Carbide cutting tools offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-speed machining and tougher materials. Porcelain tools, while less durable, provide excellent chemical stability and are suited for precision cutting in softer, non-metallic applications.
Table of Comparison
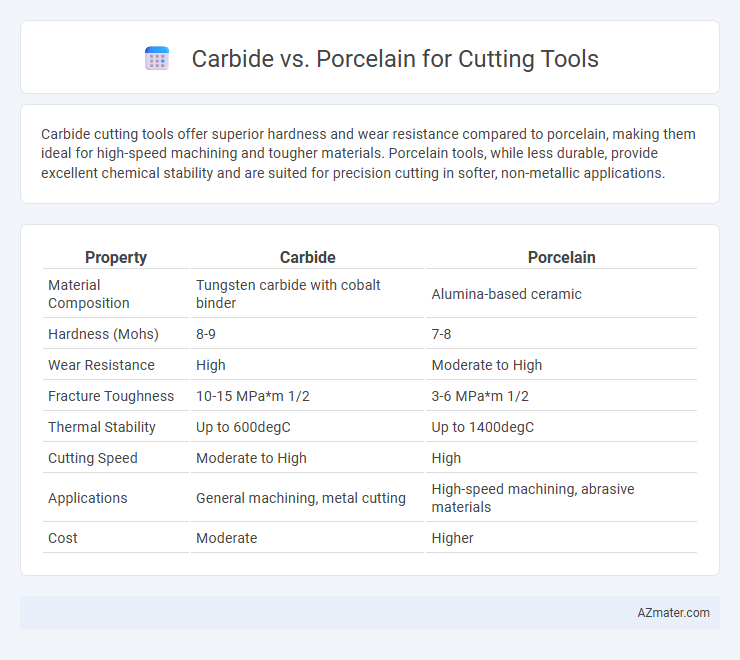
| Property | Carbide | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Tungsten carbide with cobalt binder | Alumina-based ceramic |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8-9 | 7-8 |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Fracture Toughness | 10-15 MPa*m 1/2 | 3-6 MPa*m 1/2 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 1400degC |
| Cutting Speed | Moderate to High | High |
| Applications | General machining, metal cutting | High-speed machining, abrasive materials |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Cutting Tool Materials
Cutting tool materials such as carbide and porcelain differ significantly in composition and performance attributes, impacting machining efficiency and durability. Carbide tools, made from tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance ideal for high-speed metal cutting applications. Porcelain tools, primarily ceramic-based, provide superior heat resistance and insulation properties but generally lack the toughness and impact resistance necessary for most machining tasks.
Overview of Carbide Cutting Tools
Carbide cutting tools, composed primarily of tungsten carbide particles bonded with a metallic binder, offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance compared to porcelain tools. These tools maintain sharpness at high temperatures and provide superior durability in machining operations involving tough materials like stainless steel and cast iron. Enhanced toughness and thermal stability make carbide cutting tools the preferred choice for high-speed cutting and extended tool life in industrial applications.
Overview of Porcelain Cutting Tools
Porcelain cutting tools offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for precision machining of non-metallic materials and ceramics. Their chemical stability and high-temperature resistance contribute to maintaining sharpness and dimensional accuracy during prolonged use. While less tough than carbide, porcelain tools excel in applications requiring minimal tool contamination and electrical insulation.
Material Composition and Properties
Carbide cutting tools consist primarily of tungsten carbide particles bound with cobalt, offering exceptional hardness and wear resistance suited for high-speed machining. Porcelain cutting tools, made from advanced ceramic materials such as alumina or zirconia, provide excellent chemical inertness and thermal stability but are more brittle than carbide. The material composition of carbide delivers superior toughness and impact resistance, while porcelain's properties favor applications requiring minimal chemical interaction and higher temperature endurance.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Carbide cutting tools offer superior hardness and heat resistance, enabling higher cutting speeds and longer tool life compared to porcelain. Porcelain tools, while more brittle, provide excellent corrosion resistance and maintain sharpness in less demanding applications. Overall, carbide outperforms porcelain in durability and performance for high-precision, heavy-duty machining tasks.
Cutting Efficiency: Carbide vs. Porcelain
Carbide cutting tools exhibit superior cutting efficiency compared to porcelain due to their exceptional hardness and thermal resistance, enabling faster machining speeds and longer tool life. Porcelain tools, while offering good wear resistance, lack the toughness and heat tolerance of carbide, resulting in slower cutting rates and more frequent tool replacements. The high durability and strength of carbide make it the preferred choice for precision cutting applications requiring consistent performance under high-stress conditions.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Carbide cutting tools excel in high-speed machining applications, especially in automotive, aerospace, and heavy metal industries due to their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Porcelain cutting tools are preferred in electrical and electronics manufacturing where precision and resistance to chemical corrosion are critical. Selecting between carbide and porcelain depends on the material hardness, machining speed, and industry-specific requirements for durability and precision.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Longevity
Carbide cutting tools have a higher initial cost compared to porcelain tools but offer superior durability, leading to lower replacement frequency and long-term savings. Porcelain tools are more affordable upfront but tend to wear out faster, increasing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors carbide for high-volume or precision tasks due to its extended tool life and performance reliability.
Maintenance and Sharpening Requirements
Carbide cutting tools require less frequent sharpening due to their superior hardness and wear resistance, reducing downtime in manufacturing processes. Porcelain cutting tools, though more brittle, demand careful handling and more frequent sharpening to maintain precision, increasing maintenance efforts. Effective sharpening of carbide tools often necessitates specialized diamond grinding equipment, while porcelain tools can be sharpened with conventional abrasive methods but with higher risk of chipping.
Choosing the Right Tool Material for Your Needs
Carbide cutting tools offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-speed machining and tougher materials like stainless steel and cast iron. Porcelain tools, while less common, provide excellent thermal insulation and corrosion resistance, suitable for applications requiring minimal thermal conductivity and chemical stability. Choosing the right tool material depends on factors such as workpiece hardness, machining speed, and environmental conditions to optimize tool life and machining efficiency.
Infographic: Carbide vs Porcelain for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com