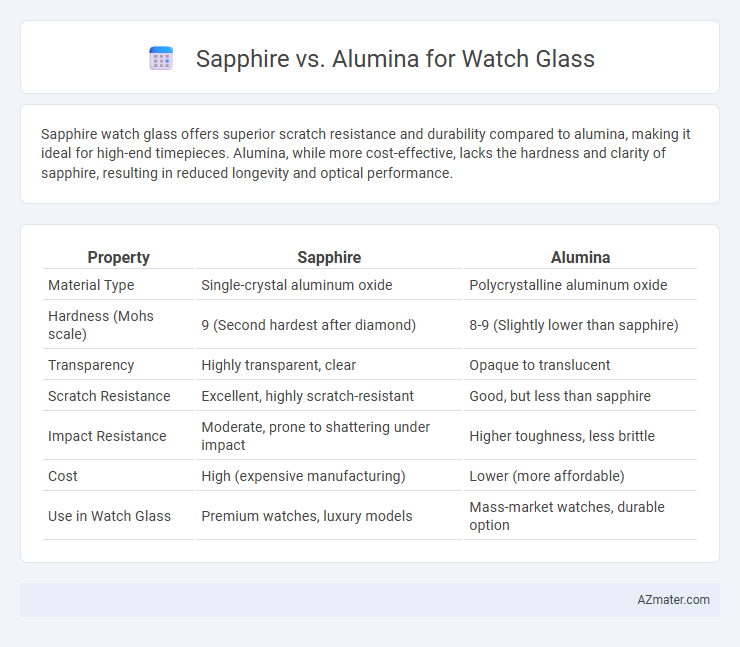
Sapphire watch glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability compared to alumina, making it ideal for high-end timepieces. Alumina, while more cost-effective, lacks the hardness and clarity of sapphire, resulting in reduced longevity and optical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sapphire | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Single-crystal aluminum oxide | Polycrystalline aluminum oxide |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 9 (Second hardest after diamond) | 8-9 (Slightly lower than sapphire) |
| Transparency | Highly transparent, clear | Opaque to translucent |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent, highly scratch-resistant | Good, but less than sapphire |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, prone to shattering under impact | Higher toughness, less brittle |
| Cost | High (expensive manufacturing) | Lower (more affordable) |
| Use in Watch Glass | Premium watches, luxury models | Mass-market watches, durable option |
Introduction to Watch Glass Materials
Sapphire and alumina are two primary materials used for watch glass, valued for their durability and scratch resistance. Sapphire glass, composed of synthetic corundum, offers exceptional hardness with a Mohs scale rating of 9, making it highly resistant to scratches and ideal for luxury and sports watches. Alumina, or aluminum oxide ceramic, provides strong impact resistance and clarity at a lower cost, commonly used in mid-range watches where balance between durability and affordability is essential.
Overview of Sapphire and Alumina
Sapphire watch glass is a synthetic crystal known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly durable for everyday wear. Alumina, or aluminum oxide, serves as the raw material for synthetic sapphire production and is also used in watch glass manufacturing, offering good hardness and transparency but less scratch resistance compared to pure sapphire crystal. Both materials provide clarity and durability, but sapphire glass surpasses alumina in terms of resistance to scratches and impact, making it a preferred choice for premium watch faces.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Sapphire watch glass offers exceptional mechanical strength with a Mohs hardness of 9, making it highly resistant to scratches and impacts compared to alumina, which typically ranks around 8 on the hardness scale. Alumina glass, while still durable, is more prone to scratching and chipping under mechanical stress due to its lower hardness and fracture toughness. The superior hardness and fracture resistance of sapphire make it the preferred choice for high-end watches requiring robust protection against daily wear and mechanical shocks.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Sapphire watch glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its hardness rating of 9 on the Mohs scale, significantly reducing the likelihood of surface abrasions compared to alumina, which rates around 9 but is typically less pure and more prone to micro-scratches. Alumina glass provides better impact resistance, as its slightly lower hardness allows it to absorb shocks and resist shattering more effectively than the more brittle sapphire counterpart. Choosing between sapphire and alumina depends on prioritizing scratch resistance for a pristine look or impact resistance for durability in rough conditions.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Sapphire watch glass offers superior optical clarity and scratch resistance due to its crystalline structure, allowing for excellent light transmission and minimal distortion. Alumina, commonly found in ceramic composites, provides good transparency but can exhibit slight haziness or reduced optical performance compared to sapphire. Sapphire's higher refractive index makes it ideal for premium watch crystals demanding exceptional transparency and durability.
Cost and Availability
Sapphire watch glass offers superior scratch resistance but comes at a higher cost, making it less accessible for budget watches. Alumina, or mineral glass, is more affordable and widely available, though it provides lower durability against scratches and impacts. Manufacturers often balance these materials based on price sensitivity and expected usage conditions.
Manufacturing Processes
Sapphire watch glass is produced through the crystallization of aluminum oxide using the Kyropoulos or Czochralski method, resulting in a highly durable, scratch-resistant transparent crystal. Alumina glass, often derived from fused or sintered aluminum oxide powders, undergoes processes like sintering or melting and rapid cooling, offering cost-effective hardness but lower optical clarity. Manufacturing complexity and cost are higher for sapphire glass due to precise crystal growth, while alumina provides a balance between durability and affordability in watch glass production.
Durability and Longevity
Sapphire glass offers exceptional scratch resistance and hardness, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, which makes it highly durable and ideal for watch faces exposed to daily wear. Alumina, often referred to as synthetic sapphire or sapphire ceramic, provides a balance of toughness and lower cost but is more prone to scratching compared to pure sapphire crystal. Watches featuring sapphire glass typically have longer-lasting clarity and resistance to damage, ensuring superior longevity over alumina-based watch glass.
Common Applications in Watchmaking
Sapphire glass is prized in watchmaking for its exceptional scratch resistance and clarity, commonly used in luxury and high-end watches to protect delicate dials. Alumina, or synthetic sapphire crystal, offers similar hardness but is more cost-effective, making it a popular choice in mid-range watch models requiring durability without premium pricing. Both materials excel in providing transparency and toughness, but sapphire's superior scratch resistance often defines its application in premium timepieces.
Choosing the Best Material for Watch Glass
Sapphire watch glass offers exceptional scratch resistance and clarity, making it ideal for luxury and high-end timepieces requiring durability and a crystal-clear view. Alumina, or aluminum oxide, provides good hardness at a lower cost, suitable for mid-range watches where affordability and moderate protection are priorities. Selecting the best material depends on balancing budget, scratch resistance, and crystal transparency to suit the watch's intended use and market positioning.
Infographic: Sapphire vs Alumina for Watch glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com