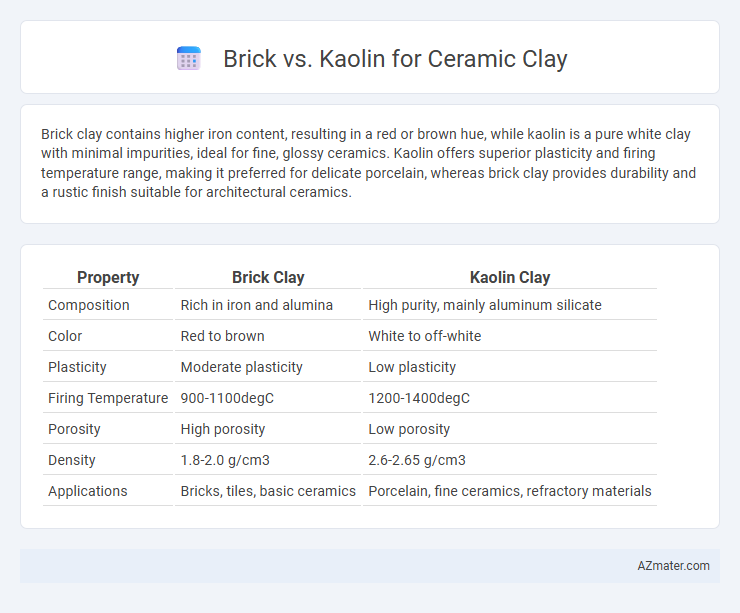
Brick clay contains higher iron content, resulting in a red or brown hue, while kaolin is a pure white clay with minimal impurities, ideal for fine, glossy ceramics. Kaolin offers superior plasticity and firing temperature range, making it preferred for delicate porcelain, whereas brick clay provides durability and a rustic finish suitable for architectural ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Rich in iron and alumina | High purity, mainly aluminum silicate |
| Color | Red to brown | White to off-white |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity | Low plasticity |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1200-1400degC |
| Porosity | High porosity | Low porosity |
| Density | 1.8-2.0 g/cm3 | 2.6-2.65 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Bricks, tiles, basic ceramics | Porcelain, fine ceramics, refractory materials |
Introduction to Ceramic Clay Materials
Brick and kaolin are essential ceramic clay materials used in pottery and construction, each offering distinct properties that influence the final product's texture, strength, and firing temperature. Brick clay typically contains higher amounts of iron oxide and alumina, providing durability and reddish hues after firing, making it ideal for structural ceramics and tiles. Kaolin, known for its high purity and whiteness due to low impurities and minimal iron content, is favored in fine porcelain and high-quality ceramics where smooth texture and translucency are desired.
Composition of Brick Clay
Brick clay is primarily composed of a higher concentration of iron oxide, alumina, and silica, giving it a coarser texture and a natural red or brown hue suitable for structural applications. Kaolin, in contrast, has a purer composition with a higher percentage of kaolinite clay minerals, making it finer, whiter, and more refractory for fine ceramics. The mineralogy and particle size distribution in brick clay affect its plasticity and firing temperature, distinguishing it from the smoother, less impure kaolin used in porcelain production.
Properties of Kaolin Clay
Kaolin clay exhibits fine particle size, high purity, and excellent plasticity, making it ideal for porcelain and high-quality ceramics. Its low iron content ensures a bright white fired color, enhancing the aesthetics of ceramic products. The strong refractory properties of kaolin allow it to withstand high temperatures without deformation or melting, differentiating it from brick clay which contains more impurities and has lower firing strength.
Key Differences: Brick vs Kaolin
Brick clay contains higher iron and alumina content, giving it a reddish color and making it suitable for sturdy, heat-resistant building materials. Kaolin clay, primarily composed of pure white alumina silicate, offers superior plasticity and whiteness, ideal for fine ceramics and porcelain production. The key difference lies in their mineral purity and firing temperature, with kaolin requiring higher temperatures for vitrification and yielding a smoother, more refined finish compared to the coarser texture of brick clay.
Workability in Ceramic Production
Brick clay typically contains higher amounts of iron and sand, resulting in a coarser texture that reduces plasticity and makes it harder to shape compared to kaolin. Kaolin, also known as china clay, is highly refined with a smooth, fine particle size that provides excellent workability, allowing for precise molding and detailed ceramic production. The superior plasticity and purity of kaolin enhance the forming process and reduce cracking during drying and firing stages.
Firing Temperatures and Effects
Brick clay typically fires at lower temperatures around 900-1100degC, resulting in a more porous and less vitrified ceramic body suitable for structural applications. Kaolin, with a higher purity and firing range between 1200-1400degC, produces a denser, more vitrified, and white-fired ceramic ideal for porcelain and fine ceramics. The higher firing temperature of kaolin enhances hardness and translucency while brick clay's lower firing maintains greater plasticity and earthy texture.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Kaolin clay offers superior strength and durability compared to brick clay due to its high purity and fine particle size, which result in a dense and stable ceramic structure. Brick clay contains more impurities like iron oxides that can weaken the final product's hardness and reduce resistance to cracking over time. Kaolin-based ceramics exhibit higher thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them more durable for high-stress applications.
Application Suitability: Brick vs Kaolin
Brick clay, rich in iron oxide, is ideal for producing sturdy, dense ceramics with a characteristic reddish hue, making it suitable for construction materials and rustic pottery. Kaolin, a pure white clay composed mainly of kaolinite, is prized for fine porcelain and high-quality ceramics due to its smooth texture, whiteness, and excellent plasticity. Choosing between brick and kaolin depends on desired ceramic properties: durability and color for brick clays versus translucency and finesse for kaolin-based ceramics.
Cost Considerations of Each Clay
Brick clay tends to be more cost-effective due to its abundant availability and lower processing requirements, making it a popular choice in large-scale ceramic production. Kaolin, known for its purity and fine particle size, generally incurs higher costs because of more intensive refining processes and limited geographic deposits. Manufacturers often weigh the budget constraints against the desired quality, as kaolin's superior whiteness and plasticity justify its premium price in high-end ceramics.
Choosing the Best Clay for Your Project
Brick clay contains higher iron content, giving ceramics a reddish hue and excellent plasticity for hand-building projects, while kaolin is prized for its purity, whiteness, and fine particle size, making it ideal for high-fire porcelain and detailed wheel throwing. Selecting the best clay depends on the desired finish and firing temperature: brick clay works well for rustic, low- to mid-fire pottery, whereas kaolin thrives in high-fired, delicate ceramics requiring smooth texture and bright white coloration. Consider factors such as shrinkage rate, firing temperature, and end-use aesthetics to choose between brick clay's durability and earthy tones or kaolin's translucency and refined surface.
Infographic: Brick vs Kaolin for Ceramic Clay
 azmater.com
azmater.com