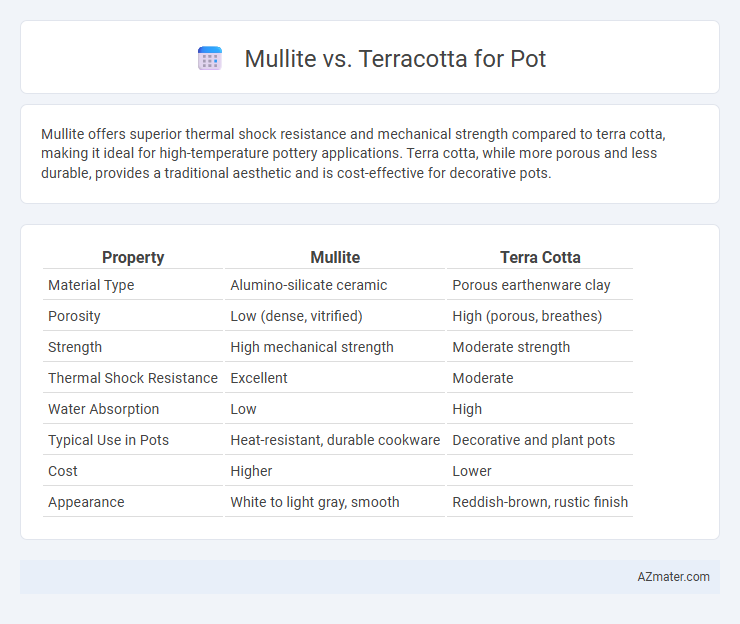
Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to terra cotta, making it ideal for high-temperature pottery applications. Terra cotta, while more porous and less durable, provides a traditional aesthetic and is cost-effective for decorative pots.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mullite | Terra Cotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alumino-silicate ceramic | Porous earthenware clay |
| Porosity | Low (dense, vitrified) | High (porous, breathes) |
| Strength | High mechanical strength | Moderate strength |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Water Absorption | Low | High |
| Typical Use in Pots | Heat-resistant, durable cookware | Decorative and plant pots |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Appearance | White to light gray, smooth | Reddish-brown, rustic finish |
Introduction to Mullite and Terra Cotta
Mullite is a rare aluminum silicate mineral known for its high thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature applications like kiln furniture and advanced ceramics. Terra cotta is a porous, fired clay material traditionally used in pottery and garden pots, valued for its natural aesthetic, breathability, and moisture regulation for plants. While mullite offers superior durability and heat resistance, terra cotta remains popular for its affordability and classic appearance in horticulture.
Composition and Material Properties
Mullite, composed primarily of alumina (Al2O3) and silica (SiO2), exhibits superior thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent mechanical strength compared to terra cotta, which is mainly made from natural clay rich in iron oxide and other impurities. The dense, crystalline structure of mullite provides enhanced resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature applications, whereas terra cotta's porous, more brittle nature limits its durability and heat tolerance. These material properties influence the suitability of mullite for industrial and specialty pottery, while terra cotta remains favored for decorative and traditional pottery due to its ease of shaping and firing.
Manufacturing Processes
Mullite pots are primarily manufactured through high-temperature sintering of kaolin and alumina-based clays, resulting in a dense, thermally stable ceramic with superior mechanical strength. Terra cotta pots use red clay shaped by molding or wheel throwing, then fired at lower temperatures, which gives them a porous structure but less thermal resistance. The firing temperature and raw material composition significantly influence the durability and thermal properties distinctive to each pot type.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Mullite pots exhibit superior strength and durability due to their high alumina content and crystalline structure, enabling them to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress better than terra cotta. Terra cotta, composed primarily of porous clay, is more susceptible to chipping and cracking under impact or extreme temperature changes. The denser, refractory nature of mullite makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting heat resistance and structural integrity.
Porosity and Water Absorption
Mullite exhibits lower porosity and water absorption compared to terra cotta, making it more durable and less prone to water damage in pots. Terra cotta's higher porosity allows for better breathability and moisture regulation for plant roots but increases susceptibility to cracking and water retention. Choosing between mullite and terra cotta pots depends on the balance between durability and breathability needed for specific plant care.
Thermal Resistance and Insulation
Mullite offers superior thermal resistance compared to terra cotta, withstanding temperatures above 1800degC, making it ideal for high-heat applications. Terra cotta, while providing decent insulation, typically withstands temperatures up to 1000degC and has lower thermal shock resistance. The dense, crystalline structure of mullite enables better heat retention and insulation efficiency, enhancing its performance in kiln furniture and refractory pots.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Mullite pots offer superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making them highly suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures. Terra cotta pots, while porous and breathable, are more prone to cracking in freezing conditions and thus perform better indoors or in mild outdoor climates. The low water absorption rate of mullite enhances its weather resistance, whereas terra cotta's high porosity requires more care to prevent damage from frost and prolonged moisture exposure.
Cost and Availability
Mullite pots generally cost more than terra cotta due to their higher temperature resistance and enhanced durability, making them suitable for specialized applications. Terra cotta is widely available and affordable, favored for traditional gardening and decorative uses because of its natural porous quality. The accessibility of terra cotta in most markets contrasts with the more limited supply of mullite, which is primarily found through specialty ceramic suppliers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mullite pots offer superior environmental benefits due to their high thermal stability and recyclability, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing landfill waste. Terra cotta, while biodegradable and made from natural clay, often requires intensive energy during firing and may have a shorter lifespan, leading to more frequent production cycles. Choosing mullite enhances sustainability by combining durability with lower environmental footprints over the product lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Pots
Mullite offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and outdoor pots that face temperature fluctuations. Terra cotta is porous and breathable, promoting healthy root aeration and moisture regulation, which benefits indoor plants and plants requiring well-drained soil. Selecting between mullite and terra cotta hinges on environmental conditions and plant needs, with mullite preferred for robustness and terra cotta favored for natural breathability.
Infographic: Mullite vs Terra cotta for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com