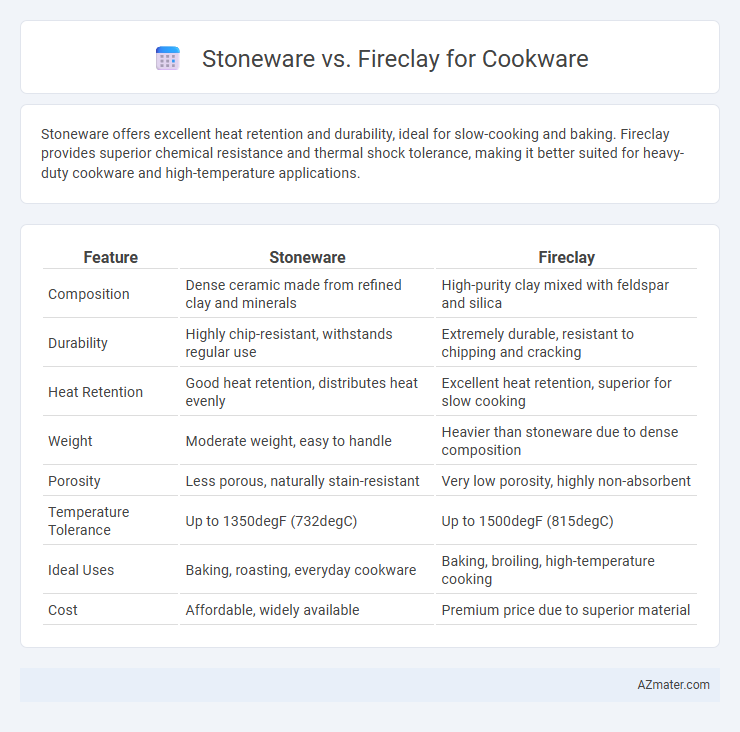
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and durability, ideal for slow-cooking and baking. Fireclay provides superior chemical resistance and thermal shock tolerance, making it better suited for heavy-duty cookware and high-temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stoneware | Fireclay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Dense ceramic made from refined clay and minerals | High-purity clay mixed with feldspar and silica |
| Durability | Highly chip-resistant, withstands regular use | Extremely durable, resistant to chipping and cracking |
| Heat Retention | Good heat retention, distributes heat evenly | Excellent heat retention, superior for slow cooking |
| Weight | Moderate weight, easy to handle | Heavier than stoneware due to dense composition |
| Porosity | Less porous, naturally stain-resistant | Very low porosity, highly non-absorbent |
| Temperature Tolerance | Up to 1350degF (732degC) | Up to 1500degF (815degC) |
| Ideal Uses | Baking, roasting, everyday cookware | Baking, broiling, high-temperature cooking |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available | Premium price due to superior material |
Introduction: Stoneware vs Fireclay Cookware
Stoneware cookware is known for its excellent heat retention and durability, often made from natural clay materials fired at high temperatures. Fireclay cookware is crafted from a dense, non-porous clay fired at even higher temperatures, offering superior chip resistance and a smooth glazed surface. Both types provide versatile cooking options, but fireclay's enhanced strength and impervious finish make it ideal for heavy-duty use in kitchens.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Stoneware cookware is crafted from dense, non-porous clay fired at temperatures between 2150degF and 2330degF, resulting in durable, chip-resistant pieces with natural heat retention. Fireclay cookware is made from a blend of clay and feldspar, fired at higher temperatures of approximately 2400degF to 2500degF, which creates a vitrified, glass-like surface known for its exceptional toughness and resistance to thermal shock. The manufacturing process for stoneware involves slow drying and firing cycles to achieve porosity and strength, whereas fireclay undergoes a more intense vitrification process that enhances its durability and glossy finish.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Stoneware cookware exhibits excellent durability due to its dense, non-porous composition that resists chipping and cracking under high temperatures. Fireclay, composed of refined clay and fired at higher temperatures, offers superior strength and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for heavy-use cookware. Both materials provide robust performance, but fireclay generally delivers enhanced resilience against mechanical stress and thermal expansion.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Conductivity
Stoneware cookware offers excellent heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 482degF (250degC), making it suitable for slow and even cooking. Fireclay cookware boasts even higher heat tolerance, often exceeding 1200degF (650degC), due to its dense, non-porous composition that also enhances thermal shock resistance. While stoneware has moderate thermal conductivity ideal for gradual heat distribution, fireclay's thermal conductivity is lower, ensuring heat retention and steady cooking without rapid temperature fluctuations.
Non-Toxicity and Food Safety
Stoneware and fireclay cookware both prioritize non-toxicity and food safety by being free from harmful chemicals such as lead, cadmium, and PTFE. Stoneware is naturally non-porous and resistant to staining, which helps prevent bacterial growth and ensures safe food preparation. Fireclay, known for its dense composition and glazed finish, offers superior resistance to chipping and cracking, maintaining a safe, non-reactive surface for cooking and serving food.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Variety
Stoneware cookware offers a rustic, earthy aesthetic with natural glaze finishes that enhance kitchen decor through its artisanal charm. Fireclay cookware stands out for its sleek, smooth surfaces and vivid, uniform colors, providing a modern and vibrant design palette. Both materials support diverse styles, but stoneware leans toward traditional looks while fireclay excels in customizable, contemporary designs.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Stoneware cookware features a non-porous, smooth glaze that resists stains and food buildup, making it easier to clean with minimal scrubbing. Fireclay cookware, while highly durable and chip-resistant, has a slightly rougher texture that can trap residue, requiring more thorough cleaning and occasional seasoning. Both materials are dishwasher safe, but stoneware's surface generally demands less maintenance to retain its appearance and performance over time.
Weight and Handling in Daily Use
Stoneware cookware is generally heavier and denser than fireclay, making it sturdy but sometimes cumbersome for everyday handling. Fireclay offers a lighter alternative with excellent thermal shock resistance, enhancing ease of use and maneuverability during cooking tasks. Both materials provide durability, but fireclay's lighter weight reduces fatigue during frequent handling and cleaning.
Cost Differences and Value for Money
Stoneware cookware typically offers a more affordable price point compared to fireclay, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers. Fireclay cookware, while more expensive, delivers superior durability and heat retention, providing exceptional long-term value for serious home chefs. Evaluating cost differences against performance benefits helps buyers make informed decisions based on their cooking needs and investment priorities.
Choosing the Best Option: Stoneware or Fireclay?
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for everyday use and baking, while fireclay provides superior durability and resistance to thermal shock, suited for high-heat cooking and professional kitchens. Stoneware typically features a porous surface that requires seasoning or sealing, whereas fireclay is dense and non-porous, ensuring easier maintenance and longer lifespan. Choosing between stoneware and fireclay depends on your cooking style, maintenance preference, and durability needs for cookware performance.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Fireclay for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com