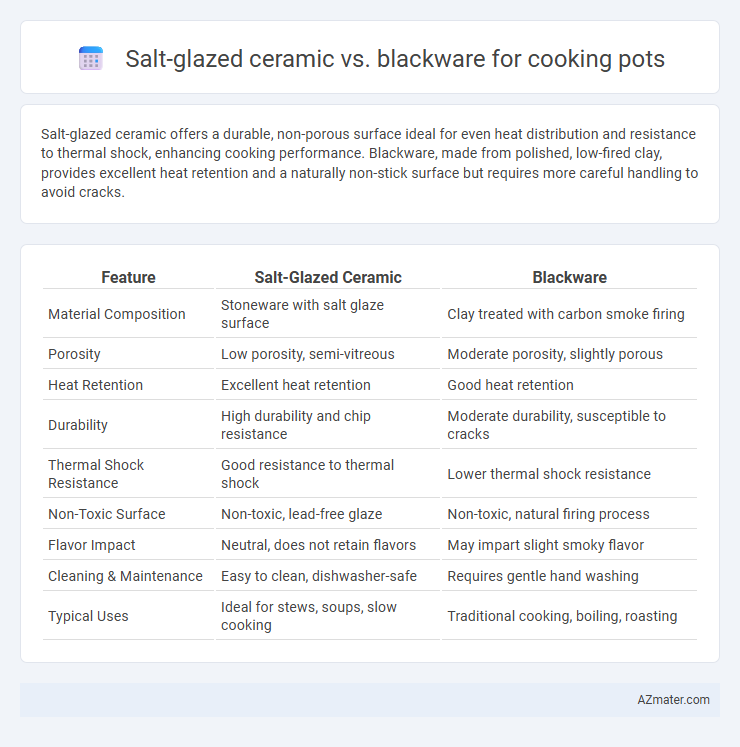
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, non-porous surface ideal for even heat distribution and resistance to thermal shock, enhancing cooking performance. Blackware, made from polished, low-fired clay, provides excellent heat retention and a naturally non-stick surface but requires more careful handling to avoid cracks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Blackware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Stoneware with salt glaze surface | Clay treated with carbon smoke firing |
| Porosity | Low porosity, semi-vitreous | Moderate porosity, slightly porous |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention | Good heat retention |
| Durability | High durability and chip resistance | Moderate durability, susceptible to cracks |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good resistance to thermal shock | Lower thermal shock resistance |
| Non-Toxic Surface | Non-toxic, lead-free glaze | Non-toxic, natural firing process |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, does not retain flavors | May impart slight smoky flavor |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher-safe | Requires gentle hand washing |
| Typical Uses | Ideal for stews, soups, slow cooking | Traditional cooking, boiling, roasting |
Introduction to Salt-glazed Ceramic and Blackware
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a glossy, textured surface created by introducing salt into the kiln during high-temperature firing, resulting in a durable, non-porous finish ideal for cooking pots that require heat retention and resistance to thermal shock. Blackware, traditionally made by Native American artisans and fired in a reduced oxygen environment, boasts a smooth, matte black finish with natural clay properties that provide excellent heat distribution and moisture retention for slow-cooking dishes. Both materials offer unique aesthetic qualities and functional benefits, with salt-glazed ceramics excelling in durability and blackware valued for its cultural craftsmanship and cooking performance.
Historical Background and Cultural Significance
Salt-glazed ceramics originated in 15th-century Germany, where sodium from salt vaporized in the kiln reacted with silica in the clay, creating a durable, glassy surface highly favored for cooking pots due to its heat resistance and non-porous qualities. Blackware pottery, notably crafted by indigenous Pueblo peoples in the American Southwest, involves reducing oxygen during firing to achieve a distinctive black sheen, symbolizing cultural identity and spiritual significance while also offering practical heat retention for cooking. Both techniques reflect regional resources and traditions, with salt-glazed ceramics rooted in European utilitarian practices and blackware embodying ceremonial artistry intertwined with everyday use in Native American communities.
