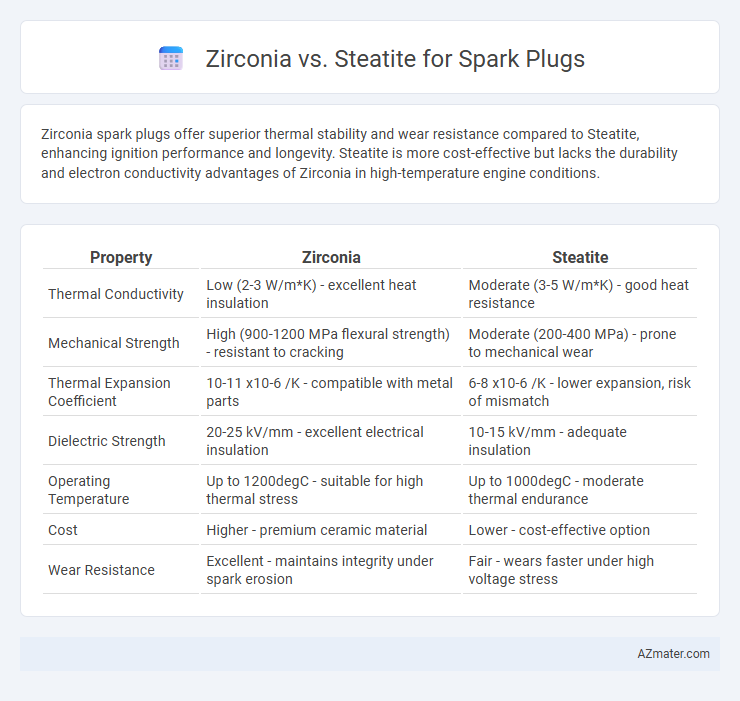
Zirconia spark plugs offer superior thermal stability and wear resistance compared to Steatite, enhancing ignition performance and longevity. Steatite is more cost-effective but lacks the durability and electron conductivity advantages of Zirconia in high-temperature engine conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconia | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (2-3 W/m*K) - excellent heat insulation | Moderate (3-5 W/m*K) - good heat resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High (900-1200 MPa flexural strength) - resistant to cracking | Moderate (200-400 MPa) - prone to mechanical wear |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 10-11 x10-6 /K - compatible with metal parts | 6-8 x10-6 /K - lower expansion, risk of mismatch |
| Dielectric Strength | 20-25 kV/mm - excellent electrical insulation | 10-15 kV/mm - adequate insulation |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC - suitable for high thermal stress | Up to 1000degC - moderate thermal endurance |
| Cost | Higher - premium ceramic material | Lower - cost-effective option |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent - maintains integrity under spark erosion | Fair - wears faster under high voltage stress |
Introduction to Spark Plug Ceramics
Spark plug ceramics primarily consist of zirconia and steatite, each offering unique properties that impact performance and durability. Zirconia is favored for its exceptional thermal stability, resistance to thermal shock, and high fracture toughness, making it ideal for high-performance engines. Steatite provides good electrical insulation and moderate thermal resistance but is generally less durable compared to zirconia in extreme operating conditions.
Overview of Zirconia and Steatite Materials
Zirconia, a high-performance ceramic, offers exceptional thermal stability, fracture toughness, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for spark plug insulators in demanding engine conditions. Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, provides good electrical insulation and moderate thermal resistance but lacks the durability and mechanical strength of zirconia under high-stress environments. The choice between zirconia and steatite materials directly impacts spark plug longevity, ignition efficiency, and overall engine reliability.
Physical Properties: Zirconia vs Steatite
Zirconia exhibits high fracture toughness, excellent thermal stability, and superior wear resistance compared to steatite, making it ideal for spark plug insulators in high-stress environments. Steatite offers good electrical insulation and moderate thermal conductivity but lacks the mechanical strength and durability of zirconia under extreme temperatures. The density of zirconia (approximately 6.0 g/cm3) is significantly higher than steatite (around 2.8 g/cm3), contributing to its enhanced physical robustness in automotive ignition systems.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Zirconia spark plugs exhibit lower thermal conductivity compared to steatite, enabling them to retain higher operating temperatures and improve combustion efficiency. Steatite plugs, with higher thermal conductivity, dissipate heat faster, reducing the risk of pre-ignition but potentially limiting optimum operating temperature ranges. The choice between zirconia and steatite hinges on balancing heat retention for efficiency and heat dissipation for engine protection.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Zirconia exhibits superior electrical insulation performance compared to steatite, with higher dielectric strength and better resistance to electrical breakdown under high voltage conditions. Its excellent thermal stability and low electrical conductivity contribute to maintaining consistent insulation even at elevated temperatures typical in spark plug operation. Steatite, while effective as an insulator, generally offers lower dielectric strength and can degrade faster under thermal stress, making zirconia the preferred choice for enhanced durability and reliable electrical isolation in spark plugs.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Zirconia spark plugs exhibit superior durability and wear resistance due to their high fracture toughness and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance and long-lasting applications. Steatite spark plugs, while offering good electrical insulation and moderate durability, are more prone to wear and degradation under extreme heat and mechanical stress. The enhanced hardness and chemical inertness of zirconia result in prolonged spark plug life and consistent ignition performance compared to steatite.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Zirconia spark plugs typically offer higher durability and better thermal stability but come at a significantly higher cost compared to steatite variants, impacting overall cost efficiency for standard applications. Steatite spark plugs are more widely available and affordable, making them a cost-effective choice for everyday engine use and mass production scenarios. The availability of steatite materials in global supply chains ensures consistent procurement, whereas zirconia, being a specialized ceramic, is less common and often results in longer lead times and increased expenses.
Applications in Automotive and Industrial Sectors
Zirconia spark plugs offer superior thermal stability and durability, making them ideal for high-performance automotive engines and industrial machinery requiring consistent ignition under extreme conditions. Steatite spark plugs provide excellent electrical insulation and cost-efficiency, suitable for standard automotive applications and less demanding industrial equipment. The choice between zirconia and steatite depends on the application's temperature tolerance, electrical requirements, and budget constraints in both automotive and industrial sectors.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Material
Zirconia spark plugs offer superior thermal conductivity and durability, enabling higher heat resistance and stable performance in extreme engine conditions, but they tend to be more expensive and susceptible to cracking under mechanical shock. Steatite spark plugs provide excellent electrical insulating properties and lower cost, making them suitable for standard engine operations, yet they have limited thermal endurance and can degrade faster in high-temperature environments. Choosing between zirconia and steatite depends on the engine's performance demands and operating temperatures, balancing cost against longevity and thermal stability.
Which is Better for Spark Plug Manufacturing?
Zirconia excels in spark plug manufacturing due to its superior thermal stability, higher fracture toughness, and excellent insulation properties compared to Steatite, which has lower mechanical strength and less resistance to thermal shock. Zirconia's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments makes it the preferred ceramic material for high-performance, long-lasting spark plugs. Steatite is generally reserved for low-cost, low-performance applications where cost is prioritized over durability and efficiency.
Infographic: Zirconia vs Steatite for Spark plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com