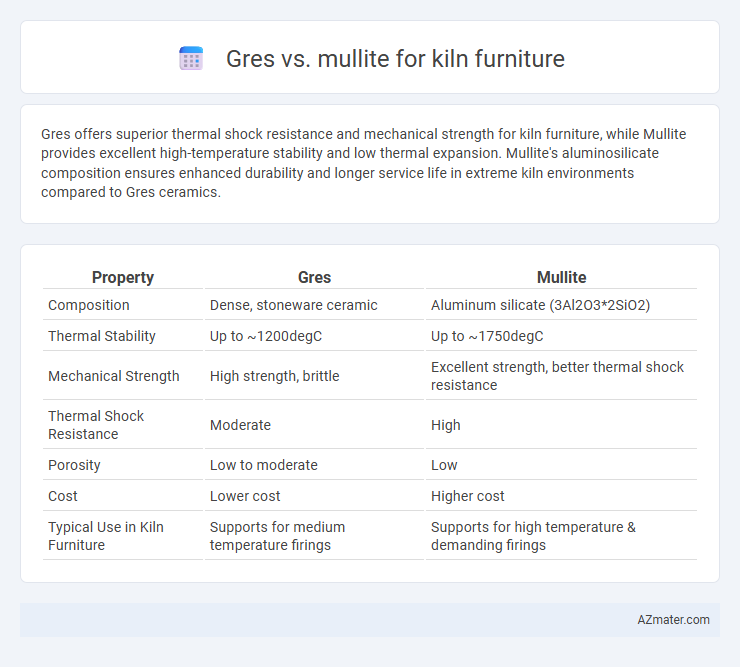
Gres offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength for kiln furniture, while Mullite provides excellent high-temperature stability and low thermal expansion. Mullite's aluminosilicate composition ensures enhanced durability and longer service life in extreme kiln environments compared to Gres ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Dense, stoneware ceramic | Aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to ~1200degC | Up to ~1750degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, brittle | Excellent strength, better thermal shock resistance |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Porosity | Low to moderate | Low |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Use in Kiln Furniture | Supports for medium temperature firings | Supports for high temperature & demanding firings |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Gres and mullite are two primary materials used in kiln furniture, essential for supporting ceramics during firing. Gres, a dense and vitrified stoneware, offers high thermal stability and resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures. Mullite, an alumino-silicate ceramic, excels in thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding high-temperature kiln environments.
What is Gres? Key Characteristics
Gres is a dense, vitrified stoneware ceramic known for its high mechanical strength, low porosity, and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for kiln furniture in high-temperature applications. Its fine-grained and homogeneous structure provides durability and stability under repeated heating and cooling cycles. Gres materials typically exhibit a melting point above 1200degC, supporting longevity and performance in kiln environments.
What is Mullite? Essential Properties
Mullite is a crucial ceramic material in kiln furniture, known for its exceptional thermal stability and high melting point around 1840degC. Its chemical composition primarily includes 3Al2O3*2SiO2, providing excellent resistance to thermal shock, mechanical strength, and low thermal conductivity. These essential properties make mullite superior to gres in high-temperature applications, ensuring durability and performance in kiln environments.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Gres exhibits high thermal stability with a maximum operating temperature around 1250degC, making it suitable for moderate kiln firing processes. Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 1600degC, providing enhanced durability in high-temperature environments. The thermal conductivity of mullite is lower than gres, resulting in better insulation properties and more efficient heat retention during kiln operations.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits superior mechanical strength and higher thermal stability compared to gres, making it more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical wear during repeated firing cycles. Gres, a stoneware ceramic, offers good durability but lacks the high-temperature creep resistance and phase stability that mullite provides, leading to shorter service life under extreme kiln conditions. The enhanced durability of mullite ensures minimal deformation and prolonged lifespan in high-temperature applications, crucial for maintaining kiln efficiency and product quality.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Gres porcelain exhibits high resistance to chemical attack due to its dense, vitrified microstructure, making it suitable for environments exposed to acidic fluxes and alkalis in kiln applications. Mullite, with its inherent alumina-silicate composition, offers superior chemical stability and resistance to molten slags and reactive atmospheres at elevated temperatures. The enhanced resistance of mullite to corrosion and degradation under harsh chemical conditions often results in longer service life for kiln furniture compared to gres materials.
Cost and Availability
Gres kiln furniture offers lower initial costs and wider availability due to its common use and mass production, making it an economical choice for many ceramics operations. Mullite, while more expensive, provides superior thermal stability and longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and potentially lowering long-term expenses. Availability of mullite can be limited and more specialized, impacting upfront procurement time and cost compared to readily available gres options.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Gres kiln furniture offers a shorter lifespan compared to mullite, as mullite withstands higher thermal shock and repeated firing cycles without significant degradation. Mullite requires less frequent maintenance due to its superior resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical wear at temperatures exceeding 1700degC. Gres, while more economical initially, demands more regular inspections and replacements to maintain kiln integrity and performance.
Application Suitability: Gres vs Mullite
Gres offers excellent thermal shock resistance and high mechanical strength, making it suitable for kiln furniture in applications involving rapid temperature changes and heavy load support. Mullite is preferred for high-temperature environments exceeding 1600degC due to its superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, ensuring dimensional integrity under extreme heat. The choice between Gres and Mullite depends on specific kiln operating conditions, with Gres favored for mid-range temperatures and mechanical durability, while Mullite excels in ultra-high-temperature industrial processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Kiln Furniture Material
Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Gres, being more cost-effective, suits lower temperature ranges but may experience faster wear and reduced durability under intense firing conditions. Selecting kiln furniture depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs, where mullite provides enhanced longevity and stability for rigorous ceramic firing processes.
Infographic: Gres vs Mullite for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com