Porcelain offers superior chemical resistance and smooth surface properties, making it ideal for non-corrosive furnace linings, while refractory brick provides excellent thermal shock resistance and high-temperature stability essential for heavy-duty industrial furnace applications. Selecting between porcelain and refractory brick depends on the furnace operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements.
Table of Comparison
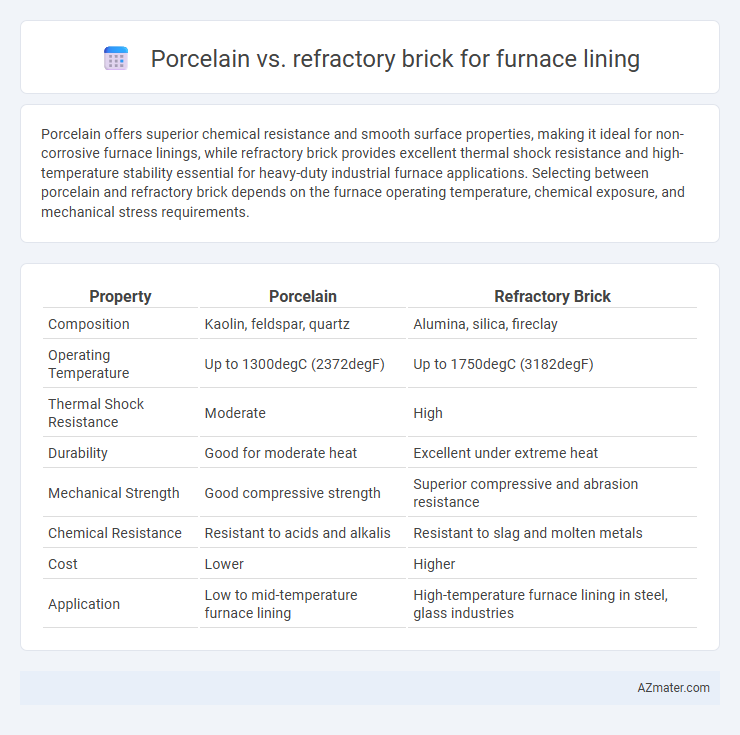
| Property | Porcelain | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | Alumina, silica, fireclay |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1300degC (2372degF) | Up to 1750degC (3182degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good for moderate heat | Excellent under extreme heat |
| Mechanical Strength | Good compressive strength | Superior compressive and abrasion resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Resistant to slag and molten metals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Low to mid-temperature furnace lining | High-temperature furnace lining in steel, glass industries |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a critical role in thermal insulation, heat resistance, and structural integrity during high-temperature operations. Porcelain offers excellent corrosion resistance and smooth surface properties, making it ideal for chemical processing environments, while refractory bricks provide superior thermal stability and mechanical strength for prolonged exposure to intense heat. Selecting between porcelain and refractory bricks depends on specific furnace conditions, such as temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements.
Understanding Porcelain: Properties and Uses
Porcelain, known for its high strength and low porosity, exhibits excellent thermal resistance, making it suitable for furnace lining applications that require durability under extreme heat. Its smooth surface and chemical inertness prevent contamination and corrosion, which enhances furnace longevity and efficiency compared to refractory bricks. Used in high-temperature environments, porcelain offers superior insulation and mechanical stability, ensuring consistent performance in industrial furnaces.
Overview of Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks, also known as firebricks, are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, making them essential for furnace linings in industrial applications. These bricks exhibit high thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical wear. Their composition typically includes alumina, silica, and fireclay, which enhances durability and prolongs furnace lifespan compared to porcelain alternatives.
Thermal Conductivity: Porcelain vs Refractory Brick
Porcelain exhibits lower thermal conductivity compared to refractory brick, making it more effective for insulating furnace linings by minimizing heat loss. Refractory bricks, often composed of alumina and silica, possess higher thermal conductivity, which allows better heat retention and distribution at extreme temperatures. Selecting between porcelain and refractory brick for furnace lining depends on balancing insulation efficiency with the required heat transfer properties for specific industrial applications.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Porcelain exhibits excellent resistance to chemical attack due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it highly durable against acidic and alkaline substances commonly found in furnace environments. Refractory bricks, composed of alumina, silica, and other oxides, offer strong chemical resistance but may vary depending on their specific composition and firing process. High-quality refractory bricks tend to withstand aggressive slags and fluxes better, yet porcelain's superior chemical inertness often results in longer service life within harsh furnace conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain furnace linings offer high mechanical strength with excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them suitable for moderate temperature applications. Refractory bricks generally provide superior durability under extreme heat and aggressive chemical environments due to their dense, heat-resistant composition. Comparing both, refractory bricks withstand higher mechanical stresses and prolonged furnace cycles, ensuring longer service life in industrial high-temperature settings.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Porcelain furnace linings offer relatively straightforward installation due to their pre-formed shapes and lightweight nature, reducing labor time and complexity. Refractory bricks require skilled masonry work to ensure proper alignment and bonding, making installation more labor-intensive but providing superior structural strength and thermal stability. Maintenance of porcelain linings involves careful handling to prevent chipping and cracking, while refractory bricks demand periodic inspection for cracks or spalling, with repair often involving patching or brick replacement to maintain furnace integrity.
Cost Comparison: Porcelain vs Refractory Brick
Porcelain furnace linings typically cost less upfront compared to refractory bricks, making them a budget-friendly option for smaller installations or lower temperature applications. Refractory bricks, though more expensive initially, offer superior durability and thermal resistance, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, lifespan, and replacement frequency, is crucial when choosing between porcelain and refractory brick furnace linings.
Application Suitability in Different Furnace Types
Porcelain bricks, known for their high strength and smooth surface, are best suited for electric and induction furnaces where thermal shock resistance and chemical stability are critical. Refractory bricks, composed of fireclay or alumina, excel in blast furnaces and gas-fired kilns due to their superior ability to withstand extreme high temperatures and aggressive slag corrosion. Choosing the appropriate lining material depends on furnace operating conditions such as temperature range, atmosphere, and mechanical wear.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Furnace Lining
Porcelain offers superior corrosion resistance and smooth surface finish, making it ideal for furnaces exposed to chemical wear. Refractory brick excels in thermal stability and structural strength, suitable for high-temperature operations requiring durable insulation. Selecting the right furnace lining depends on balancing chemical resistance needs with temperature and mechanical durability requirements.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Refractory Brick for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com