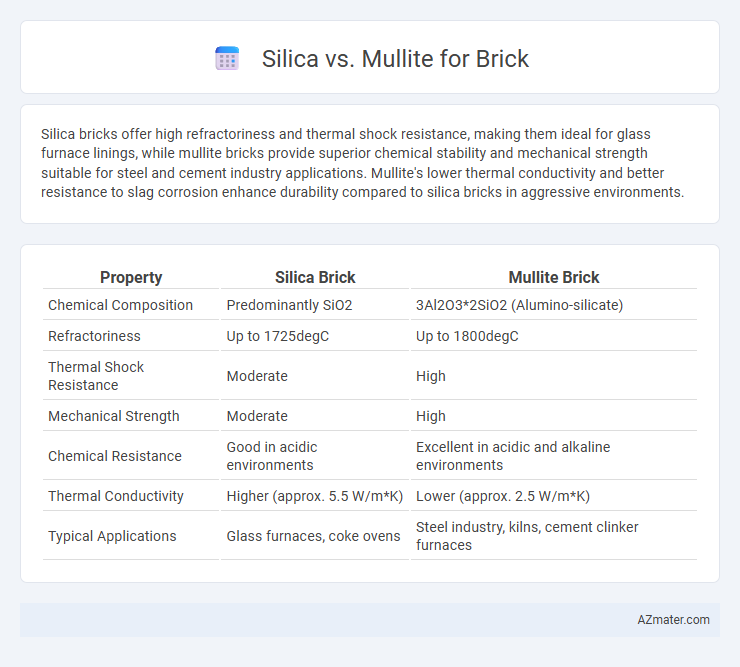
Silica bricks offer high refractoriness and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for glass furnace linings, while mullite bricks provide superior chemical stability and mechanical strength suitable for steel and cement industry applications. Mullite's lower thermal conductivity and better resistance to slag corrosion enhance durability compared to silica bricks in aggressive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Brick | Mullite Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Predominantly SiO2 | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumino-silicate) |
| Refractoriness | Up to 1725degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good in acidic environments | Excellent in acidic and alkaline environments |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher (approx. 5.5 W/m*K) | Lower (approx. 2.5 W/m*K) |
| Typical Applications | Glass furnaces, coke ovens | Steel industry, kilns, cement clinker furnaces |
Introduction to Refractory Materials
Refractory materials such as silica and mullite bricks are essential in high-temperature industrial applications due to their thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Silica bricks, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance and high melting points, making them suitable for coke ovens and glass furnaces. Mullite bricks, containing aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2), offer superior mechanical strength and slag resistance, ideal for steelmaking and cement kilns where durability under aggressive conditions is critical.
Overview of Silica Bricks
Silica bricks are primarily composed of high-purity quartz sand, offering excellent resistance to acidic slags and thermal shock, making them ideal for glass furnaces and coke ovens. Their crystalline structure provides superior refractoriness above 1700degC and good creep resistance under high temperatures compared to mullite bricks. Silica bricks exhibit lower thermal conductivity and high abrasion resistance, which ensures durability in harsh industrial environments.
Overview of Mullite Bricks
Mullite bricks are high-performance refractory materials primarily composed of 72% alumina and silica, offering superior thermal stability and resistance to corrosion compared to silica bricks. Their unique microstructure provides excellent mechanical strength and low thermal expansion, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnaces and kilns. Mullite bricks outperform silica bricks in environments prone to thermal shock and chemical attack, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Silica bricks primarily consist of over 90% silicon dioxide (SiO2), providing high refractoriness and resistance to acidic slags, while mullite bricks contain approximately 70-80% alumina (Al2O3) with 15-30% silica, offering superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength due to the formation of the mullite phase (3Al2O3*2SiO2). The chemical composition of silica bricks results in lower alumina content, limiting their performance in highly basic environments, whereas mullite bricks combine both alumina and silica, enhancing their chemical stability across a wider range of conditions. Understanding these compositional differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate brick type in industries requiring specific resistance to thermal stress and chemical corrosion.
Thermal Performance: Silica vs Mullite
Mullite bricks exhibit superior thermal performance compared to silica bricks due to their higher refractoriness and better resistance to thermal shock. Mullite demonstrates a stable thermal expansion coefficient and maintains structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1750degC, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Silica bricks, although offering good resistance to abrasion, have lower refractoriness and are prone to phase transformations that can reduce thermal stability at elevated temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Silica bricks exhibit higher thermal resistance but generally lower mechanical strength compared to mullite bricks, which contain 70-80% alumina contributing to their superior structural integrity and resistance to thermal shock. Mullite bricks offer enhanced durability under high-temperature conditions due to their stable crystallographic structure, minimizing deformation and extending service life in industrial furnaces. The choice between silica and mullite bricks fundamentally depends on the specific application, with mullite preferred for environments demanding high mechanical strength and long-term durability.
Resistance to Corrosion and Slag
Silica bricks exhibit excellent resistance to corrosive environments due to their high chemical stability, making them ideal for applications involving acidic slags. Mullite bricks offer superior slag resistance and thermal shock durability, as their crystalline structure withstands aggressive, basic slags typically found in steel furnaces. Selecting between silica and mullite bricks depends on the specific slag chemistry and corrosion conditions present in the industrial setting.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Silica bricks generally cost less than mullite bricks due to the abundant availability of high-purity silica sand, which leads to lower raw material expenses and wider market accessibility. Mullite bricks, synthesized from kaolin and alumina, tend to be more expensive because of the complex manufacturing process and limited natural deposits of high-quality kaolin. Availability of silica bricks is higher in most global markets, making them a cost-effective choice for standard high-temperature applications, whereas mullite bricks are preferred for specialized uses requiring superior mechanical and thermal stability despite their higher price.
Application Suitability in Industry
Silica bricks offer superior thermal conductivity and refractoriness suitable for high-temperature furnaces and glass tank applications, making them ideal for glass manufacturing and steel industries. Mullite bricks provide excellent resistance to corrosion, thermal shock, and mechanical wear, favoring their use in cement rotary kilns and petrochemical furnaces. The choice between silica and mullite bricks depends on specific operational temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress within industrial processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Brick Material
Selecting between silica and mullite bricks depends on the specific application requirements, as mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Silica bricks provide excellent resistance to slags and acidic conditions but have limited thermal stability compared to mullite. For industries requiring durability and long service life under extreme heat, mullite bricks represent a more effective choice, while silica bricks suit applications involving corrosive conditions at moderately high temperatures.
Infographic: Silica vs Mullite for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com