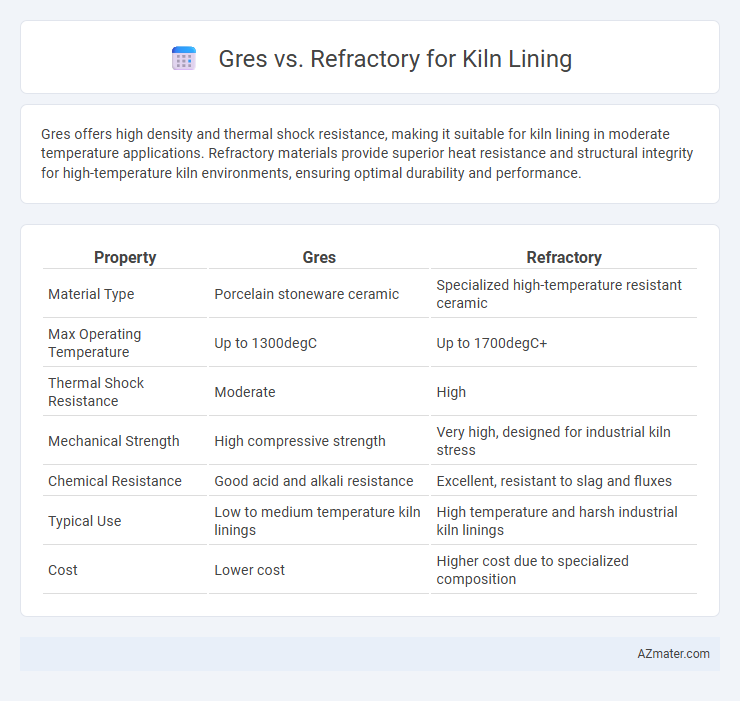
Gres offers high density and thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for kiln lining in moderate temperature applications. Refractory materials provide superior heat resistance and structural integrity for high-temperature kiln environments, ensuring optimal durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porcelain stoneware ceramic | Specialized high-temperature resistant ceramic |
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1700degC+ |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength | Very high, designed for industrial kiln stress |
| Chemical Resistance | Good acid and alkali resistance | Excellent, resistant to slag and fluxes |
| Typical Use | Low to medium temperature kiln linings | High temperature and harsh industrial kiln linings |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized composition |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials are crucial for thermal insulation and structural integrity, with gres and refractory materials serving distinct roles. Gres, a dense, vitrified ceramic, offers excellent abrasion resistance and thermal shock absorption, ideal for moderate temperature zones. Refractory materials, composed of alumina, silica, and other oxides, withstand extreme temperatures above 1600degC, providing superior heat resistance and mechanical strength essential for high-temperature kiln sections.
What is Gres? Characteristics and Uses
Gres, also known as stoneware, is a dense, vitrified ceramic material characterized by high mechanical strength, low porosity, and excellent thermal resistance, making it suitable for kiln lining applications. Its ability to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations and chemical attack allows gres to maintain structural integrity in harsh firing environments. Commonly used in kiln furniture and protective linings, gres enhances durability and energy efficiency in industrial kilns.
Understanding Refractory Materials
Refractory materials used in kiln lining are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical attack, making them essential for maintaining kiln efficiency and longevity. Unlike gres, which are dense, low-porosity ceramic tiles primarily used for decorative and surface applications, refractory bricks and castables contain high alumina or silica content that provides superior insulation and mechanical strength under harsh kiln conditions. Understanding the composition and thermal properties of refractory materials helps in selecting the right lining to optimize heat retention, reduce energy consumption, and prevent structural damage in industrial kilns.
Thermal Resistance: Gres vs Refractory
Gres materials typically exhibit lower thermal resistance compared to refractory linings, limiting their effectiveness in high-temperature kiln environments. Refractory linings are engineered to withstand extreme thermal stresses, providing superior insulation and durability at temperatures exceeding 1400degC. This thermal resistance makes refractory linings essential for maintaining kiln efficiency and longevity under intense heat conditions.
Chemical Durability in Kiln Environments
Gres tiles exhibit superior chemical durability in kiln environments due to their dense, non-porous structure that resists alkalis, acids, and thermal shocks, ensuring long-lasting performance under high-temperature conditions. Refractory materials, while designed to withstand extreme heat, vary in chemical resilience depending on their composition, with some types more susceptible to corrosion from kiln gases and molten slags. Selecting gres for kiln lining enhances resistance to chemical degradation, reducing maintenance costs and extending kiln service life in aggressive firing atmospheres.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Gres materials for kiln lining offer moderate mechanical strength with good resistance to abrasion but typically fall short in withstanding extreme thermal shocks compared to refractory bricks. Refractory linings, especially those made from high-alumina or fireclay bricks, exhibit superior compressive strength and enhanced durability under high-temperature cycling conditions. The choice between gres and refractory depends largely on the kiln's operating temperature and mechanical stress requirements, with refractory linings preferred for environments demanding maximum structural integrity.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Gres lining offers easier installation due to its modular tile system, which enables quick replacements and reduces kiln downtime compared to refractory castable materials that require specialized mixing and curing. Maintenance of gres is typically less labor-intensive because damaged tiles can be individually replaced without extensive kiln cooling, whereas refractory linings demand periodic inspections and full-surface repairs to maintain thermal integrity. Selecting gres or refractory depends on kiln operating conditions, with gres providing cost-effective, rapid maintenance solutions in lower temperature zones and refractory favored for high-temperature durability and resistance.
Cost Analysis: Gres vs Refractory
Gres kiln linings generally offer lower upfront material costs compared to refractory linings but may incur higher maintenance expenses due to lower thermal resistance and durability. Refractory linings, though initially more expensive, provide longer service life and improved thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption and replacement frequency. Overall, a cost-benefit analysis often favors refractory linings for long-term kiln operation efficiency and total cost savings.
Lifespan and Performance in Kiln Operations
Refractory materials typically offer superior lifespan and thermal resistance compared to gres when used for kiln lining, sustaining higher temperatures and intense cycling without significant wear. Gres, a type of dense ceramic, provides good resistance to abrasion and chemical attack but generally falls short in enduring prolonged thermal shock and extreme heat levels found in kiln environments. Optimal kiln performance relies on refractory linings to maintain consistent thermal insulation, reduce energy consumption, and extend operational intervals between maintenance shutdowns.
Choosing the Best Kiln Lining: Gres or Refractory?
Selecting the best kiln lining material involves comparing Gres and refractory bricks based on heat resistance, durability, and thermal conductivity. Gres bricks offer superior thermal shock resistance and are ideal for rapid temperature changes, while refractory bricks provide higher melting points and better structural integrity under extreme temperatures. Optimal kiln performance depends on matching the lining material's properties with the specific firing conditions and operational requirements.
Infographic: Gres vs Refractory for Kiln Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com