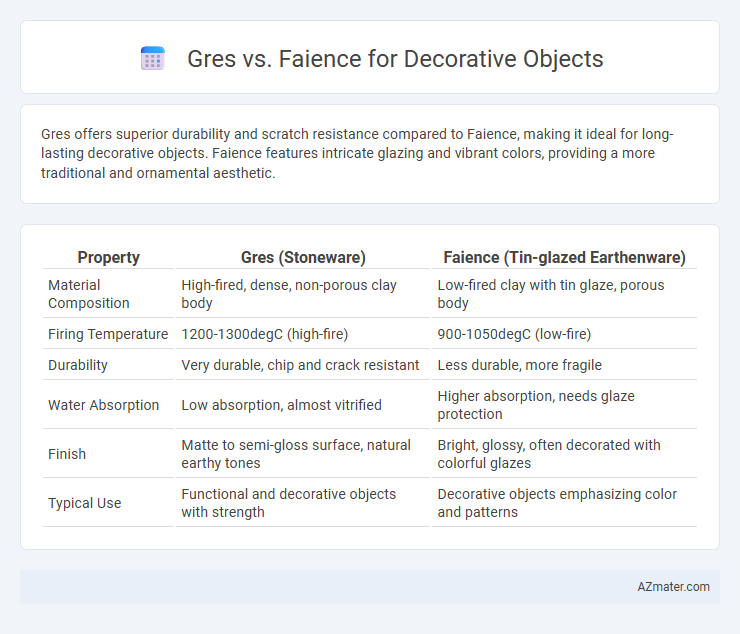
Gres offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to Faience, making it ideal for long-lasting decorative objects. Faience features intricate glazing and vibrant colors, providing a more traditional and ornamental aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres (Stoneware) | Faience (Tin-glazed Earthenware) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-fired, dense, non-porous clay body | Low-fired clay with tin glaze, porous body |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC (high-fire) | 900-1050degC (low-fire) |
| Durability | Very durable, chip and crack resistant | Less durable, more fragile |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption, almost vitrified | Higher absorption, needs glaze protection |
| Finish | Matte to semi-gloss surface, natural earthy tones | Bright, glossy, often decorated with colorful glazes |
| Typical Use | Functional and decorative objects with strength | Decorative objects emphasizing color and patterns |
Understanding Gres and Faience: Definitions
Gres, a dense and durable stoneware fired at high temperatures, is known for its strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for functional and decorative objects. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, features a porous ceramic body covered with a smooth, colorful glaze that allows for detailed artistic decoration. Understanding these definitions highlights gres's robustness versus faience's decorative appeal, crucial for selecting materials in decorative object design.
Key Differences Between Gres and Faience
Gres, a dense and durable stoneware, is fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a non-porous, sturdy material ideal for functional and decorative objects. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, is fired at lower temperatures and often features vibrant, colorful glazes with a slightly porous body. Key differences between Gres and Faience include their firing temperature, density, porosity, and the visual finish, with Gres being more robust and matte while Faience specializes in glossy, decorative surfaces.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Gres, a dense and vitrified stoneware, is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, fired at high temperatures around 1200-1300degC, resulting in a durable and non-porous material ideal for heavy-use decorative objects. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, utilizes a clay body coated with an opaque white glaze made from tin oxide, and is fired at lower temperatures between 900-1100degC, producing a glossy, colorful surface suited for intricate decorative designs. The manufacturing process of gres emphasizes high-temperature firing and durability, while faience focuses on glazing techniques that allow for vivid artistic detailing and a more delicate finish.
Aesthetic Qualities: Texture and Finish
Gres features a dense, stone-like texture with a matte or slightly rough finish, providing a natural, earthy appearance ideal for minimalist decorative objects. Faience, known for its smooth, glossy glaze, offers vibrant colors and intricate patterns that enhance ornamental appeal and create a luxurious visual effect. The contrasting finishes make gres suitable for rustic, contemporary designs, while faience excels in classic, decorative art pieces requiring bright, polished surfaces.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres, a dense and vitrified ceramic, offers superior durability and resistance to chipping compared to faience, which is more porous and prone to cracking under impact. The high firing temperature of gres results in increased strength, making it ideal for decorative objects subjected to frequent handling or outdoor display. Faience, while appealing for its vibrant glazes, generally requires careful placement to avoid damage due to its lower mechanical resistance.
Design Versatility for Decorative Objects
Gres offers exceptional design versatility for decorative objects due to its dense, durable composition, allowing intricate textures and detailed sculptural forms. Faience's glazed surface provides vibrant color options and a glossy finish, enhancing aesthetic appeal but may limit delicate design execution compared to gres. Choosing between gres and faience depends on the desired balance between detailed craftsmanship and vivid, colorful presentation in decorative pieces.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Gres offers exceptional durability and water resistance, making it highly suitable for both indoor and outdoor decorative objects exposed to varying weather conditions. Faience, while admired for its intricate glaze and vibrant colors, is more fragile and better suited for indoor use where it can be protected from moisture and temperature fluctuations. Choosing gres ensures long-lasting performance outdoors, whereas faience excels in decorative indoor settings with controlled environments.
Cost Considerations: Gres vs Faience
Gres typically costs more than faience due to its denser composition and higher firing temperatures, making it more durable and suitable for floor tiles and heavy-use items. Faience, being more porous and lighter, is generally more affordable but less resistant to wear and moisture, which limits its use for decorative objects in high-traffic areas. Budget-conscious buyers often choose faience for decorative purposes where cost savings outweigh the need for extreme durability.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Gres tiles offer high durability and are resistant to scratches, stains, and moisture, making them ideal for low-maintenance decorative objects that require minimal cleaning, typically just a damp cloth and mild detergent. Faience, with its porous and glazed surface, demands more careful maintenance to prevent chipping and staining, requiring gentle cleaning with non-abrasive cleaners and avoiding harsh chemicals. Choosing gres ensures easier upkeep and longer-lasting aesthetics for decorative pieces in busy or high-traffic environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Decorative Art Pieces
Gres offers superior durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for decorative objects exposed to outdoor or humid environments. Faience boasts vibrant glazes and intricate detailing, perfect for indoor decorative art where aesthetic appeal is paramount. Selecting between gres and faience depends on balancing durability requirements with the desired finish and artistic expression in decorative pieces.
Infographic: Gres vs Faience for Decorative object
 azmater.com
azmater.com