Porcelain dinnerware offers superior durability, non-porous surface, and elegant translucency, making it ideal for formal dining and long-term use. Earthenware is more affordable with a rustic appeal but is porous, less durable, and prone to chipping, suitable for casual settings.
Table of Comparison
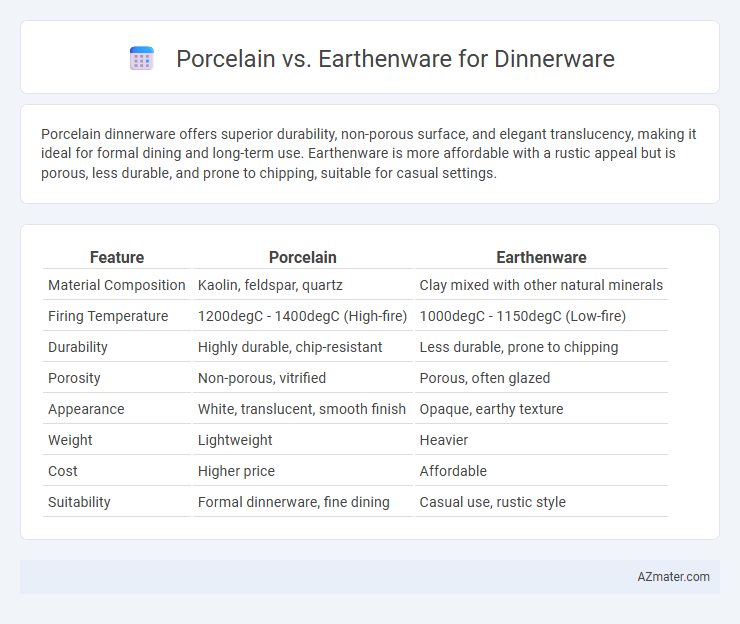
| Feature | Porcelain | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | Clay mixed with other natural minerals |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1400degC (High-fire) | 1000degC - 1150degC (Low-fire) |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Porosity | Non-porous, vitrified | Porous, often glazed |
| Appearance | White, translucent, smooth finish | Opaque, earthy texture |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher price | Affordable |
| Suitability | Formal dinnerware, fine dining | Casual use, rustic style |
Introduction to Porcelain and Earthenware
Porcelain is a highly durable, non-porous ceramic made from kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, renowned for its strength, whiteness, and translucency. Earthenware is a more porous, less durable ceramic fired at lower temperatures, often characterized by its rustic, opaque appearance and thicker body. These fundamental differences influence their suitability for daily use, aesthetic appeal, and maintenance in dinnerware applications.
Material Composition: What Sets Them Apart
Porcelain is crafted from a refined mixture of kaolin clay and fired at high temperatures, yielding a dense, non-porous, and highly durable surface ideal for fine dinnerware. Earthenware consists of more porous clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a softer, more porous finish that requires glazing to prevent liquid absorption. The key distinction lies in porcelain's vitrification process, which enhances strength and translucency, whereas earthenware remains more brittle and opaque.
Appearance and Aesthetic Qualities
Porcelain dinnerware is prized for its smooth, translucent surface and elegant, bright white finish that reflects light beautifully, enhancing table presentation. Earthenware typically features a more rustic, matte appearance with earthy tones and variations in glaze, delivering a warm and artisanal aesthetic. Porcelain's refined look complements formal dining settings, while earthenware offers a cozy, casual vibe suited for everyday use.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Porcelain dinnerware offers exceptional durability and strength due to its high firing temperature and dense, vitrified composition, making it resistant to chipping and cracking compared to earthenware. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures, is more porous and prone to breakage, requiring careful handling and regular replacement in high-use settings. Its lower density also makes earthenware more susceptible to staining and less suitable for heavy daily use than porcelain.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Porcelain dinnerware is typically lighter and thinner than earthenware due to its fine, dense clay and high firing temperature, which creates a strong, translucent finish. Earthenware is generally heavier and thicker because it is made from coarser clay and fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less durable material. These differences in weight and thickness affect the overall feel, durability, and care requirements of the dinnerware.
Heat Retention and Microwave Safety
Porcelain dinnerware offers superior heat retention due to its dense, non-porous composition, keeping food warmer for longer periods compared to earthenware. Earthenware, being more porous and less dense, cools down faster and is generally less efficient at maintaining food temperature. Porcelain is typically microwave safe and resistant to thermal shock, while earthenware may crack or absorb moisture in microwaves, requiring careful microwave use or avoidance.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Porcelain dinnerware is non-porous, making it highly resistant to stains and easy to clean with just mild soap and water, often dishwasher safe without risk of damage. Earthenware, being porous and more fragile, tends to absorb liquids and stains, requiring gentle hand washing and immediate drying to prevent cracks and discoloration. Regular sealing of earthenware pieces enhances durability and ease of maintenance but porcelain remains the superior choice for hassle-free, low-maintenance dinnerware.
Cost and Value Considerations
Porcelain dinnerware generally commands a higher price due to its durability, non-porous surface, and elegant finish, making it a long-term investment for everyday use and special occasions. Earthenware, while more affordable upfront, tends to be less durable and more prone to chipping, which may lead to more frequent replacements and lower overall value. Evaluating cost against longevity and aesthetic appeal helps consumers choose between the premium expense of porcelain and the budget-friendly nature of earthenware.
Best Uses: Everyday vs. Special Occasions
Porcelain dinnerware is ideal for special occasions due to its high durability, elegant finish, and resistance to chipping and staining, making it suitable for formal dining settings. Earthenware, being more porous and less durable, is best used for everyday meals, offering a rustic aesthetic and affordable option for daily use. Choosing between porcelain and earthenware depends on balancing durability and elegance for special events against practicality and cost-effectiveness for everyday dining.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Porcelain dinnerware, made from refined clay fired at high temperatures, offers greater durability and longer lifespan, reducing waste compared to earthenware which is more porous and prone to chipping. The production of porcelain consumes more energy due to higher kiln temperatures but its extended use can offset this initial carbon footprint over time. Earthenware typically requires less energy to produce but has a shorter lifespan, leading to more frequent replacements and increased environmental impact associated with resource extraction and manufacturing.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Earthenware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com