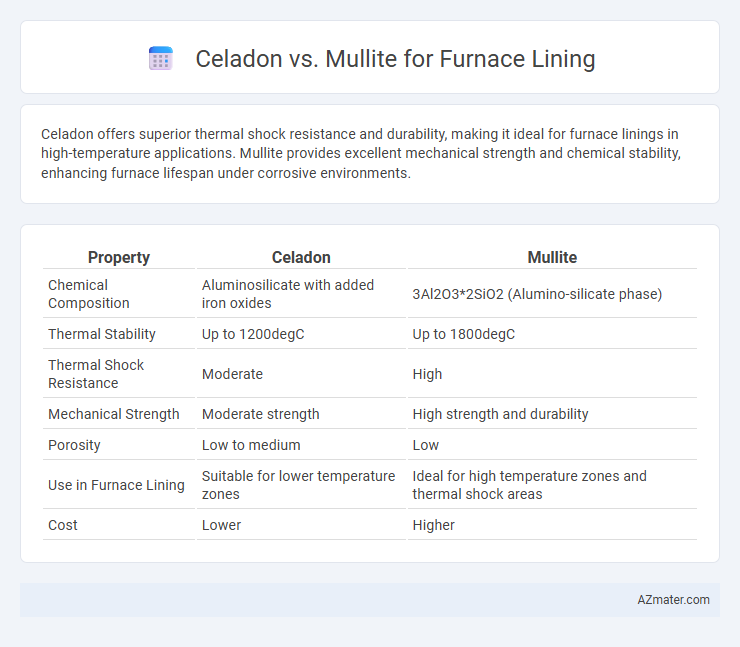
Celadon offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for furnace linings in high-temperature applications. Mullite provides excellent mechanical strength and chemical stability, enhancing furnace lifespan under corrosive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Celadon | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Aluminosilicate with added iron oxides | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumino-silicate phase) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength | High strength and durability |
| Porosity | Low to medium | Low |
| Use in Furnace Lining | Suitable for lower temperature zones | Ideal for high temperature zones and thermal shock areas |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Celadon and mullite are two prominent materials used for furnace lining, each offering unique thermal and mechanical properties crucial for high-temperature applications. Celadon, a type of ceramic glaze, provides moderate thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for less intense heat environments. Mullite, an alumino-silicate compound, excels in thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, making it the preferred choice for industrial furnace linings subjected to extreme temperatures.
Overview of Celadon and Mullite
Celadon refractory is a traditional ceramic material known for its smooth texture and moderate thermal resistance, commonly used in low to medium-temperature furnace linings. Mullite, a high-performance aluminosilicate mineral, offers superior thermal stability, resistance to thermal shock, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace applications. Both materials play crucial roles in furnace linings, with celadon suited for less extreme conditions and mullite preferred in environments requiring enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Celadon refractories primarily consist of high silica (SiO2) content around 70-75%, coupled with alumina (Al2O3) levels near 20-25%, providing excellent resistance to acidic slags and thermal shock. Mullite, with a higher alumina concentration typically between 60-70% and silica around 30-40%, offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability at elevated temperatures. The chemical composition difference impacts their application in furnace linings: Celadon's silica-rich matrix suits acidic environments, while Mullite's alumina dominance enhances durability against basic slags and prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Celadon offers moderate thermal stability suitable for low to medium temperature furnaces, but it softens around 1300degC, limiting its high-temperature performance. Mullite exhibits exceptional thermal stability with a melting point above 1840degC, maintaining structural integrity and resistance to thermal shock in high-temperature furnace linings. Mullite's superior alumina-silicate composition enhances durability and efficiency, making it the preferred choice for demanding thermal environments.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Celadon refractories exhibit moderate resistance to thermal shock due to their high alumina content and fine-grained microstructure, making them suitable for furnace linings subjected to rapid temperature changes. Mullite refractories outperform celadon with superior thermal shock resistance attributed to their stable crystal structure, low thermal expansion, and high creep resistance under cyclic heating and cooling. The enhanced durability of mullite linings reduces maintenance frequency and extends furnace lifespan in environments experiencing frequent thermal cycling.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Celadon offers moderate mechanical strength suitable for low to medium temperature furnace linings, whereas mullite exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. The crystalline structure of mullite provides enhanced durability and stability under thermal cycling, outperforming celadon in longevity and resistance to spalling. Mullite's higher melting point and structural integrity deliver extended service life, reducing maintenance frequency in industrial furnaces.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Celadon refractory materials typically offer lower initial costs compared to mullite for furnace linings due to their simpler production process and widespread availability. Mullite, known for its superior thermal stability and resistance to slag attack, commands higher prices but often requires less frequent replacement, potentially reducing long-term operational expenses. The availability of celadon is generally broader, especially in regions with abundant clay sources, while mullite may face supply constraints due to its specialized manufacturing requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Celadon furnace linings require meticulous installation due to their dense, glassy structure, ensuring minimal porosity and high resistance to chemical corrosion but demanding skilled labor for flawless application. Mullite linings offer easier installation with their refractory ceramic composition, providing excellent thermal shock resistance and durability, leading to lower maintenance frequency and simplified repairs. Maintenance for celadon linings involves careful inspection for cracks and chemical degradation, while mullite linings benefit from routine cleaning and patching to maintain structural integrity and thermal efficiency.
Suitability for Various Furnace Applications
Celadon offers excellent thermal shock resistance and is well-suited for glass furnaces and moderate temperature applications, providing cost-effective durability. Mullite excels in high-temperature stability and chemical inertness, making it ideal for steelmaking, cement kilns, and environments with aggressive slags. When selecting furnace lining materials, mullite is preferred for extreme heat and corrosive conditions, while celadon serves efficiently in less demanding thermal cycles.
Final Recommendation: Celadon vs Mullite
Mullite exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to celadon, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings exposed to rapid temperature changes. Celadon offers better chemical stability and lower thermal conductivity, suitable for applications where corrosion resistance and energy efficiency are prioritized. For furnace lining, selecting mullite is recommended in environments requiring durability under thermal stress, while celadon is preferred for applications emphasizing chemical inertness and insulation.
Infographic: Celadon vs Mullite for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com