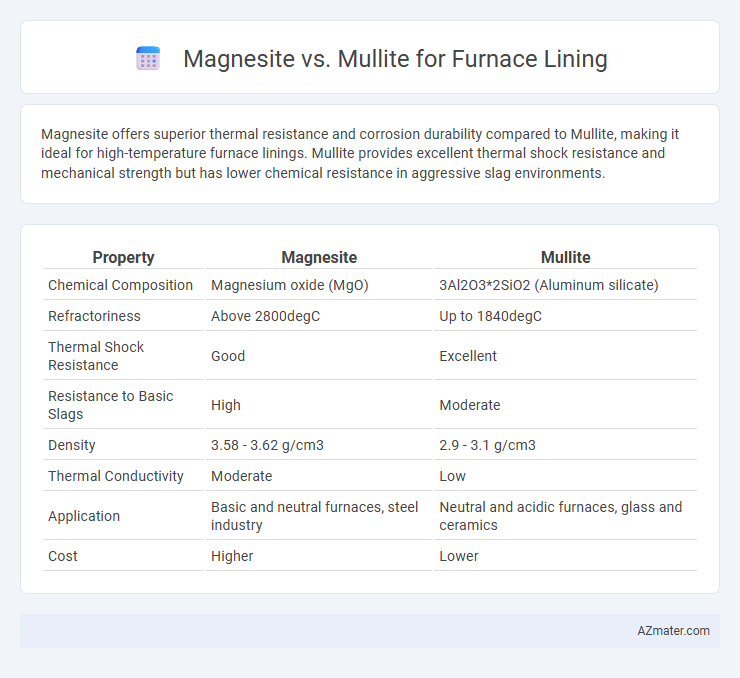
Magnesite offers superior thermal resistance and corrosion durability compared to Mullite, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength but has lower chemical resistance in aggressive slag environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnesite | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Magnesium oxide (MgO) | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Aluminum silicate) |
| Refractoriness | Above 2800degC | Up to 1840degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Basic Slags | High | Moderate |
| Density | 3.58 - 3.62 g/cm3 | 2.9 - 3.1 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate | Low |
| Application | Basic and neutral furnaces, steel industry | Neutral and acidic furnaces, glass and ceramics |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials such as magnesite and mullite play a critical role in high-temperature industrial processes by providing thermal insulation and chemical resistance. Magnesite, primarily composed of magnesium carbonate, offers excellent refractoriness and resistance to basic slags, making it ideal for steelmaking furnaces. Mullite, an alumino-silicate mineral with exceptional thermal shock resistance and low thermal conductivity, is preferred in applications requiring durability against acidic slags and thermal cycling.
Overview of Magnesite: Properties and Applications
Magnesite, primarily composed of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), transforms into magnesium oxide (MgO) upon calcination, offering exceptional refractoriness and thermal conductivity ideal for furnace linings. Its high melting point above 2800degC and excellent corrosion resistance against basic slags make it a preferred refractory material in steelmaking and cement industries. Magnesite's mechanical strength and resistance to chemical attack ensure durability and efficiency in high-temperature applications compared to mullite, which is alumino-silicate based and suited for acidic environments.
Mullite Explained: Characteristics and Advantages
Mullite, a stable aluminosilicate ceramic with a high melting point around 1840degC, offers excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for furnace linings subjected to rapid temperature fluctuations. Its chemical inertness provides superior corrosion resistance against slag and molten metals compared to magnesite, which is more reactive in acidic environments. Mullite's mechanical strength and durability enhance furnace lifespan while maintaining energy efficiency, crucial for high-temperature industrial applications.
Thermal Stability: Magnesite vs Mullite
Magnesite offers excellent thermal stability with a high melting point around 2852degC, making it highly resistant to slag and corrosion in basic environments. Mullite, with a melting point near 1840degC, provides superior thermal shock resistance and maintains structural integrity at high temperatures in oxidizing conditions. While magnesite is preferred for high-basicity slags in steel furnaces, mullite is favored in applications requiring thermal stability combined with resistance to rapid temperature changes.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Magnesite offers superior chemical resistance against basic slags and alkalis due to its high magnesium oxide content, making it ideal for steel furnace linings. Mullite exhibits excellent resistance to acidic slags and thermal shock because of its high alumina and silica composition, which helps maintain structural integrity in varying conditions. Choosing between magnesite and mullite depends on the specific slag chemistry and operational environment of the furnace.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Magnesite and mullite are widely used refractory materials for furnace linings due to their high mechanical strength and durability. Magnesite exhibits excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it suitable for high-temperature applications with aggressive slag environments. Mullite offers superior mechanical strength at elevated temperatures and exceptional thermal stability, enhancing furnace longevity and reducing maintenance frequency.
Cost Analysis of Magnesite and Mullite Linings
Magnesite linings generally offer lower initial costs compared to mullite due to the abundance and lower processing expenses of magnesite raw materials. Mullite linings, although more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal stability and longer service life, which can reduce overall maintenance and replacement costs. A comprehensive cost analysis should factor in both material price and lifecycle performance to determine the most cost-effective solution for furnace lining applications.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Magnesite refractories offer ease of installation due to their high thermal conductivity and fast drying times, but require strict moisture control during maintenance to prevent spalling. Mullite refractories provide superior thermal shock resistance and dimensional stability, reducing the frequency of repairs, though they demand more precise installation techniques to ensure optimal sintering and bonding. Maintenance of mullite linings involves less frequent shutdowns, as their chemical stability minimizes degradation in aggressive furnace atmospheres compared to magnesite.
Suitability for Different Furnace Types
Magnesite offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability, making it highly suitable for electric arc and basic oxygen furnaces where slag resistance is critical. Mullite, with superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, excels in high-temperature environments such as glass furnaces and metallurgical furnaces requiring frequent temperature cycling. Selection between magnesite and mullite linings depends on specific furnace operating conditions, including slag chemistry and thermal cycling demands.
Choosing the Best Material: Magnesite or Mullite?
Magnesite offers excellent thermal conductivity and high resistance to basic slags, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings in steelmaking applications. Mullite, characterized by superior thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, excels in environments with rapid temperature fluctuations and acidic slag conditions. Selecting between magnesite and mullite depends on the specific furnace operating conditions, such as temperature range, slag composition, and thermal cycling demands.
Infographic: Magnesite vs Mullite for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com