Manufacturing Processes: Salt-glaze vs Black Firing
Salt-glazed ceramics are produced by throwing salt into the kiln at high temperatures, causing a chemical reaction with the silica in the clay that creates a glossy, textured surface resistant to moisture and heat. Blackware pottery undergoes a reduction firing process where oxygen is limited, and organic materials in the kiln produce carbon that impregnates the clay, resulting in a matte black finish. These distinct manufacturing processes impact the cookware's durability and thermal properties, with salt-glazed pots offering enhanced heat resistance and blackware pots retaining heat evenly due to their dense, carbon-infused structure.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a durable, glass-like surface with a slightly textured, glossy finish due to sodium vapor reacting with the clay body, making them highly resistant to liquid absorption and thermal shock. Blackware, created through a reduction firing process that limits oxygen, results in a matte to semi-gloss black surface with a smoother texture and excellent heat retention, ideal for even cooking. While salt-glazed pots emphasize robustness and chemical resistance, blackware pots are prized for their unique aesthetic and enhanced thermal properties, influencing both functionality and visual appeal in cooking applications.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Salt-glazed ceramic cooking pots exhibit excellent heat retention due to their dense, vitrified surface, allowing slow and even heat distribution ideal for simmering and slow cooking. Blackware pots, often made from fired clay with a smoky finish, typically have more porous surfaces, which may result in quicker heat loss but provide more responsive temperature changes for sauteing or quick cooking. Choosing between salt-glazed ceramic and blackware depends on whether consistent heat retention or rapid heat modulation is prioritized in cooking methods.
Impact on Food Flavor and Cooking Results
Salt-glazed ceramic cooking pots impart a subtle mineral note to food due to the high-temperature salt firing process, enhancing the complexity of flavors while providing excellent heat retention and even cooking. Blackware pots, traditionally made by smoke-firing, contribute a smoky, earthy aroma that deepens the taste profile and maintains moisture for tender, flavorful dishes. Both materials offer unique culinary benefits, with salt-glazed ceramics favoring crisp textures and balanced heat distribution, whereas blackware excels at slow, moist cooking that intensifies savory flavors.
Durability and Resistance to Thermal Shock
Salt-glazed ceramics offer exceptional durability due to their dense, glassy surface, which enhances resistance to moisture and stains, making them ideal for cooking pots. However, they may be more susceptible to thermal shock compared to blackware, which is known for its resilience to rapid temperature changes thanks to its unique firing process that creates micro-porosity. Blackware's ability to withstand sudden heat fluctuations without cracking makes it a preferred choice for cookware exposed to direct flame or quick heating and cooling cycles.
Safety and Chemical Leaching Concerns
Salt-glazed ceramics create a durable, glassy surface by fusing salt into the clay during high-temperature firing, which reduces porosity and limits chemical leaching, making them generally safe for cooking. Blackware pottery, traditionally fired in a reduced oxygen environment, often lacks this vitrified glaze, increasing the risk of absorbing and releasing contaminants, especially if untreated or not food-safe certified. Both types must be verified for lead and cadmium content to ensure safety, as older or decorative pieces may pose higher chemical leaching risks during cooking.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a durable, glass-like surface that resists sticking and stains, making cleaning relatively straightforward with mild detergents and gentle scrubbing. Blackware pots, typically made from high-fired clay and polished to a smooth finish, require seasoning and careful handwashing to maintain their natural non-stick properties and prevent cracking. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh abrasives and dishwashers, but salt-glazed ceramics often have an edge in ease of maintenance due to their vitrified, semi-nonporous glaze.
Which Is Better for Cooking Pots?
Salt-glazed ceramic cooking pots offer a durable, non-porous surface resistant to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for slow cooking and retaining heat evenly. Blackware pots, typically crafted from fine-grained clay and fired at lower temperatures, provide excellent thermal shock resistance and a natural non-stick surface, but may require more careful seasoning and handling. For consistent heat retention and chemical durability, salt-glazed ceramics are better suited for cooking pots, while blackware excels in slow, gentle cooking with a rustic finish.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Blackware for Cooking Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com