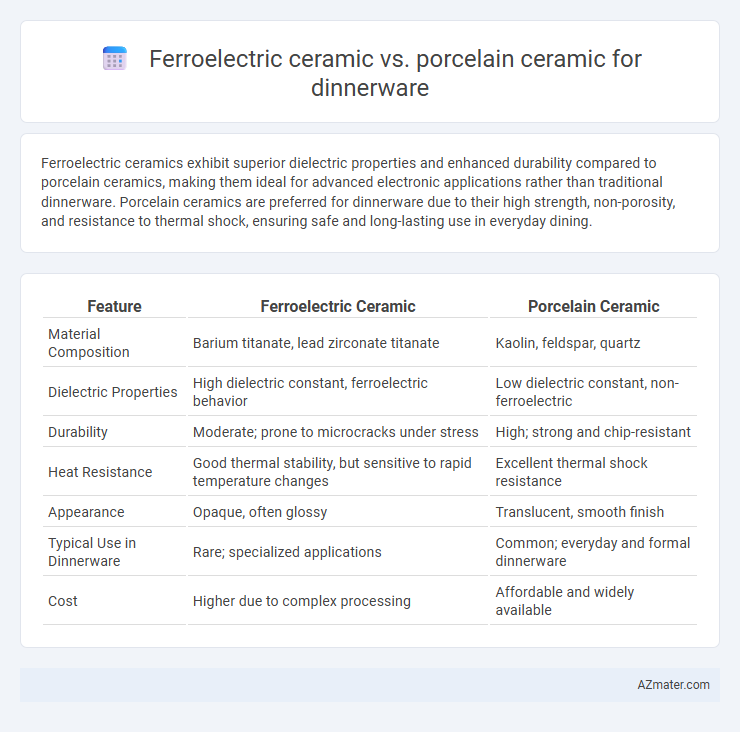
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior dielectric properties and enhanced durability compared to porcelain ceramics, making them ideal for advanced electronic applications rather than traditional dinnerware. Porcelain ceramics are preferred for dinnerware due to their high strength, non-porosity, and resistance to thermal shock, ensuring safe and long-lasting use in everyday dining.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Porcelain Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Barium titanate, lead zirconate titanate | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Dielectric Properties | High dielectric constant, ferroelectric behavior | Low dielectric constant, non-ferroelectric |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to microcracks under stress | High; strong and chip-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Good thermal stability, but sensitive to rapid temperature changes | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Appearance | Opaque, often glossy | Translucent, smooth finish |
| Typical Use in Dinnerware | Rare; specialized applications | Common; everyday and formal dinnerware |
| Cost | Higher due to complex processing | Affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Ceramic Materials in Dinnerware
Ferroelectric ceramic and porcelain ceramic are two distinct materials used in dinnerware, each with unique properties. Porcelain ceramic, known for its durability, smooth texture, and resistance to chipping, is commonly used for elegant and everyday dinnerware. Ferroelectric ceramics, while typically utilized in electronic applications for their electric polarization properties, are less common in dinnerware but offer potential in smart or responsive tableware designs.
Understanding Ferroelectric Ceramics
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by an external electric field, a property not found in porcelain ceramics typically used for dinnerware. These materials are composed of crystalline compounds like barium titanate and lead zirconate titanate, which enable unique dielectric and piezoelectric characteristics, whereas porcelain is primarily alumina and silica-based and prized for its strength and translucency. Understanding ferroelectric ceramics helps in exploring potential applications beyond dinnerware, such as sensors and actuators, while porcelain remains favored for its traditional aesthetic and durability in tableware.
Properties of Porcelain Ceramics
Porcelain ceramics exhibit exceptional hardness, low porosity, and high resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for durable dinnerware. Their fine-grained, glassy texture provides a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and bacterial growth. Compared to ferroelectric ceramics, porcelain offers superior aesthetic appeal and enhanced mechanical strength, ensuring long-lasting and elegant tableware.
Comparison of Electrical Characteristics
Ferroelectric ceramic exhibits spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by an external electric field, making it highly responsive to electric stimuli with high dielectric constants and piezoelectric properties. Porcelain ceramic, on the other hand, is electrically insulating with low dielectric constants and negligible piezoelectric effects, offering stable performance without electrical activity. The electrical characteristics of ferroelectric ceramics are critical in sensor applications, whereas porcelain ceramics prioritize durability and chemical resistance in dinnerware without electrical functionality.
Durability and Strength in Daily Use
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit enhanced durability due to their unique crystal structure, providing superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress compared to porcelain ceramics. Porcelain ceramics, while traditionally strong and chip-resistant, are more prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes and heavy impact in daily use. The ferroelectric properties contribute to improved resilience, making ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware a more robust option for frequent handling and washing.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability and heat resistance due to their intrinsic polarization properties and high Curie temperatures, making them more resilient under thermal stress compared to porcelain ceramics. Porcelain dinnerware, while offering good heat resistance and moderate thermal shock resistance, tends to be more susceptible to cracking under rapid temperature changes due to its lower thermal expansion coefficient. Selecting ferroelectric ceramics for dinnerware applications enhances durability in high-temperature environments, supporting prolonged heat exposure without compromising structural integrity.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Ferroelectric ceramics are not recommended for dinnerware due to potential safety risks from their electrical properties and possible leaching of harmful substances when in contact with food. Porcelain ceramic is widely favored for safety and food compatibility, as it is non-porous, chemically inert, and resistant to staining or absorbing flavors. Its FDA approval and established use in food service ensure that porcelain ceramic dinnerware is safe for daily consumption and free from toxic substances.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Ferroelectric ceramics feature unique dielectric properties allowing for innovative glazing techniques that enhance surface luster and color vibrancy, creating a modern and dynamic aesthetic appeal. Porcelain ceramics offer exceptional translucency and a smooth, refined finish, enabling intricate designs and delicate patterns with high precision. The inherent material flexibility of porcelain supports a broader range of shapes and detailed craftsmanship, making it ideal for classic and elegant dinnerware designs.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware generally costs more due to specialized material properties and limited production, impacting its market availability. Porcelain ceramic is widely more accessible with lower manufacturing costs, making it a popular choice for affordable and durable dinnerware options. Market demand and mass production have stabilized porcelain prices while ferroelectric ceramics remain niche and pricier.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Ceramic Dinnerware
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware offers superior strength and durability due to its unique polarization properties, making it resistant to chipping and thermal shock. Porcelain ceramic excels in elegance and translucency, highly valued for formal dining settings though it tends to be more delicate and prone to cracks under impact. Choosing the right ceramic dinnerware depends on prioritizing functional durability with ferroelectric ceramics or aesthetic appeal and traditional craftsmanship embodied in porcelain ceramics.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Porcelain ceramic for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com