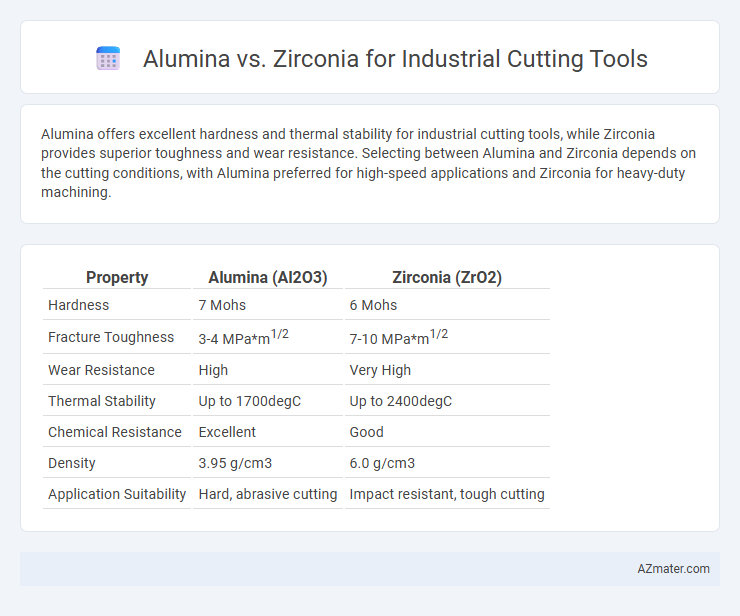
Alumina offers excellent hardness and thermal stability for industrial cutting tools, while Zirconia provides superior toughness and wear resistance. Selecting between Alumina and Zirconia depends on the cutting conditions, with Alumina preferred for high-speed applications and Zirconia for heavy-duty machining.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Zirconia (ZrO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 7 Mohs | 6 Mohs |
| Fracture Toughness | 3-4 MPa*m1/2 | 7-10 MPa*m1/2 |
| Wear Resistance | High | Very High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1700degC | Up to 2400degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Density | 3.95 g/cm3 | 6.0 g/cm3 |
| Application Suitability | Hard, abrasive cutting | Impact resistant, tough cutting |
Introduction to Alumina and Zirconia Cutting Tools
Alumina cutting tools, made from aluminum oxide, are renowned for their excellent hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making them ideal for machining ferrous metals. Zirconia cutting tools, composed of zirconium dioxide, offer superior toughness and fracture resistance, suitable for high-impact and high-speed cutting operations. Both materials provide durable solutions with distinct properties tailored to specific industrial cutting applications.
Key Material Properties: Alumina vs Zirconia
Alumina offers high hardness and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools requiring durability and precision. Zirconia provides superior fracture toughness and thermal shock resistance, enhancing tool longevity under severe cutting conditions. The choice between alumina and zirconia hinges on balancing hardness with toughness to optimize performance for specific industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Comparison
Alumina cutting tools are produced through conventional sintering processes, offering cost-effective manufacturing with good wear resistance, while zirconia tools utilize advanced hot isostatic pressing to achieve superior toughness and fracture resistance but at a higher production cost. The sintering of alumina enables mass production with lower energy consumption, making it suitable for high-volume applications, whereas zirconia's complex processing demands more precise temperature control and longer cycle times, escalating manufacturing expenses. Cost-wise, alumina tools are generally less expensive upfront, but zirconia's enhanced durability can reduce tool replacement frequency, potentially lowering long-term operational costs in demanding cutting environments.
Mechanical Strength and Toughness
Zirconia exhibits superior mechanical strength and toughness compared to alumina, making it highly suitable for demanding industrial cutting tools that require enhanced resistance to chipping and fracture. Alumina offers lower cost and excellent hardness but lacks the fracture toughness of zirconia, which incorporates transformation toughening mechanisms for improved durability. Choosing zirconia cutting tools results in longer tool life and greater reliability under high-stress machining conditions.
Wear Resistance and Tool Longevity
Alumina exhibits excellent wear resistance due to its hardness and chemical stability, making it suitable for cutting tools exposed to high temperatures and abrasive materials. Zirconia offers superior toughness and fracture resistance, which enhances tool longevity by reducing chipping and breakage under heavy cutting loads. Combining alumina's hardness with zirconia's toughness through composite formulations can optimize wear resistance and extend industrial cutting tool life significantly.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Alumina offers excellent heat resistance with a melting point around 2072degC, making it suitable for high-temperature industrial cutting tools that demand durability under intense heat. Zirconia exhibits superior thermal stability and toughness, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to approximately 2700degC, which enhances cutting performance and tool lifespan in extreme thermal environments. The choice between alumina and zirconia depends on the specific temperature range and wear resistance required for industrial machining applications.
Applications in Industrial Cutting Operations
Alumina is widely used in industrial cutting tools for machining ferrous metals due to its excellent hardness and wear resistance at high temperatures. Zirconia offers superior toughness and fracture resistance, making it ideal for cutting operations involving abrasive materials and interrupted cuts. Both materials enhance tool life and efficiency, with alumina preferred for high-speed cutting and zirconia for heavy-duty, impact-prone applications.
Machining Performance and Surface Finish
Alumina cutting tools offer excellent wear resistance and high hardness, making them suitable for machining abrasive materials while maintaining thermal stability. Zirconia tools provide superior toughness and fracture resistance, enabling enhanced impact performance and longer tool life under intermittent cutting conditions. Surface finish quality is generally finer with zirconia due to its ability to sustain higher cutting speeds and reduced tool chipping, whereas alumina tools produce moderate surface finishes but excel in maintaining dimensional accuracy over extended machining operations.
Pros and Cons: Alumina vs Zirconia Tools
Alumina cutting tools offer excellent hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for machining abrasive materials, but they tend to be brittle and less impact-resistant. Zirconia tools provide superior toughness and fracture resistance with improved thermal stability, enhancing performance in high-stress cutting applications, though they may wear faster under extreme abrasion. The choice between alumina and zirconia depends on the specific industrial cutting conditions, balancing hardness and durability requirements.
Choosing the Right Ceramic Tool for Your Application
Alumina offers excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for machining steels and cast irons, while zirconia provides superior toughness and impact resistance, ideal for high-stress applications and interrupted cuts. Choosing the right ceramic cutting tool depends on the specific machining requirements, material hardness, and cutting conditions to optimize tool life and performance. Understanding the differences in thermal stability and fracture toughness between alumina and zirconia is critical for maximizing efficiency in industrial cutting operations.
Infographic: Alumina vs Zirconia for Industrial Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com