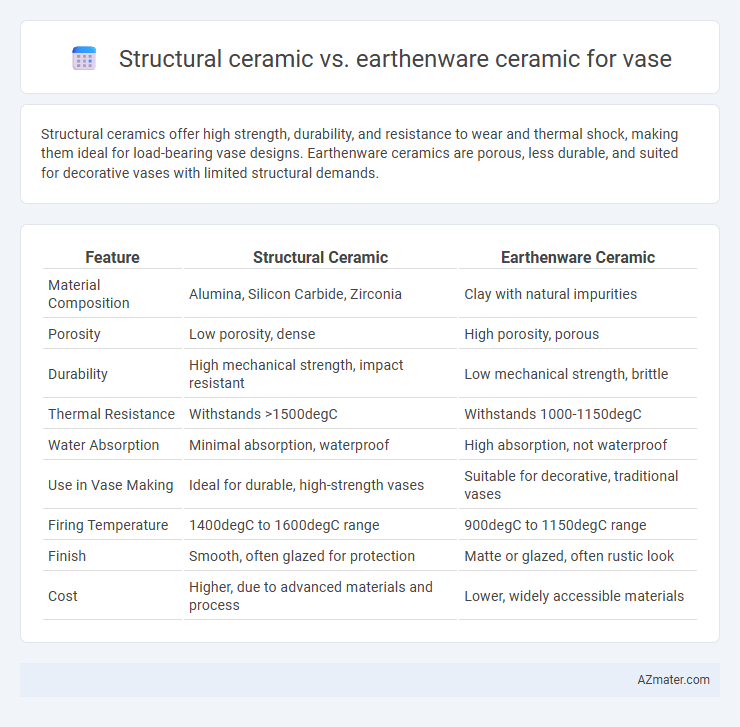
Structural ceramics offer high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and thermal shock, making them ideal for load-bearing vase designs. Earthenware ceramics are porous, less durable, and suited for decorative vases with limited structural demands.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Ceramic | Earthenware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina, Silicon Carbide, Zirconia | Clay with natural impurities |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense | High porosity, porous |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, impact resistant | Low mechanical strength, brittle |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands >1500degC | Withstands 1000-1150degC |
| Water Absorption | Minimal absorption, waterproof | High absorption, not waterproof |
| Use in Vase Making | Ideal for durable, high-strength vases | Suitable for decorative, traditional vases |
| Firing Temperature | 1400degC to 1600degC range | 900degC to 1150degC range |
| Finish | Smooth, often glazed for protection | Matte or glazed, often rustic look |
| Cost | Higher, due to advanced materials and process | Lower, widely accessible materials |
Introduction to Structural and Earthenware Ceramics
Structural ceramics, known for their high strength and durability, are engineered materials often used in applications requiring resistance to mechanical stress and thermal stability, making them ideal for robust vase designs. Earthenware ceramics, characterized by their porous and softer composition, are fired at lower temperatures and exhibit a more rustic, porous texture, often glazed to enhance water resistance and aesthetic appeal. The choice between structural and earthenware ceramics for vases depends on the desired balance of strength, finish, and traditional or modern styling.
Key Differences Between Structural and Earthenware Ceramics
Structural ceramics, composed of materials like alumina and silicon carbide, offer high strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making them suitable for functional vases requiring mechanical toughness. Earthenware ceramics are typically porous and fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a softer, more fragile vase ideal for decorative purposes rather than heavy use. Key differences lie in firing temperature, porosity, mechanical strength, and typical applications, with structural ceramics excelling in performance and earthenware valued for aesthetic qualities.
Composition and Material Properties
Structural ceramics for vases are composed primarily of advanced materials like alumina, silicon carbide, or zirconia, exhibiting high mechanical strength, fracture toughness, and thermal resistance. Earthenware ceramics consist mainly of clay minerals, such as kaolin and ball clay, with lower firing temperatures resulting in porous, less durable, and more brittle materials. The superior density and hardness of structural ceramics ensure enhanced durability and structural integrity compared to the porous and more absorbent nature of earthenware ceramics.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Structural ceramics exhibit significantly higher strength and durability compared to earthenware ceramics, making them ideal for vases requiring long-term stability. With their dense microstructure and resistance to wear, structural ceramics provide superior impact resistance and minimal porosity, reducing the risk of cracking or chipping. Earthenware ceramics, while aesthetically versatile, are more porous and fragile, resulting in lower mechanical strength and reduced durability under stress or environmental exposure.
Aesthetic Qualities: Appearance and Finish
Structural ceramics offer a sleek, refined appearance with smooth finishes and high durability, making them ideal for modern, minimalist vase designs that emphasize sharp lines and uniform textures. Earthenware ceramics feature a rustic, organic look with porous surfaces and natural variation in color and glaze, creating warm, handcrafted aesthetic qualities prized in traditional and artisanal vases. The choice between structural and earthenware ceramics significantly impacts the visual appeal and tactile experience of the vase, depending on the desired artistic style and ambiance.
Water Resistance and Porosity
Structural ceramics exhibit low porosity and high water resistance, making them ideal for vases that require durability and moisture retention. Earthenware ceramics have higher porosity, resulting in increased water absorption and less suitability for holding liquids unless sealed with a glaze. The water resistance of structural ceramics surpasses that of earthenware, contributing to their long-lasting performance in functional vase applications.
Suitability for Decorative and Functional Vases
Structural ceramic offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for functional vases that require resistance to chipping and cracking. Earthenware ceramics provide a porous, rustic appearance favored in decorative vases but are less suited for holding water without a glaze due to their absorbency. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with structural ceramics excelling in practical use and earthenware enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Cost and Accessibility
Structural ceramics, made from advanced materials like alumina and silicon carbide, offer high durability but come with significantly higher production costs, making them less accessible for mass-market vase production. Earthenware ceramics, composed primarily of natural clay fired at lower temperatures, provide a more affordable and widely accessible option ideal for decorative vases. The cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing earthenware drive its popularity in both artisanal and commercial vase markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural ceramics used for vases often involve energy-intensive processes with high firing temperatures, which result in significant carbon emissions, yet their durability contributes to longer life cycles and reduced waste. Earthenware ceramics typically require lower firing temperatures, leading to less energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint, but they are more porous and less durable, which can decrease product lifespan and increase replacement frequency. Selecting earthenware over structural ceramic vases can enhance sustainability by minimizing energy use during production, although balancing durability and environmental impact is essential for optimizing overall sustainability.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for Vase Applications
Structural ceramics offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for functional vases exposed to harsh environments or heavy handling. Earthenware ceramics provide aesthetic versatility with porous, rustic finishes suitable for decorative vases but require sealing to prevent water absorption and damage. Choosing the right ceramic depends on the vase's intended use, where structural ceramics ensure longevity and performance, while earthenware emphasizes artistic expression and affordability.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Earthenware ceramic for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com