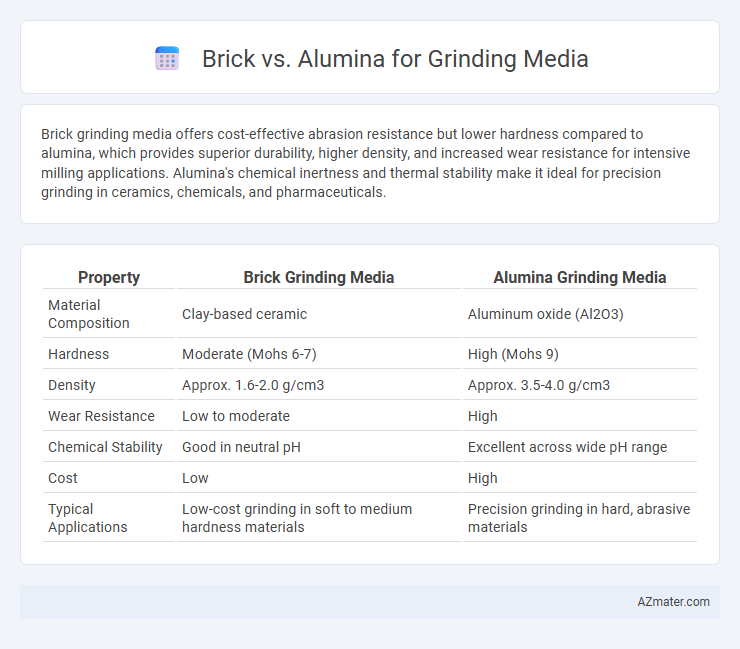
Brick grinding media offers cost-effective abrasion resistance but lower hardness compared to alumina, which provides superior durability, higher density, and increased wear resistance for intensive milling applications. Alumina's chemical inertness and thermal stability make it ideal for precision grinding in ceramics, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick Grinding Media | Alumina Grinding Media |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based ceramic | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Hardness | Moderate (Mohs 6-7) | High (Mohs 9) |
| Density | Approx. 1.6-2.0 g/cm3 | Approx. 3.5-4.0 g/cm3 |
| Wear Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | Good in neutral pH | Excellent across wide pH range |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Typical Applications | Low-cost grinding in soft to medium hardness materials | Precision grinding in hard, abrasive materials |
Introduction to Grinding Media Materials
Grinding media materials such as brick and alumina are essential components in various milling and grinding processes, influencing efficiency and product quality. Brick grinding media offer affordability and moderate hardness, making them suitable for low-impact grinding tasks, while alumina provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and chemical inertness, ideal for high-precision applications. Selecting the appropriate material depends on grinding environment, desired particle size, and material compatibility, impacting operational costs and final product characteristics.
Overview of Brick Grinding Media
Brick grinding media comprises dense clay-based balls known for their high abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness in grinding applications. These media offer moderate hardness and toughness, making them suitable for wet and dry milling processes in industries such as ceramics, chemicals, and mineral processing. Compared to alumina grinding media, bricks deliver less wear resistance but provide economic advantages for less demanding grinding tasks.
Overview of Alumina Grinding Media
Alumina grinding media is highly valued for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for precision grinding applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and ceramics. These media provide superior durability compared to brick media, reducing contamination and increasing grinding efficiency in high-speed mills. The high density and uniform size distribution of alumina grinding balls contribute to consistent particle size reduction and improved product quality.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Brick grinding media typically exhibit lower mechanical strength and higher wear rates compared to alumina, making them less durable in high-stress grinding applications. Alumina grinding media possess superior hardness and fracture toughness, resulting in enhanced resistance to abrasion and impact during milling processes. This increased mechanical strength of alumina prolongs service life and improves grinding efficiency in industrial milling environments.
Wear and Durability Analysis
Alumina grinding media exhibit superior wear resistance and durability compared to brick media, owing to their higher hardness and chemical stability, which significantly reduces abrasion and contamination in milling processes. The dense and consistent microstructure of alumina ensures prolonged service life and enhanced grinding efficiency, especially in high-impact and high-temperature applications. In contrast, brick media tend to wear faster due to their porous nature and lower mechanical strength, leading to increased maintenance costs and potential process interruptions.
Chemical Resistance Properties
Brick grinding media exhibit moderate chemical resistance, suitable for use with mildly abrasive and neutral pH materials, but may degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis. Alumina grinding media offers superior chemical resistance, maintaining structural integrity in aggressive chemical environments including highly acidic and alkaline conditions. Due to its high purity and inert composition, alumina minimizes contamination risk and extends equipment lifespan in corrosive processing applications.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Brick grinding media generally offer lower initial costs compared to alumina, making them an economical choice for budget-sensitive operations. Alumina grinding media, while more expensive upfront, provide higher durability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and overall maintenance costs. The cost efficiency of alumina is particularly advantageous in high-wear applications where its superior hardness minimizes downtime and operational expenses.
Application Suitability: When to Use Brick vs Alumina
Brick grinding media offers cost-effective performance and is best suited for grinding less abrasive materials like cement clinker and minerals with low hardness. Alumina grinding media, with superior wear resistance and high density, excels in applications requiring high precision and durability such as fine ceramic powders and pigment grinding. Selection depends on material hardness, desired product fineness, and abrasion intensity in the grinding process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brick grinding media, typically made from natural clay and shale, offer a lower environmental footprint due to their biodegradability and lower energy consumption in production. Alumina grinding media, composed of synthetic aluminum oxide, require intensive energy and resource extraction, resulting in higher carbon emissions and non-renewable raw material usage. Sustainable grinding choices favor brick media for reducing ecological harm and promoting circular material cycles in mineral processing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Grinding Media
Brick grinding media offer cost-effective abrasion resistance but may wear faster in high-intensity milling environments. Alumina grinding media provide superior hardness and chemical inertness, resulting in longer service life and reduced contamination in precision applications. Selecting the right grinding media depends on balancing factors such as material hardness, chemical compatibility, milling efficiency, and overall operational costs.
Infographic: Brick vs Alumina for Grinding Media
 azmater.com
azmater.com