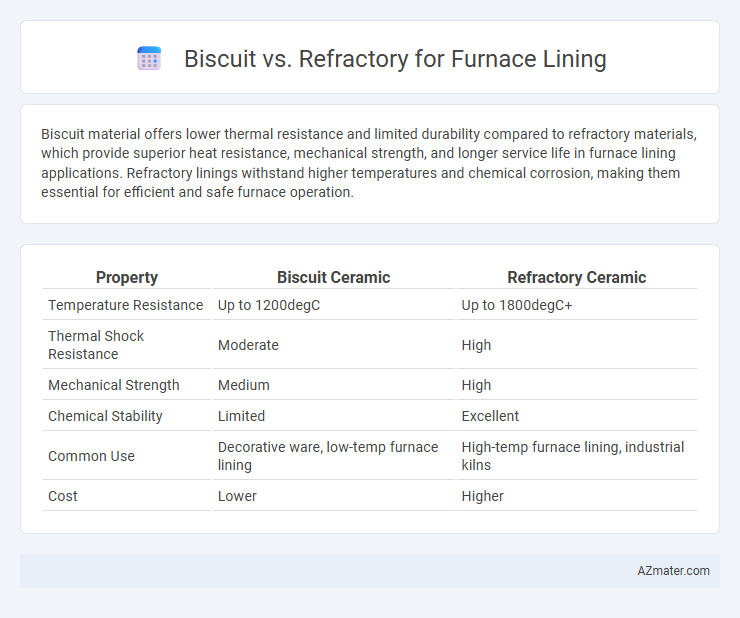
Biscuit material offers lower thermal resistance and limited durability compared to refractory materials, which provide superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and longer service life in furnace lining applications. Refractory linings withstand higher temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them essential for efficient and safe furnace operation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biscuit Ceramic | Refractory Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC+ |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | High |
| Chemical Stability | Limited | Excellent |
| Common Use | Decorative ware, low-temp furnace lining | High-temp furnace lining, industrial kilns |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials such as biscuit and refractory bricks serve critical roles in thermal insulation and structural integrity within high-temperature industrial furnaces. Biscuit bricks, typically pre-fired and partially vitrified, offer moderate thermal resistance and are often used in less demanding zones, whereas refractory bricks, composed of high-purity alumina or silica, provide superior heat resistance and mechanical strength essential for extreme temperature and corrosive environments. Selection between biscuit and refractory linings depends on operational temperature, thermal conductivity, and chemical exposure requirements to optimize furnace efficiency and durability.
What Are Biscuit Linings?
Biscuit linings in furnace construction are pre-formed ceramic pieces designed for quick installation and rapid heat-up times, offering excellent thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike refractory castables that are applied as a wet mixture, biscuit linings come in standardized shapes and sizes, ensuring consistent density and strength. These linings are preferred in high-temperature applications where minimizing downtime and maximizing durability are critical for operational efficiency.
Understanding Refractory Linings
Refractory linings in furnaces are critical for thermal insulation and structural integrity, with biscuit and refractory materials serving distinct functions. Biscuit, an unfired shaped refractory, offers easier handling and installation before final firing within the furnace, whereas refractory materials provide heat resistance and durability after firing. Optimizing furnace performance depends on selecting the appropriate refractory lining type based on temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure.
Key Differences: Biscuit vs Refractory
Biscuit and refractory materials serve distinct roles in furnace lining, with biscuit acting as a preliminary protective layer formed from partially calcined fireclay, while refractory materials provide the main, durable thermal insulation resistant to extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. Biscuit lining offers easier installation and repairability but lacks the high-temperature stability and mechanical strength found in refractory bricks or castables. Refractory linings are engineered for long-term furnace performance, emphasizing thermal shock resistance, minimal thermal conductivity, and compatibility with specific industrial firing conditions.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Biscuit refractories exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for furnace linings exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations. Refractory bricks, particularly fireclay or high-alumina types, provide excellent insulation and maintain structural integrity over sustained high temperatures but may have slower heat transfer rates compared to biscuits. Selecting between biscuit and traditional refractory linings depends on specific thermal cycles and operational demands, with biscuits offering enhanced thermal conductivity and quicker response times in high-temperature furnace environments.
Durability and Longevity
Biscuit refractories offer exceptional durability due to their high density and low porosity, making them suitable for high-temperature furnace linings with extended service life. Refractory bricks typically exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance and structural integrity, ensuring longevity under cyclic heating conditions. While both materials provide robust performance, biscuit refractories tend to deliver superior lifespan in environments with consistent high-temperature exposure.
Installation Processes
Biscuit furnace linings are pre-fired, rigid shapes that require careful handling and precise placement during installation to ensure proper alignment and avoid damage, resulting in a quicker and cleaner setup. Refractory castables, consisting of a dry mix that is combined with water and cast or pumped into place, demand skilled labor for mixing, casting, and curing phases, which can extend installation time but allow for custom shapes and seamless linings. The choice between biscuit and refractory installation hinges on factors such as furnace design complexity, downtime tolerances, and the skill level of the installation team.
Cost Analysis and Efficiency
Biscuit refractory linings typically offer lower initial installation costs compared to traditional refractory bricks due to faster drying times and easier handling, reducing labor expenses. Efficiency-wise, biscuits provide good thermal shock resistance and quicker heat-up cycles, enhancing furnace performance and reducing downtime. However, traditional refractory linings may deliver longer service life under extreme conditions, potentially lowering long-term operational costs despite higher upfront investment.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Biscuits offer easier maintenance and faster repair turnaround due to their lightweight and modular structure, enabling quick replacement of damaged sections in furnace linings. Refractory castables, while more durable, often require longer downtime and specialized equipment for repairs, increasing maintenance complexity and costs. Selection between biscuit and refractory linings should factor in operational schedules and availability of skilled maintenance personnel.
Choosing the Right Lining for Your Furnace
Choosing the right furnace lining between biscuit and refractory materials depends on factors such as temperature resistance, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. Biscuit linings, typically lightweight and insulating, excel in lower temperature applications requiring energy efficiency, while refractory linings offer superior durability and stability at extremely high temperatures, supporting heavy-duty industrial processes. Evaluating operational conditions and maintenance needs ensures optimal performance and longevity for your furnace lining selection.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Refractory for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com