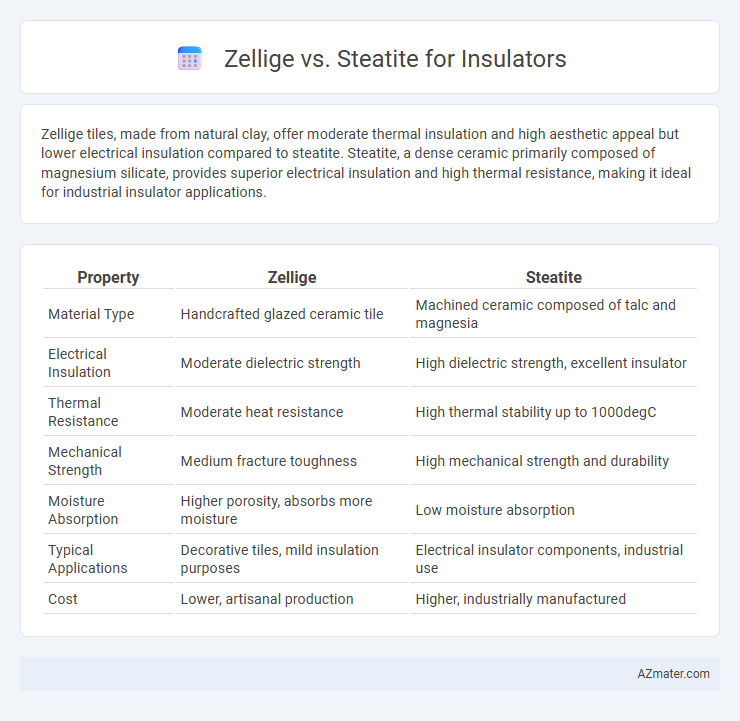
Zellige tiles, made from natural clay, offer moderate thermal insulation and high aesthetic appeal but lower electrical insulation compared to steatite. Steatite, a dense ceramic primarily composed of magnesium silicate, provides superior electrical insulation and high thermal resistance, making it ideal for industrial insulator applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zellige | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Handcrafted glazed ceramic tile | Machined ceramic composed of talc and magnesia |
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate dielectric strength | High dielectric strength, excellent insulator |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High thermal stability up to 1000degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium fracture toughness | High mechanical strength and durability |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher porosity, absorbs more moisture | Low moisture absorption |
| Typical Applications | Decorative tiles, mild insulation purposes | Electrical insulator components, industrial use |
| Cost | Lower, artisanal production | Higher, industrially manufactured |
Introduction to Zellige and Steatite Insulators
Zellige insulators are made from glazed terracotta known for their high dielectric strength and resistance to thermal shock, making them suitable for medium-voltage applications. Steatite insulators consist of dense ceramic material rich in talc, offering superior mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties for high-voltage equipment. Both materials provide effective insulation, with Zellige favored for aesthetic and moderate durability needs while Steatite excels in robustness and high-performance electrical insulation.
Material Composition and Properties
Zellige, a glazed terracotta ceramic composed mainly of natural clay baked at high temperatures, offers excellent electrical insulation, thermal resistance, and aesthetic appeal due to its crystalline glaze surface. Steatite, primarily made of soapstone (magnesium silicate), provides superior mechanical strength, high dielectric strength, and exceptional thermal stability, making it ideal for high-voltage insulators. The key distinction lies in Zellige's decorative ceramic nature with moderate conductivity resistance versus Steatite's dense, robust mineral composition delivering enhanced robustness and electrical insulation performance.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Zellige insulators are handcrafted from natural clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a glossy, irregular finish ideal for decorative applications but with variable thermal properties. Steatite insulators are produced through a precise ceramic sintering process involving powdered talc pressed and fired, creating a dense, mechanically robust material with excellent electrical insulation and consistent performance. The manufacturing of Steatite emphasizes strict control over purity and firing conditions, ensuring superior dielectric strength compared to the artisanal and less uniform production of Zellige insulators.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Zellige displays moderate electrical insulation properties due to its natural ceramic composition, providing reliable resistance to electrical current but with limited high-voltage performance. Steatite, a dense ceramic material rich in magnesium silicate, offers superior dielectric strength and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high-voltage insulator applications. Its low loss tangent and high resistivity ensure minimal electrical leakage and enhanced insulation performance compared to Zellige in demanding electrical environments.
Thermal Resistance Capabilities
Zellige and steatite differ significantly in thermal resistance capabilities, with steatite exhibiting superior thermal insulation due to its high dielectric strength and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulators. Zellige, a glazed terracotta tile, offers moderate thermal resistance but is primarily valued for aesthetic and decorative purposes rather than industrial applications. Steatite's dense, ceramic nature ensures better performance in environments requiring consistent heat resistance and electrical insulation.
Durability and Longevity
Zellige insulators, crafted from glazed terracotta, offer moderate durability but are prone to chipping under mechanical stress, affecting longevity in harsh environments. Steatite insulators, made from a dense ceramic material rich in talc, provide superior mechanical strength and exceptional resistance to thermal shock, ensuring extended service life in high-stress electrical applications. The longevity of steatite insulators typically surpasses that of zellige due to their enhanced toughness and stability under electrical and environmental loads.
Cost and Availability
Zellige tiles typically have higher costs due to their artisanal craftsmanship and limited production, making them less widely available compared to steatite. Steatite, a dense talc-based material, is more affordable and commonly sourced in bulk for insulator applications, ensuring better market availability. The choice between Zellige and Steatite insulators heavily depends on budget constraints and the need for consistent supply in industrial settings.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Zellige tiles offer superior design flexibility with their vibrant colors and handcrafted, irregular shapes that create unique, textured surfaces ideal for artistic insulator designs. Steatite, known for its smooth, uniform finish and natural stone appearance, provides a more traditional aesthetic but less variation in form and color, limiting customization options. Choosing between Zellige and Steatite depends on whether the priority is bold, decorative visual impact or classic, consistent elegance in insulator applications.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Zellige insulators, crafted from natural clay and traditionally fired, offer excellent eco-friendliness due to their biodegradability and minimal environmental impact during production compared to synthetic alternatives. Steatite insulators, made from talc-based ceramic, provide high durability and electrical insulation but involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes that contribute to a larger carbon footprint. Emphasizing sustainability, zellige's use of natural materials and low-energy methods makes it a preferable choice in green building and eco-conscious electrical applications.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Zellige vs Steatite
Zellige offers excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic appeal with its glazed surface, making it ideal for decorative applications that require moderate heat resistance. Steatite, composed primarily of soapstone, provides superior electrical insulation and high-temperature endurance, making it the preferred choice for industrial and electrical insulators. When selecting the right insulator, prioritize steatite for technical performance in high-heat or electrical environments, while zellige suits environments valuing design and moderate insulation.
Infographic: Zellige vs Steatite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com