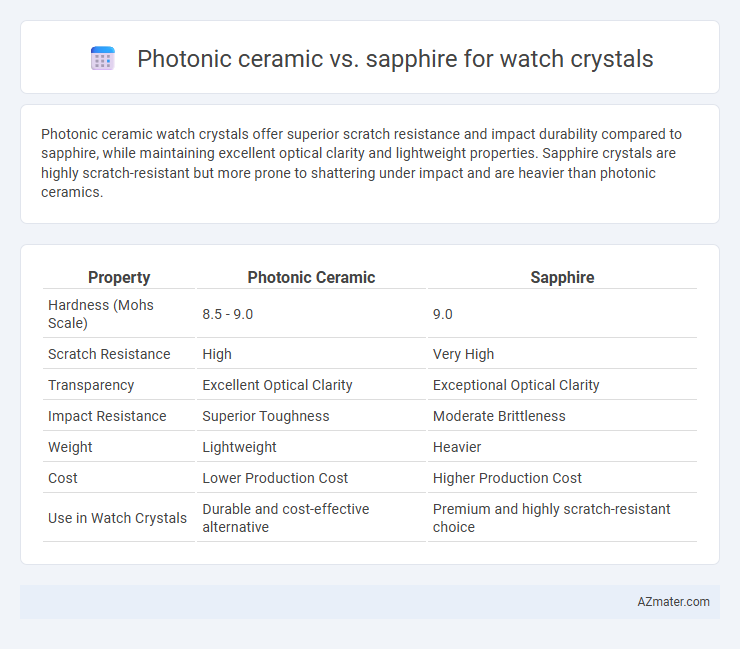
Photonic ceramic watch crystals offer superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to sapphire, while maintaining excellent optical clarity and lightweight properties. Sapphire crystals are highly scratch-resistant but more prone to shattering under impact and are heavier than photonic ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Sapphire |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 8.5 - 9.0 | 9.0 |
| Scratch Resistance | High | Very High |
| Transparency | Excellent Optical Clarity | Exceptional Optical Clarity |
| Impact Resistance | Superior Toughness | Moderate Brittleness |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Lower Production Cost | Higher Production Cost |
| Use in Watch Crystals | Durable and cost-effective alternative | Premium and highly scratch-resistant choice |
Introduction to Watch Crystal Materials
Photonic ceramics and sapphire are prominent materials used for watch crystals, each offering unique properties in durability and optical clarity. Sapphire crystal, a synthetic form of corundum, is highly valued for its exceptional scratch resistance and clarity, making it a premium choice in luxury and high-performance watches. Photonic ceramics, emerging as a cutting-edge alternative, combine advanced ceramic engineering with photonic technologies to provide enhanced toughness and anti-reflective properties, positioning them as innovative solutions in watch crystal materials.
Overview of Photonic Ceramic
Photonic ceramic watch crystals offer exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, surpassing many traditional materials including sapphire. Engineered from advanced ceramic compounds, these crystals provide outstanding clarity and durability while maintaining lightweight properties, making them ideal for high-performance timepieces. Their inherent resistance to impact and thermal shocks ensures long-lasting protection, setting photonic ceramic apart as a premium alternative to sapphire in luxury watchmaking.
Overview of Sapphire Crystal
Sapphire crystal, composed of synthetic corundum, is renowned for its exceptional hardness ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly resistant to scratches and daily wear. Its optical clarity and transparency ensure minimal distortion and excellent visibility for watch dials, while its brittleness requires careful handling to avoid shattering. Compared to photonic ceramics, sapphire crystals offer superior scratch resistance but lower impact strength, balancing durability with premium aesthetics in watchmaking.
Optical Clarity Comparison
Photonic ceramics offer excellent optical clarity with high transparency and durability, rivaling traditional watch crystals. Sapphire crystals provide superior scratch resistance and exceptional light transmission, resulting in sharp, clear visibility under various lighting conditions. Both materials ensure minimal distortion, but sapphire typically outperforms photonic ceramics in clarity and hardness for premium watch applications.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Photonic ceramic watch crystals exhibit superior scratch resistance due to their ultra-hard nanocomposite structure, surpassing traditional sapphire crystals which, while hard, are more prone to shattering upon impact. The impact resistance of photonic ceramics is significantly higher, offering enhanced durability against drops and collisions, unlike sapphire crystals that may chip or crack under sudden force. This combination of high scratch resistance and impact toughness makes photonic ceramics an advanced material choice for durable watch crystals.
Weight and Wearability
Photonic ceramic watch crystals offer significantly lower weight compared to sapphire, enhancing overall wearability without compromising durability. The reduced density of photonic ceramics contributes to a lighter watch, making it more comfortable for extended daily use. While sapphire remains highly scratch-resistant, photonic ceramics provide an optimal balance of lightweight comfort and robust performance for advanced watch designs.
Cost and Availability
Photonic ceramic watch crystals offer a cost-effective alternative to sapphire, providing durable scratch resistance at a lower price point. Sapphire crystals are more expensive due to their superior hardness and clarity but face limited availability from high-quality suppliers. Photonic ceramics benefit from easier manufacturing processes and broader availability, making them attractive for budget-conscious watchmakers.
Aesthetic Differences
Photonic ceramic watch crystals exhibit a matte finish with subtle translucency, offering a modern and understated aesthetic compared to the high-gloss, transparent clarity of sapphire crystals. Sapphire's brilliant luster enhances dial visibility and imparts a luxurious appeal, while photonic ceramic provides a unique, soft-focus effect that reduces glare and adds a distinctive contemporary character. The choice between these materials impacts not only scratch resistance but also the overall visual presentation and perceived sophistication of the timepiece.
Suitability for Smartwatches and Traditional Watches
Photonic ceramics offer exceptional scratch resistance and impact durability, making them highly suitable for rugged smartwatches designed for active lifestyles. Sapphire crystals provide superior clarity and premium luxury appeal, which is preferred in traditional high-end watches seeking an elegant, transparent display. Smartwatches benefit from photonic ceramics' ability to integrate with touchscreen technology, whereas sapphire maintains a classic aesthetic favored by traditional watch enthusiasts.
Future Trends in Watch Crystal Technology
Photonic ceramics offer enhanced scratch resistance and optical clarity, making them a cutting-edge alternative to traditional sapphire watch crystals. Innovations in nanostructured photonic materials are driving increased durability and reduced weight, appealing to high-performance and luxury watchmakers. The integration of photonic ceramics with smart watch displays signals a future trend toward multifunctional, hybrid watch crystals combining robustness with advanced optical functionalities.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Sapphire for Watch crystal
 azmater.com
azmater.com