly reduces water absorption, enhancing durability and resistance to stains compared to earthenware, which has higher porosity and can absorb liquids if not properly glazed. The glazing on porcelain is typically smooth and glass-like, providing a non-porous barrier that prevents staining and makes cleaning easier, while earthenware glazing is often more porous and prone to wear over time. This difference in porosity and glazing quality makes porcelain a preferred choice for stain-resistant, long-lasting tableware in both everyday use and formal settings.
Pricing and Accessibility
Earthenware tableware is generally more affordable and widely available due to its lower production costs and simpler manufacturing process, making it a popular choice for everyday use. Porcelain, known for its durability and refined appearance, typically commands higher prices reflecting the more intricate firing techniques and higher quality raw materials involved. Accessibility for porcelain is often limited to specialized retailers or premium brands, whereas earthenware can be found easily in discount stores and mainstream markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Earthenware tableware, made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, generally consumes less energy during production compared to porcelain, which requires higher kiln temperatures and more refined raw materials. Porcelain's durability and longer lifespan can reduce waste over time, while earthenware's biodegradability offers an advantage in end-of-life environmental impact. Choosing between earthenware and porcelain depends on balancing the energy intensity of manufacturing with the product's longevity and recyclability for overall sustainability.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Tableware Needs
Earthenware offers warmth and rustic charm with its porous, thicker composition, making it ideal for casual dining and everyday use due to its affordability and ease of repair. Porcelain, crafted from refined clay and fired at higher temperatures, provides a durable, non-porous, and elegant finish that resists chipping and suits formal settings or frequent use in the kitchen. When choosing the best option, consider factors such as durability, aesthetic preference, budget, and intended use to match your tableware needs effectively.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Porcelain for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com