Photonic ceramic tiles feature advanced nanostructures that enhance light manipulation and durability, offering superior thermal resistance compared to traditional porcelain tiles. Porcelain tiles, made from fine clay fired at high temperatures, provide excellent hardness and water resistance but lack the innovative photonic properties of photonic ceramics.
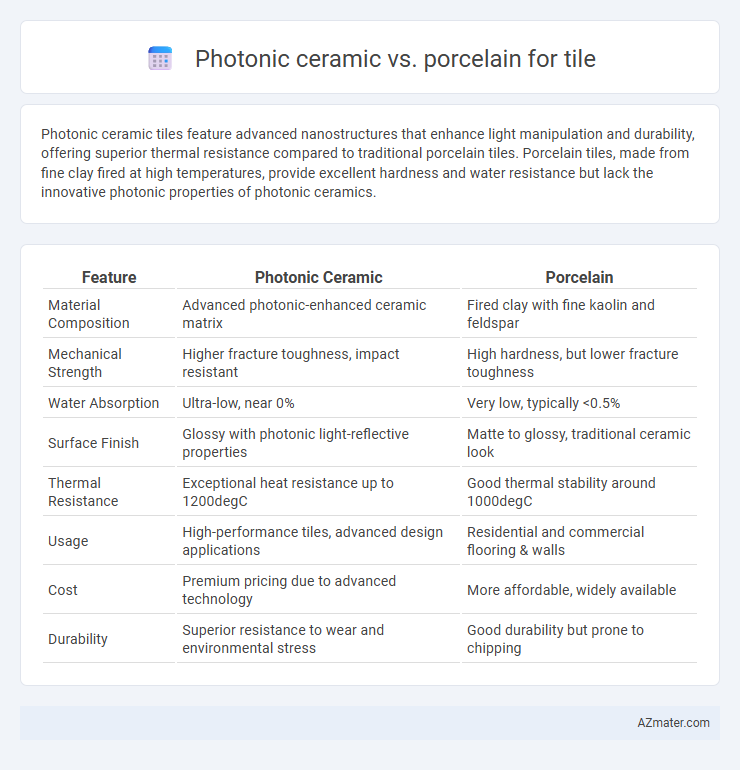
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photonic Ceramic | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced photonic-enhanced ceramic matrix | Fired clay with fine kaolin and feldspar |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher fracture toughness, impact resistant | High hardness, but lower fracture toughness |
| Water Absorption | Ultra-low, near 0% | Very low, typically <0.5% |
| Surface Finish | Glossy with photonic light-reflective properties | Matte to glossy, traditional ceramic look |
| Thermal Resistance | Exceptional heat resistance up to 1200degC | Good thermal stability around 1000degC |
| Usage | High-performance tiles, advanced design applications | Residential and commercial flooring & walls |
| Cost | Premium pricing due to advanced technology | More affordable, widely available |
| Durability | Superior resistance to wear and environmental stress | Good durability but prone to chipping |
Introduction to Photonic Ceramic vs Porcelain Tiles
Photonic ceramic tiles utilize advanced nanotechnology to enhance light reflection and durability, offering superior energy efficiency and longevity compared to traditional porcelain tiles. Porcelain tiles, known for their density, water resistance, and versatility, remain a popular choice for both residential and commercial flooring but lack the enhanced photonic properties of photonic ceramics. The integration of photonic crystals in photonic ceramic tiles provides unique optical features that improve aesthetic appeal and functionality beyond the capabilities of conventional porcelain.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Photonic ceramic tiles utilize advanced photonic materials characterized by engineered dielectric constants, offering enhanced light manipulation properties, whereas porcelain tiles consist primarily of dense, fine-grained clay mixed with silica and feldspar, fired at high temperatures for durability. The manufacturing process of photonic ceramics involves precision layering and sintering to achieve specific optical behaviors, contrasting with the traditional porcelain process of slip casting or dry pressing followed by vitrification. This distinction in material composition and production techniques results in photonic ceramics excelling in optical applications while porcelain remains favored for structural resilience and water resistance in flooring and wall tiles.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Photonic ceramic tiles exhibit superior durability due to their advanced nanostructured composition, offering enhanced resistance to wear, scratches, and impact compared to traditional porcelain tiles. Porcelain tiles, while highly durable and dense with a water absorption rate typically below 0.5%, can be more prone to chipping under extreme pressure or heavy impact. The unique photonic ceramic formulation results in higher flexural strength and improved toughness, making it a preferred choice for high-traffic areas demanding long-term performance.
Design and Aesthetic Versatility
Photonic ceramic tiles offer enhanced design and aesthetic versatility with their ability to replicate natural materials and intricate patterns through advanced nanotechnology, resulting in sharper detail and more vibrant colors than traditional porcelain. Porcelain tiles maintain a classic, timeless appeal with a wide range of finishes and textures, but typically lack the ultra-realistic visual depth found in photonic ceramics. The superior color fastness and surface texture customization of photonic ceramic tiles provide design flexibility for modern, high-end applications seeking both durability and artistic expression.
Water and Stain Resistance Properties
Photonic ceramic tiles exhibit superior water resistance compared to porcelain, thanks to their advanced microstructure that minimizes absorption rates below 0.1%, enhancing durability in wet environments. Porcelain tiles, while also highly water-resistant with absorption rates under 0.5%, may be more prone to staining if not properly glazed or sealed. The unique composition of photonic ceramic ensures enhanced stain resistance by preventing liquid penetration, making it ideal for areas exposed to frequent moisture and spills.
Cost Differences and Value for Money
Photonic ceramic tiles typically cost more than traditional porcelain tiles due to advanced manufacturing processes and enhanced durability features. Porcelain tiles offer excellent value for money with their affordability, high resistance to moisture and wear, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. While photonic ceramic provides superior strength and aesthetic appeal, porcelain remains the cost-efficient option for large-scale or everyday tiling needs.
Installation Process and Maintenance Needs
Photonic ceramic tiles offer a faster installation process due to their lightweight composition and uniform thickness, which simplifies handling and cutting compared to porcelain tiles' denser, harder structure. Maintenance for photonic ceramic is generally easier as it resists stains and requires less frequent sealing, whereas porcelain demands occasional sealing to prevent moisture penetration and maintain durability. Both materials require routine cleaning, but photonic ceramic tiles typically reduce long-term upkeep costs associated with grout and surface wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Photonic ceramic tiles utilize advanced nanomaterials that enable energy-efficient production processes, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional porcelain tiles. Porcelain tiles, while durable and recyclable, generally require higher firing temperatures, leading to greater energy consumption and environmental impact. Opting for photonic ceramic tiles supports sustainability goals through lower resource use and enhanced recyclability.
Popular Applications and Use Cases
Photonic ceramics are widely used in advanced electronics and optical devices due to their superior light transmission and durability, making them ideal for smart home applications and high-performance sensors. Porcelain tiles dominate residential and commercial flooring markets because of their low porosity, strength, and resistance to wear, commonly found in kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor patios. Both materials excel in tailored use cases where specific mechanical and aesthetic properties drive their popularity in construction and technology industries.
Conclusion: Which Tile is Right for You?
Photonic ceramic tiles offer enhanced durability and superior resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for high-traffic or industrial areas. Porcelain tiles excel in aesthetic versatility and moisture resistance, perfect for residential spaces such as bathrooms and kitchens. Choosing between photonic ceramic and porcelain depends on balancing performance needs with design preferences and budget considerations.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com