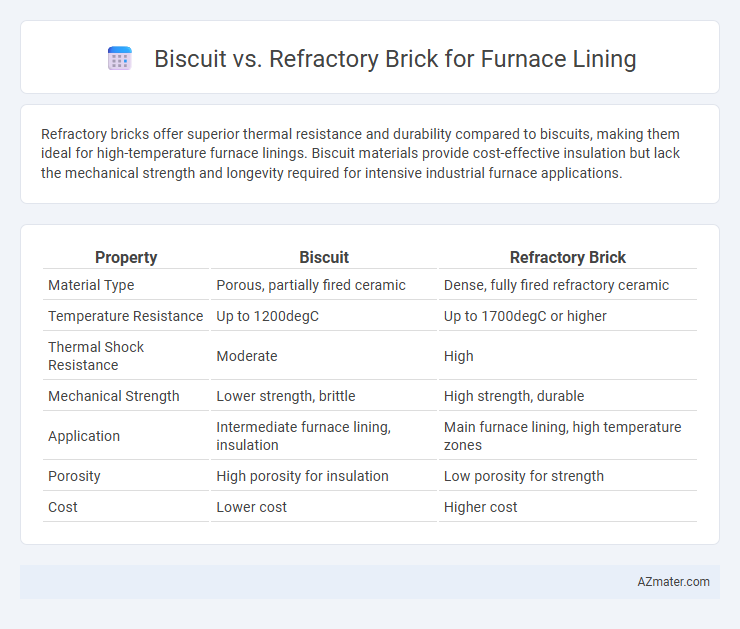
Refractory bricks offer superior thermal resistance and durability compared to biscuits, making them ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. Biscuit materials provide cost-effective insulation but lack the mechanical strength and longevity required for intensive industrial furnace applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biscuit | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, partially fired ceramic | Dense, fully fired refractory ceramic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1700degC or higher |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, brittle | High strength, durable |
| Application | Intermediate furnace lining, insulation | Main furnace lining, high temperature zones |
| Porosity | High porosity for insulation | Low porosity for strength |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials are critical for thermal insulation and structural integrity in high-temperature applications. Biscuit bricks, made from semi-refractory clay, offer moderate heat resistance and are often used in less intense thermal zones. Refractory bricks consist of specialized materials like alumina or silica, providing superior thermal stability and durability essential for extreme furnace environments.
What are Biscuits in Furnace Lining?
Biscuits in furnace lining refer to pre-fired refractory shapes designed to provide structural support and thermal insulation within industrial furnaces. These refractory biscuits are made from high-purity clay or alumina materials, offering excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and thermal shock. Compared to refractory bricks, biscuits allow for easier installation and repair while maintaining high durability under extreme temperatures.
Understanding Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks, including biscuit bricks, are essential materials for furnace lining due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock. Biscuit bricks are pre-fired and partially sintered, offering higher strength and stability before installation, whereas standard refractory bricks are often raw or less dense, requiring in-situ firing. Selecting the appropriate refractory brick depends on specific furnace operating conditions, such as maximum temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure durability and efficiency.
Key Differences: Biscuit vs Refractory Brick
Biscuit and refractory brick differ primarily in composition, density, and thermal resistance, with biscuits being dense, pre-fired ceramic blocks offering superior thermal shock resistance, while refractory bricks are molded and cured ceramic materials designed for structural support and high-temperature durability. Biscuits typically exhibit higher alumina content, enhancing their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes, whereas refractory bricks often prioritize mechanical strength for long-term furnace lining stability. Selection between biscuit and refractory brick depends on specific furnace operating conditions, including temperature fluctuation intensity and mechanical stress requirements.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Biscuit bricks exhibit superior thermal shock resistance, withstanding rapid temperature fluctuations up to 1600degC due to their dense, fine-grained structure, making them ideal for intermittent heating cycles in furnace lining. Refractory bricks, typically composed of fireclay or alumina, offer higher thermal conductivity and stability at continuous high temperatures exceeding 1700degC, ensuring durability under prolonged thermal stress. The choice between biscuit and refractory bricks hinges on the furnace's operational temperature range and thermal cycling frequency, where biscuit bricks excel in thermal shock scenarios, while refractory bricks provide sustained heat retention and structural integrity.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Biscuit bricks, often composed of semi-refractory clay, exhibit moderate durability with a typical lifespan suited for low-heat furnace linings, generally lasting 1 to 3 years under regular thermal stress. Refractory bricks, made from high alumina or silica materials, offer superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, extending furnace lining durability to 5-10 years or more depending on operating conditions. The enhanced thermal resistance and resistance to chemical corrosion in refractory bricks result in significantly longer service life, making them the preferred choice for high-temperature industrial applications.
Installation Methods and Challenges
Biscuit bricks are easier to install due to their lightweight and uniform shape, allowing for quick assembly with minimal mortar use, which reduces downtime during furnace lining maintenance. Refractory bricks, however, require careful mortar application and precise alignment because of their heavier weight and varied sizes, posing challenges in achieving a seamless, durable lining. Installation of refractory bricks demands skilled labor to handle thermal expansion and potential cracking, whereas biscuit bricks offer more flexibility but may compromise on structural strength in high-temperature zones.
Cost Considerations: Biscuit vs Refractory Brick
Biscuit refractory bricks typically offer a lower initial cost compared to traditional refractory bricks due to simpler manufacturing processes and reduced material expenses. However, their shorter lifespan and lower thermal shock resistance may lead to higher maintenance and replacement costs over time. In contrast, refractory bricks, while more expensive upfront, provide greater durability and insulation efficiency, potentially lowering long-term operational expenses for furnace lining applications.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Biscuit bricks offer excellent thermal shock resistance and are ideal for glass furnace crown linings and metallurgical kilns where rapid temperature changes occur, while refractory bricks provide superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance suitable for steelmaking and cement industry furnace walls. Biscuit bricks' lightweight structure enables quick heat absorption and release, enhancing efficiency in energy-sensitive applications, whereas refractory bricks withstand heavy abrasion and corrosive slags in high-temperature environments. Industries such as glass manufacturing, non-ferrous metals, and ceramics prefer biscuit bricks for their thermal properties, whereas refractory bricks dominate in steel production, cement manufacturing, and petrochemical refineries for durability and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Lining Material for Your Furnace
Selecting the right lining material for your furnace depends on temperature tolerance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical stability. Biscuit refractory bricks offer excellent insulation and are suitable for moderate temperatures with good resistance to thermal cycling, while refractory bricks provide superior durability and resistance at higher temperatures in demanding industrial applications. Evaluating the specific operating conditions and desired lifespan of the furnace will guide the optimal choice between biscuit and refractory bricks for efficient and long-lasting furnace lining.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Refractory Brick for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com