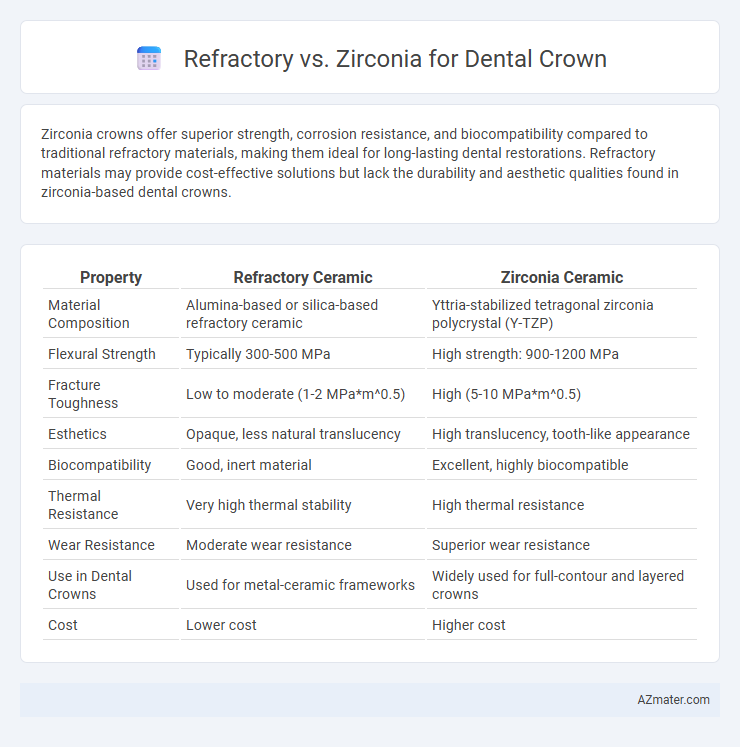
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility compared to traditional refractory materials, making them ideal for long-lasting dental restorations. Refractory materials may provide cost-effective solutions but lack the durability and aesthetic qualities found in zirconia-based dental crowns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory Ceramic | Zirconia Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina-based or silica-based refractory ceramic | Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) |
| Flexural Strength | Typically 300-500 MPa | High strength: 900-1200 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness | Low to moderate (1-2 MPa*m^0.5) | High (5-10 MPa*m^0.5) |
| Esthetics | Opaque, less natural translucency | High translucency, tooth-like appearance |
| Biocompatibility | Good, inert material | Excellent, highly biocompatible |
| Thermal Resistance | Very high thermal stability | High thermal resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | Superior wear resistance |
| Use in Dental Crowns | Used for metal-ceramic frameworks | Widely used for full-contour and layered crowns |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Refractory materials and zirconia are prominent choices for dental crown fabrication, each offering distinct properties suited for specific clinical needs. Refractory ceramics provide excellent heat resistance and shape stability during porcelain firing, ideal for layered metal-ceramic crowns. Zirconia crowns stand out for their superior strength, biocompatibility, and aesthetic translucency, making them popular for both anterior and posterior restorations.
Understanding Refractory Crowns
Refractory crowns are essential in dental restoration for creating precise ceramic crowns through high-temperature firing processes. These crowns use refractory materials that withstand extreme heat during porcelain layering and glazing, ensuring dimensional stability and accurate fit. Compared to zirconia crowns, refractory crowns provide superior support for aesthetic glass-ceramic coatings but require additional lab steps due to their heat-resistant framework.
Overview of Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns are known for their superior strength, biocompatibility, and natural tooth-like appearance, making them a popular choice in restorative dentistry. These crowns exhibit excellent fracture resistance and durability compared to refractory ceramic materials, ensuring long-term performance in areas subjected to high bite forces. Advanced CAD/CAM technology allows precise fabrication of zirconia crowns, resulting in optimal marginal fit and enhanced patient comfort.
Material Composition and Properties
Refractory dental crowns are primarily composed of heat-resistant ceramic materials that provide excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, ideal for high-temperature processing. Zirconia crowns consist of zirconium dioxide, a crystalline oxide known for its superior fracture toughness, biocompatibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion. The material composition of zirconia offers enhanced durability and an aesthetic finish compared to traditional refractory ceramics, making it a preferred choice in modern restorative dentistry.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and durability compared to refractory crowns, with zirconia's flexural strength ranging between 900 to 1200 MPa, making it highly resistant to fracture and wear. Refractory crowns, typically composed of ceramic materials with lower flexural strength around 300 to 400 MPa, tend to be more brittle and less durable under heavy masticatory forces. The long-term clinical success of zirconia crowns is enhanced by their high fracture toughness and resistance to chipping, which outperforms the mechanical limitations seen in refractory dental crown materials.
Aesthetics: Natural Appearance and Color Matching
Zirconia crowns offer superior aesthetics with their translucent properties closely mimicking natural tooth enamel, enabling precise color matching for seamless integration. Refractory crowns, while durable, lack the translucency and natural brightness of zirconia, often resulting in a less lifelike appearance. Advanced zirconia materials also resist staining and maintain color stability, enhancing long-term aesthetic outcomes in dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to traditional refractory materials, minimizing allergic reactions and tissue irritation in patients. Their inert chemical composition reduces the risk of cytotoxicity, promoting healthier gum integration and long-term oral health. Patient safety is enhanced as zirconia resists corrosion and degradation, providing durable, non-toxic dental restorations.
Clinical Applications and Indications
Refractory materials are predominantly used for metal-ceramic crowns due to their high-temperature resistance and ability to support ceramic layering without deformation, making them ideal for frameworks requiring precision and strength. Zirconia crowns, favored for their exceptional biocompatibility, fracture toughness, and aesthetic translucency, are commonly indicated in posterior restorations and patients with bruxism, offering a metal-free alternative with superior durability. Clinical applications dictate that refractory materials suit procedures demanding robust frameworks under high thermal stress, whereas zirconia is preferred for all-ceramic restorations requiring optimal esthetics and mechanical performance.
Longevity and Performance Outcomes
Refractory crowns offer high durability and excellent heat resistance, making them suitable for long-term dental restorations with stable performance in high-stress environments. Zirconia crowns provide superior strength, biocompatibility, and wear resistance, resulting in exceptional longevity and aesthetic outcomes for patients. Clinical studies indicate zirconia crowns maintain structural integrity better over time compared to refractory materials, supporting enhanced performance in daily oral functions.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Refractory crowns generally offer a lower initial cost compared to zirconia crowns, making them more accessible for patients with budget constraints. Zirconia crowns, while more expensive, provide superior durability and aesthetic appeal, which can translate to long-term cost savings by reducing the need for replacements or repairs. Accessibility to refractory materials is widespread in dental labs, whereas zirconia requires advanced milling technology, potentially limiting availability in some regions.
Infographic: Refractory vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com